FAUNA, MORPHOLOGY AND SYSTEMATICS OF PARASITES
The purpose of the research is to extend information across the distribution of zooanthroponotic helminth infections transmitted through freshwater fish in the Magadan Region.
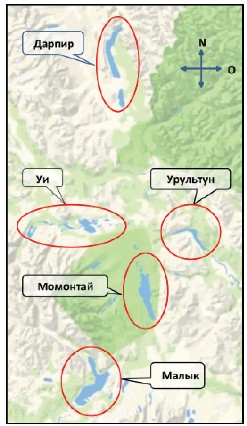
Materials and methods. The study area is located in the Upper Kolyma basin on the Magadan Region and the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia) border. The Omulevsky Park is also located here, one of the clusters of the Chersky National Park named after A. V. Andreev. The existing lake and river systems (Darpir, Momontai, Malyk, Urultun and Ui) are inhabited by 7 fish species: Arctic char (Salvelinus alpinus), east-Siberian grayling (Thymallus arcticus pallasi), round fish (Prosopium cylindraceum), Siberian sucker (Catostomus catostomus rostratus), burbot (Lota lota leptura), common minnow (Phoxinus phoxinus) and sculpin from the Kolyma (Cottus kolymensis). 685 specimens of fish were undergone parasitological survey using established procedures. The found helminths were fixed in 70% ethanol and clarified in glycerol.
Results and discussion. In the study of the fish helminth fauna in the lake and river systems of the Upper Kolyma Highlands, three helminth species that posed a danger to humans and animals were identified, Dibothriocephalus dendriticus, D. ditremus (Diphyllobothriidae) and Eustrongylides excisus (Dioctophymatidae). Information was provided on fish infection with these parasites in the lake and river systems, and their distribution in the Magadan Region, and a brief description of these types of helminths was given. In domestic scientific and methodological publications, the problem of eustrongylidiasis as a zooanthroponotic disease is not sufficiently covered, therefore, emphasis is placed on nematodes of the genus Eustrongylides. The research results may attract the attention of sanitary and veterinary service specialists to this issue, especially given the creation of a national park in the Magadan Region. Data on the freshwater fish infection with Diphyllobothriidae in the Upper Kolyma Lake and river systems expand the diphyllobothriasis nosoarea in the Magadan Region and allows the Susumansky District to be included in its boundaries.
BIOLOGY AND ECOLOGY OF PARASITES
The purpose of the research is to determine the physiological characteristics of the single-host tick Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) annulatus depending on environmental factors, including the season of the year.
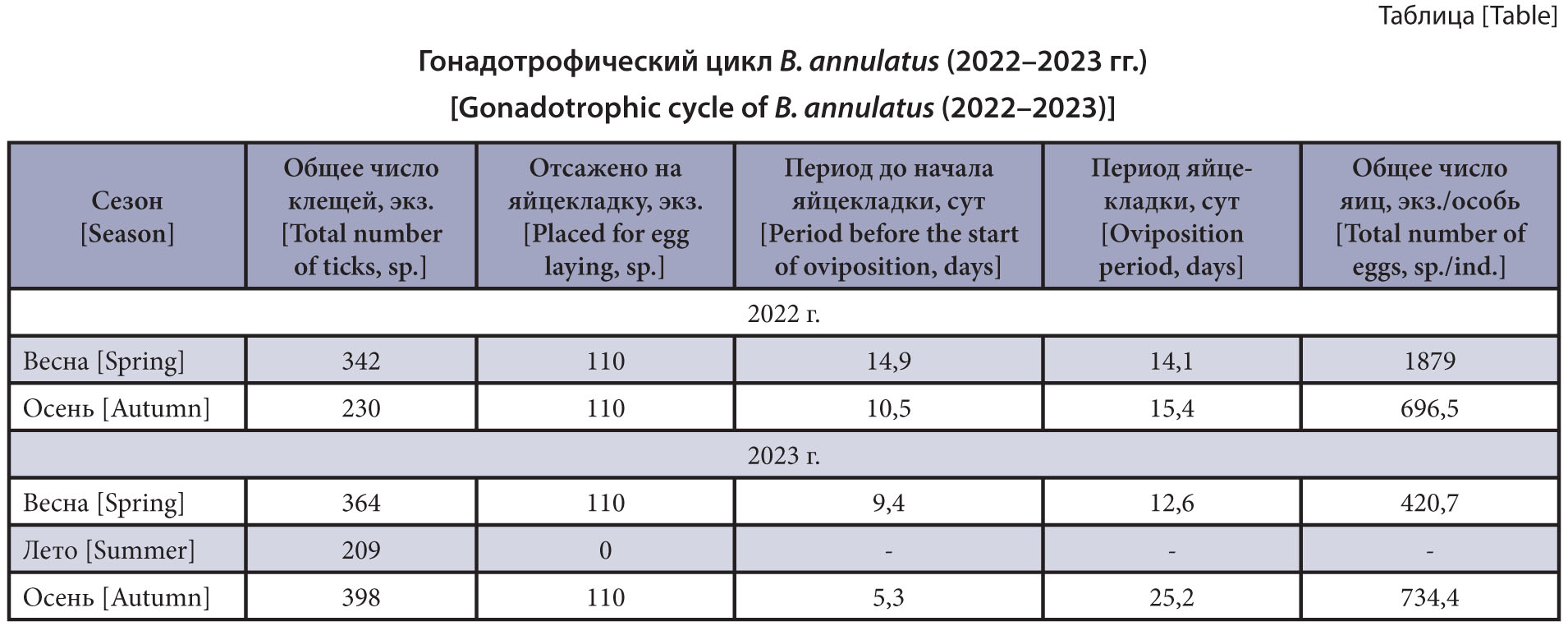
Materials and methods. The study of the gonadotrophic cycle and fertility of B. annulatus was carried out during their seasonal activity from March 2022 to November 2023. The work consisted of two stages: field and laboratory. Ticks were collected manually from cattle in different settlements. Material was collected in natural biotopes according to the generally accepted method using a standard flag and drag. Nourished females were selected for oviposition and kept in laboratory conditions while maintaining optimal temperature and humidity. A total of 1,743 specimens were collected and identified. The sex ratio was 1: 7 with a predominance of females.
Results and discussion. The gonadotrophic cycle and reproductive potential of B. annulatus vary by season. In autumn, the oviposition period, taking into account the incubation period, extends to an average of 28 days. The reproductive potential of females varied from 23 to 2194 eggs/ind. In spring, the cycle duration is comparatively shorter and, on average, does not exceed 25 days. Tick fertility can range from 19 to 5503 eggs/ind. which determines their abundance in summer and autumn months. The data obtained confirm the need for acaricidal treatment of animal grazing areas in the foothill zone in late autumn in order to reduce the number of B. annulatus both after winter diapause and throughout the year.
EPIZOOTOLOGY, EPIDEMIOLOGY AND MONITORING OF PARASITIC DISEASES
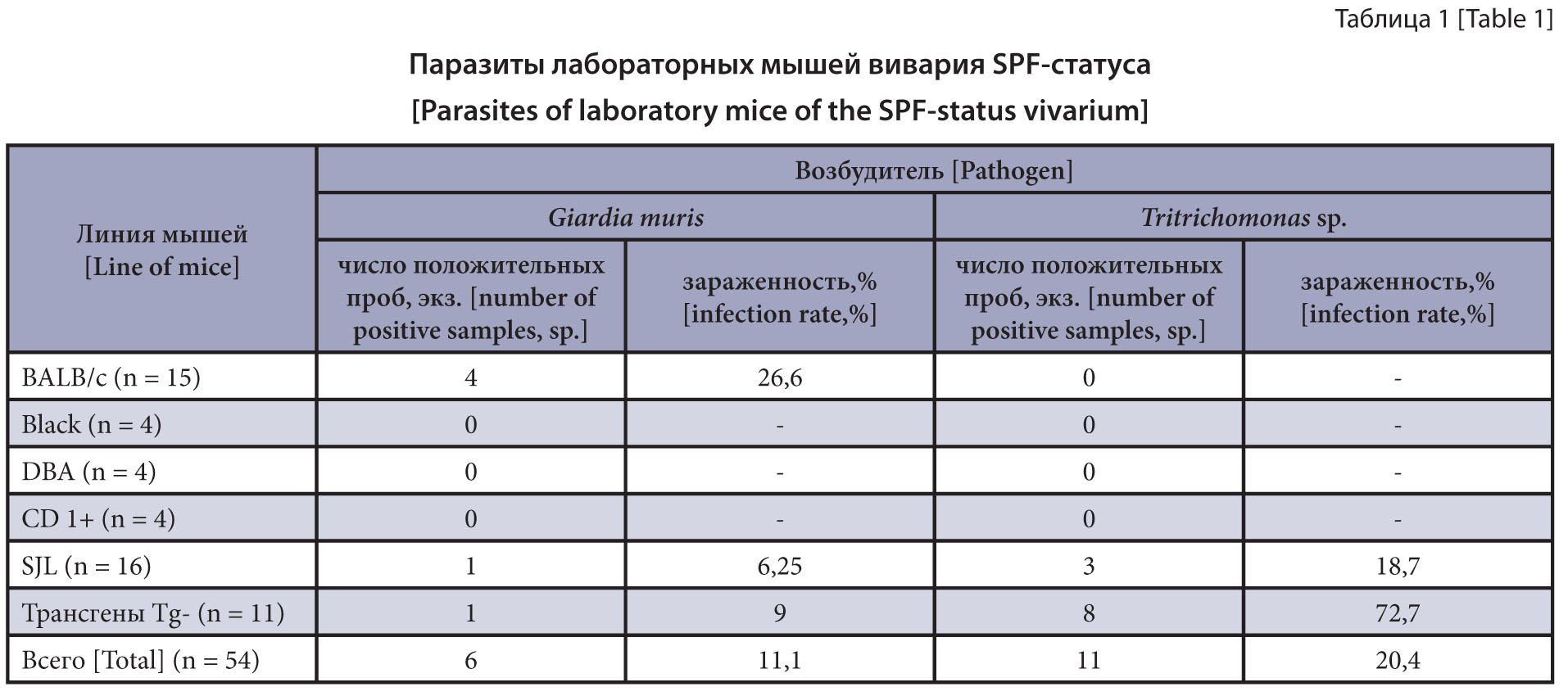
The purpose of the research is to study the parasite fauna in laboratory rats and mice in SPF-status and open-type vivariums and to compare the infection rate depending on the maintenance type within each type of samples.
Materials and methods. The studies were conducted using life-time diagnosis (flotation method and Scotch-tape test), and the material were fecal samples from laboratory rodents and litter samples. Ten percent of the vivarium population and all newly arrived mice and rats in quarantine were examined. Fifty-four individual samples from pure line mice, and 24 litter samples were examined. A total of 234 samples were collected from the laboratory rats: 93 individual samples, 55 combined samples, and 17 sawdust samples; 69 samples were examined by Scotch-tape test.
Results and discussion. Twenty six percent of the laboratory SPF vivarium mice were found to have protozoa: Giardia muris (11.1%) and Trichomonas sp. (20.4%). Nematodes Aspiculuris tetraptera (51.0%) and Syphacia obvelata (20.6%), and cestode Rodentolepis nana (12.0%) were recorded in the open-type vivarium mice. The laboratory open-type vivarium rats were found to have nematodes S. muris (up to 60.9%), A. tetraptera (5.4%), Trichosomoides crassicauda (1.8%), cestode R. nana (27.3%), protozoa Eimeria sp. (7.2%) and Giardia sp. (9.0%). The compared infection of individual with combined mouse fecal samples showed statistically significant differences for all parasites in general and for individual species. Pairwise comparisons of the infection showed that the combined sample detected R. nana statistically significantly more often versus the individual sample (27.3 vs. 5.4%, P < 0.001). The comparison of the infection depending on the type of rat maintenance within each sample type did not show statistically significant differences.
BIOCHEMISTRY, BIOTECHNOLOGY AND DIAGNOSTICS
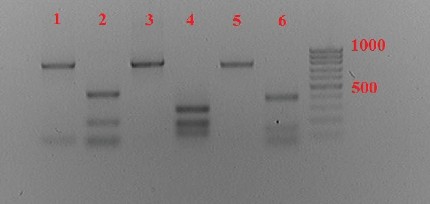
The purpose of the research is to apply molecular genetic research methods to identify the taxonomic affiliation of gastrointestinal parasitic sheep nematodes of the family Trichostrongylidae using nested PCR followed by the restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) analysis.
Materials and methods. Parasitic nematodes, L3 Strongylata larvae obtained from incubated fecal samples of sheep. The genomic DNA was isolated using a commercial kit for DNA extraction from micro-quantities of tissues (Synthol, Moscow) as per the manufacturer’s guidelines. For DNA amplification, a T-100 Bio-Rad thermal cycler and a commercial Eurogen Master Mix reagent kit were used. The PCR regime was performed according to the WAAVP guidelines, 2006. The restriction endonuclease Rsa I of amplified Trichostrongylidae fragments was performed according to guidelines of the enzyme manufacturer (Sibenzyme, Novosibirsk).
Results and discussion. To determine the taxonomic affiliation of Strongylata larvae isolated after incubation of feces from sheep, molecular genetic studies were performed using nested PCR followed by the restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) analysis. This method makes it possible to identify, with the least effort, the genotypes of three species of Strongylata Haemonchus contortus, Trichostrongylus colubriformis, and Teladorsagia circumcincta at the larval stage.
PHARMACOLOGY, TOXICOLOGY
The purpose of the research is to study the effects of ivermectin-containing drug in recommended and increased doses on adult dogs and cats.
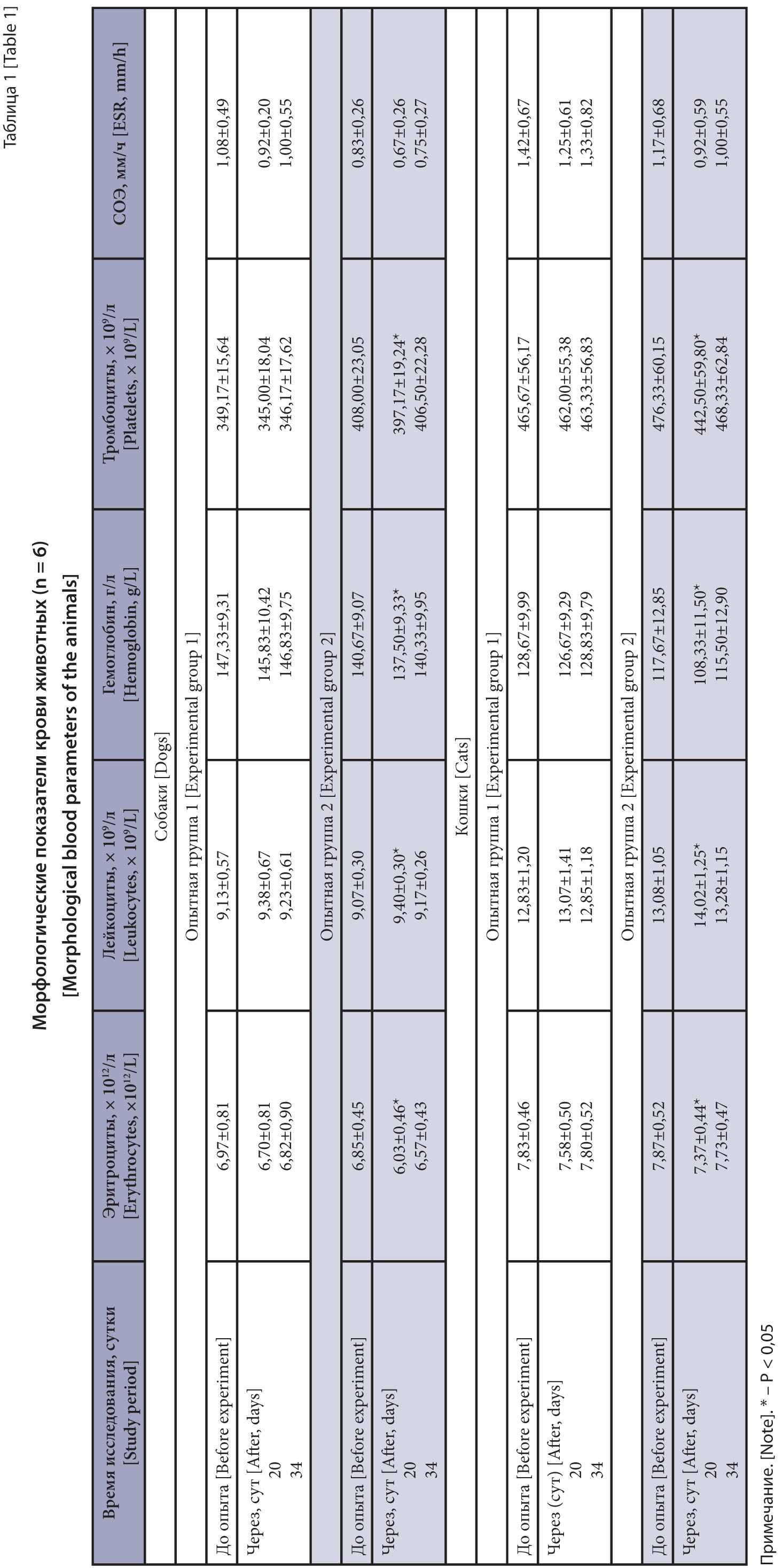
Materials and methods. The drug tolerance on dogs and cats was studied on 24 clinically healthy animals that were divided into experimental groups of 6 animals each, according to the principle of analogs, at the Podolsk Experimental Production Base of the VNIIP – FSC VIEV. The drug was administered seven times with a 3-day interval at a therapeutic dose of 0.2 mg of ivermectin per 1 kg of body weight to the first experimental group; and 0.6 mg of ivermectin per 1 kg of body weight to the second experimental group. The overall health status of the dogs and the cats was monitored daily, and blood samples were taken on days 20 and 34 of the experiment to study some morphological and biochemical parameters. Statistical data was processed in Microsoft Excel 2016 using the paired Student's t-test for dependent samples.
Results and discussion. The studied ivermectin-containing drug had no negative effects on the adult dogs and cats’ overall health status, physiological status and behavior, or morphological and biochemical blood parameters. When using the drug in a threefold increased dose, three dogs and one cat showed depression which spontaneously disappeared within 48 hours. In addition, the animals from the second experimental group developed an allergic reaction, decreased functional activity of the liver and kidneys, and metabolic processes intensity, and red blood system destabilization. On day 34 of the experiment, the above changes were absent in the dogs and the cats, which indicates the restored physiological and biochemical status in the experimental animals.
The purpose of the research is to study the acute oral and dermal toxicity of a veterinary drug (fipronil, pyriproxyfen) in mice and rats.
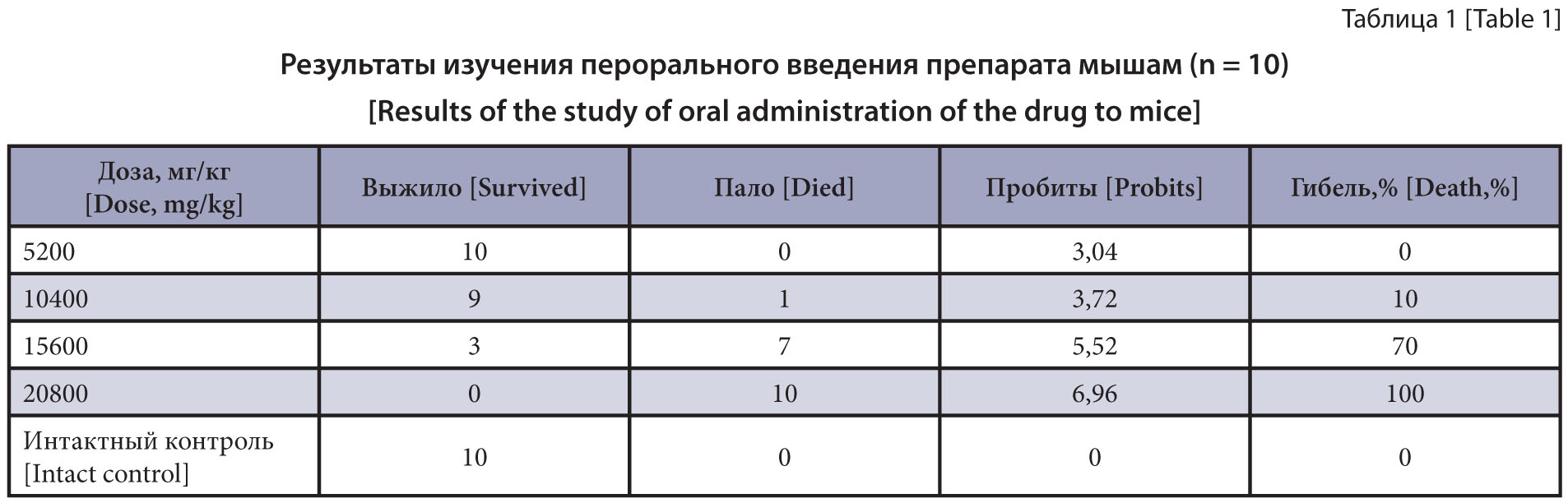
Materials and methods. The studies were performed according to the Methodical Guidelines of the State Pharmacological Committee in the vivarium of the VNIIP – FSC VIEV from February to April 2021. White outbred male mice and male rats were used as a test system to study toxicological characteristics of the study drug. The veterinary drug Insektal Shampoo is a topical solution that contains fipronil and pyriproxyfen as active ingredients. In studying the acute oral toxicity and acute dermal toxicity of the study drug on laboratory animals, established procedures were used.
Results and discussion. The median lethal dose (LD50) was 12 500 (11,532÷13,468) mg/kg when administered to the white male mice intragastrically as per Miller-Tainter method. According to the generally accepted hygiene classification, the drug was classified as hazard class 4 according to GOST 12.1.007-76. For the white male rats, LD50 was more than 20,800 mg/ kg (hazard class 4). When applied to intact rat skin, LD50 was more than 10 400 mg/kg, which corresponds to hazard class 4.
The purpose of the research is to evaluate some toxicological parameters of antiparasitic selamectin-based drug.
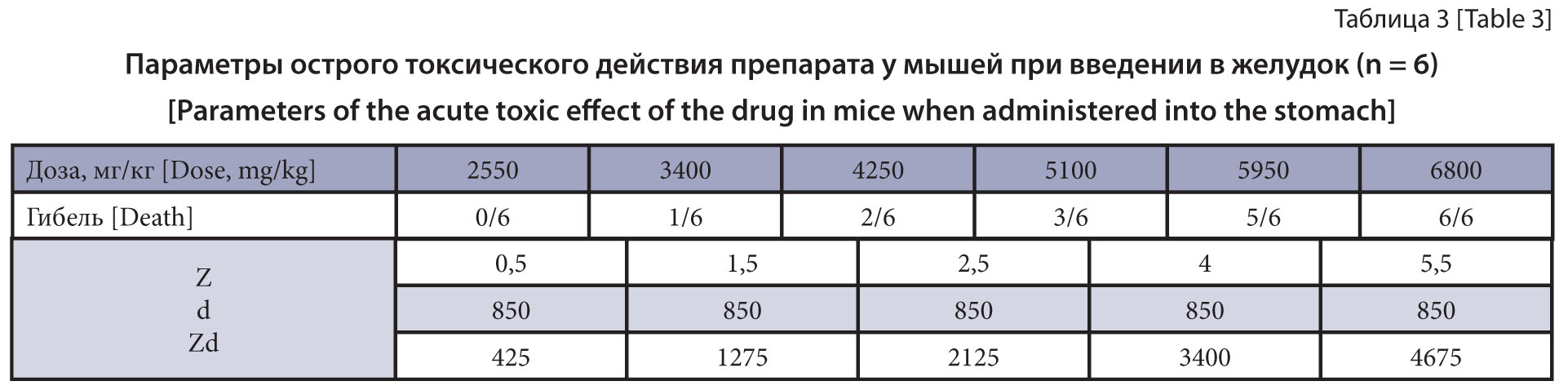
Materials and methods. The study drug is a solution for external use, 1 mL of which contains the active component selamectin (120 mg), as well as additives. The experiments used a total of 66 white outbred male rats, 42 white outbred male mice and 3 guinea pigs. The parameters of acute oral toxicity (in mice and rats), acute dermal toxicity (in rats), and dermal and mucous membrane irritation (in rats and guinea pigs) of antiparasitic selamectin-based drug were evaluated. LD50 was calculated and the irritation of the drug was evaluated using established procedures in toxicology.
Results and discussion. The maximum tolerated dose of the selamectin-based drug was 2550 mg/kg in the mice and 4250 mg/kg in the rats. The absolutely lethal dose for the mice and the rats was 6800 and 8500 mg/kg, respectively. It was established that the drug belonged to hazard class 3 (moderately hazardous substances) when administered intragastrically to the animals: LD50 for the mice was 4816.7 mg/kg, and LD50 for the rats was 6091.7 mg/kg. In determining acute dermal toxicity in the rats, the drug was classified as hazard class 4 (low-hazardous substances): LD50 more than 8500 mg/kg. The drug irritant effect on the skin of the rats at doses of 4250, 6375 and 8500 mg/kg was not established. The drug had a mild effect on the mucous membrane of the eyes of the guinea pigs with its recovery to normal within 24 hours.
The purpose of the research is to investigate subacute cutaneous toxicity in rats, allergenic properties in guinea pigs and tolerance of increased doses of drugs based on imidacloprid, moxidectin and pyriproxyfen by dogs and cats of different age groups.
Materials and methods. Toxicological studies (subacute cutaneous toxicity, study of allergenic properties) were conducted in the vivarium of the All-Russian Research Institute of Plant Protection, a branch of the Federal Scientific Center for Experimental Veterinary Medicine of the Russian Academy of Sciences, on male rats and guinea pigs. Experiments on the tolerance of drugs by target animal species (dogs, cats) were conducted in the Podolsk department of the All-Russian Research Institute of Plant Protection. The choice of doses, frequency and methods of administration of the studied drugs were determined in accordance with the Guidelines for Experimental (Preclinical) Study of New Pharmacological Substances. All doses were calculated for the drug taking into account the density (1.08 g/cm3).
Results and discussion. When studying the acute cutaneous toxicity of the drug on rats, LD50 exceeded the maximum possible dose of 10 000 mg/kg (hazard class 4 according to GOST 12.1.007-76). In a subacute experiment on rats, it was established that doses of 1000 and 500 mg/kg are ineffective (safe), the threshold and toxic doses could not be established. These drugs, when treating animals 8 times with an interval of 3 days in a three- and five-fold increase in the maximum therapeutic dose during the experimental period, did not have a negative effect on the general condition of the animals, their physiological status and behavior; no statistically significant changes in the morphological and biochemical parameters of the blood, physicochemical parameters of urine were noted in animals from the experimental groups compared to the control. However, in one adult dog from the second experimental group, which was used a five-fold increase in the maximum therapeutic dose of the drug, depression was noted on the 20th day of the experiment. The physiological state of the animal returned to normal within 24 hours voluntarily without the use of symptomatic therapy.
TREATMENT AND PREVENTION
The purpose of the research is to evaluate the comparative efficacy of two veterinary drugs («Inspector ear drops» and «Rolf Club 3D ear drops») to treat dogs and cats for otodectic mange complicated by otitis media of bacterial etiology.
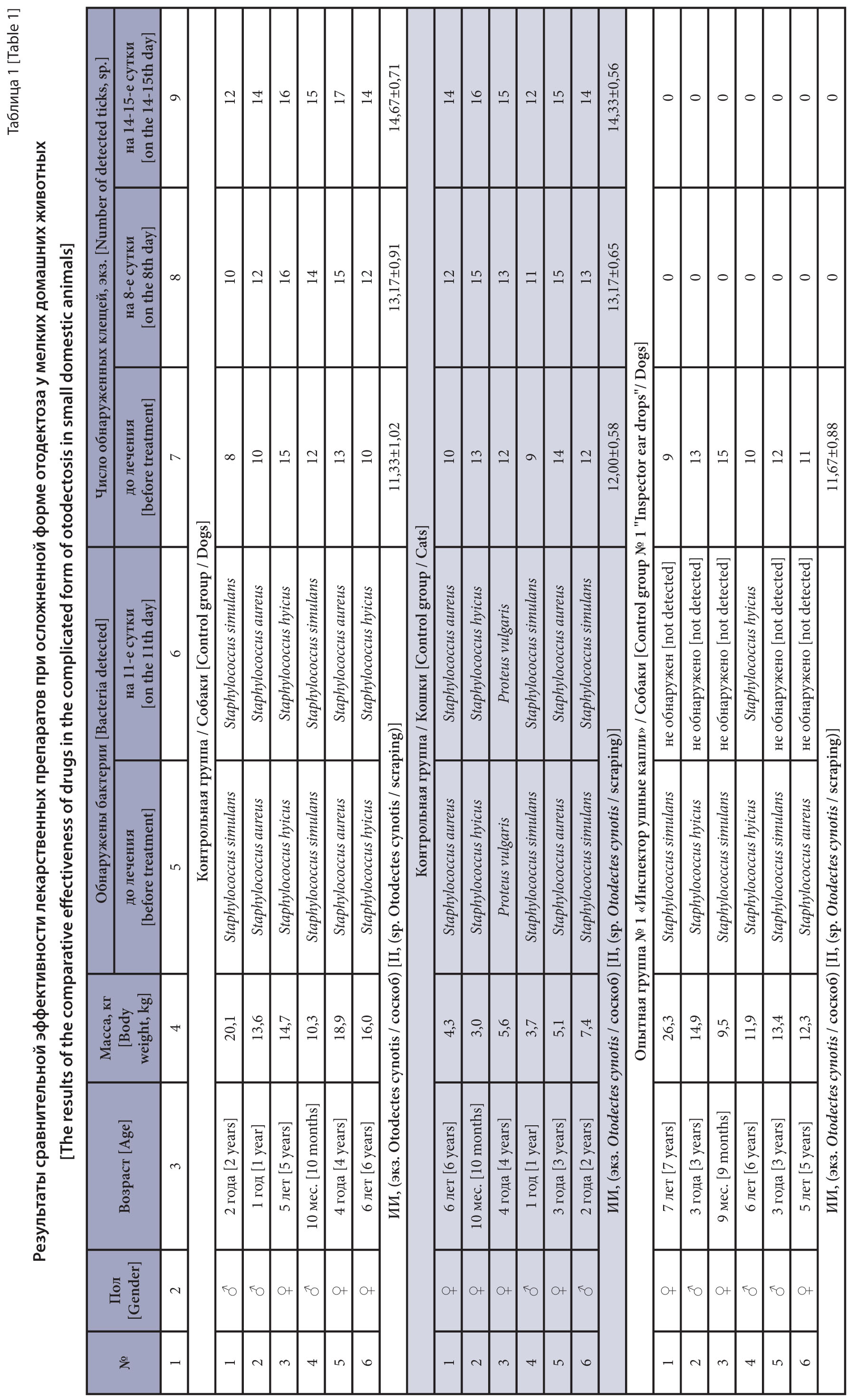
Materials and methods. A total of 36 animals participated in the studies. The studies were carried out at the VNIIP – FSC VIEV. The diagnosis was confirmed comprehensively from epidemiological data, clinical signs and laboratory tests. Microscopy of scrapings taken from the inner surface of the ears was performed to detect Otodectes cynotis. Bacteriological and mycological examination of ear canal discharge was conducted according to established procedures. Ear canal otoscopic examination was performed using a veterinary otoscope. For therapeutic purposes, the experimental animals were treated with «Inspector ear drops» and «Rolf Club 3D ear drops» as per instructions for use.
Results and discussion. The initial comprehensive clinical examination diagnosed otodectic mange in all animals as complicated by acute otitis media of bacterial etiology. On treatment day 8, the animals showed a positive effect of the studied drugs; clinical signs of the disease reduced significantly. In a repeated clinical examination on day 11, most animals showed clinical recovery that was confirmed by negative bacteriological and mycological studies. Acarological studies showed no mites on days 8 and 14-15. However, the course of treatment was extended to 14 days for two dogs, after which their complete clinical recovery was observed. After the end of the study, the animals from the control group were treated with «Rolf Club 3D ear drops». Thus, an assessment of the results revealed that the drugs for veterinary use, «Inspector ear drops» and «Rolf Club 3D ear drops» showed an identical therapeutic effect in dogs and cats against otodectic mange complicated by acute bacterial otitis media.
The purpose of the research is to study the efficacy of a macrocyclic lactone drug using the spot-on method against passalurosis and psoroptic mange in rabbits.
Materials and methods. The study was conducted at the Department of Parasitology and Veterinary-Sanitary Expertise of the MVA named after K. I. Skryabin in 2022–2023 to determine the efficacy of antiparasitic drops (active ingredients: phenylpyrazole derivative, pyrazinoisoquinoline derivative, macrocyclic lactone, insect growth regulator, manufactured by AVZ S-P, LLC) against passalurosis and psoroptic mange. The antiparasitic drops were applied by the spot-on method to rabbits of different age and sex groups in doses of 0.5 mL per animal for body weight of up to 4 kg and 1 mL per animal for body weight of 4 to 8 kg against passalurosis and psoroptic mange. Rabbit fecal samples were examined using the Fülleborn method. Skin scrapings from the inner auricle surface were studied for Psoroptes cuniculi mites as per D. A. Priselkova.
Results and discussion. The antiparasitic drug was found to have 100 % efficacy against ticks Psoroptes cuniculi and nematodes Passalurus ambigus.
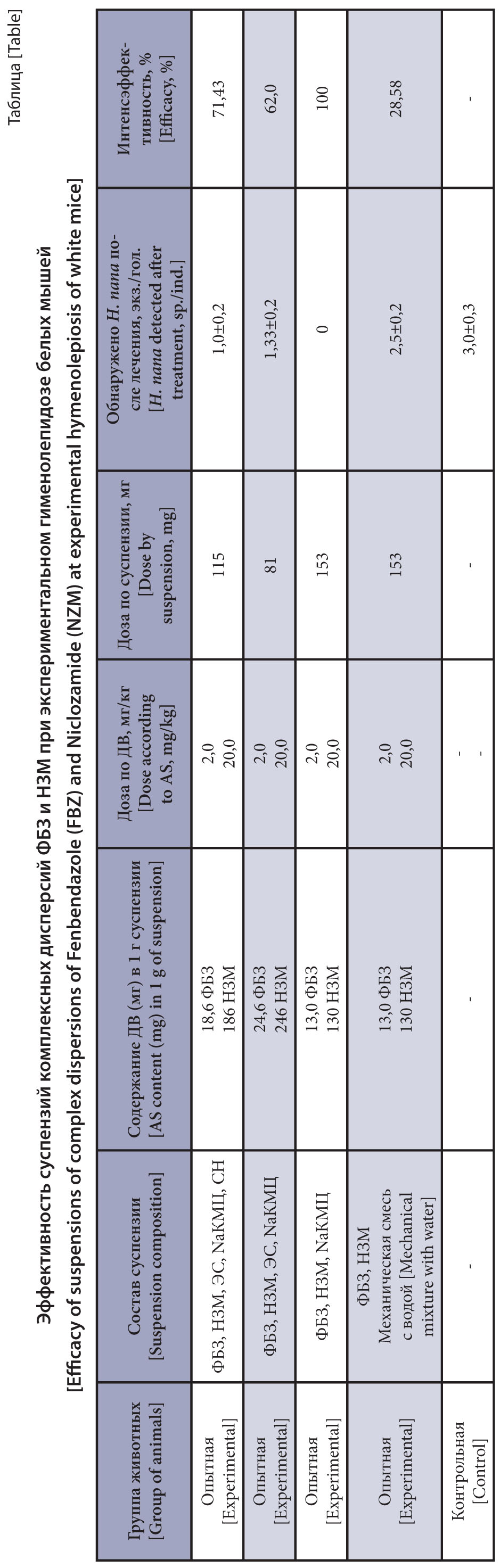
The purpose of the research is to study the anthelmintic efficacy of suspensions based on a combined solid dispersion of Fenbendazole and Niclosamide.
Materials and methods. Mechanochemistry methods were used to prepare suspensions of Fenbendazole (FBZ) and Niclosamide (NSM) substances, in particular, liquid phase grinding of substances with additives (licorice extract, polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP)) in water or in aqueous sodium carboxymethylcellulose (NaCMC) solution. The grinding was conducted in LE-101 roller mill at energy intensity of 1 g for 1 hour at a roll rotation speed of 60–70 rpm. The resulting suspension samples of combined FBZ and NSM dispersions were studied for cestodocidal activity on a laboratory model of hymenolepiosis of white mice that were infected at a dose of 200 infective Hymenolepis nana eggs per animal.
Results and discussion. The 100% efficacy of a combined NaCMC-based drug suspension containing FBZ 13 mg and NSM 130 mg in 1 g of suspension was achieved at a dose of 20 mg/kg of NSM and 2 mg/kg of FBZ. The suspension based on licorice extract, NaCMC, and dioctyl sulfosuccinate sodium salt containing FBZ 18.6 mg and NSM 186 mg in 1 g of suspension at the same dose, i.e. 20 mg/kg of NSM and 2 mg/kg of FBZ showed 71.43% efficacy against H. nana. The suspension based on licorice extract and NaCMC containing FBZ 24.6 mg and NSM 246 mg in 1 g of suspension at the same dose showed a 62.0% effect against H. nana. The activity of the basic drug, the FBZ and NSM suspension was 28.58% at this dose without using mechano-chemical treatment.
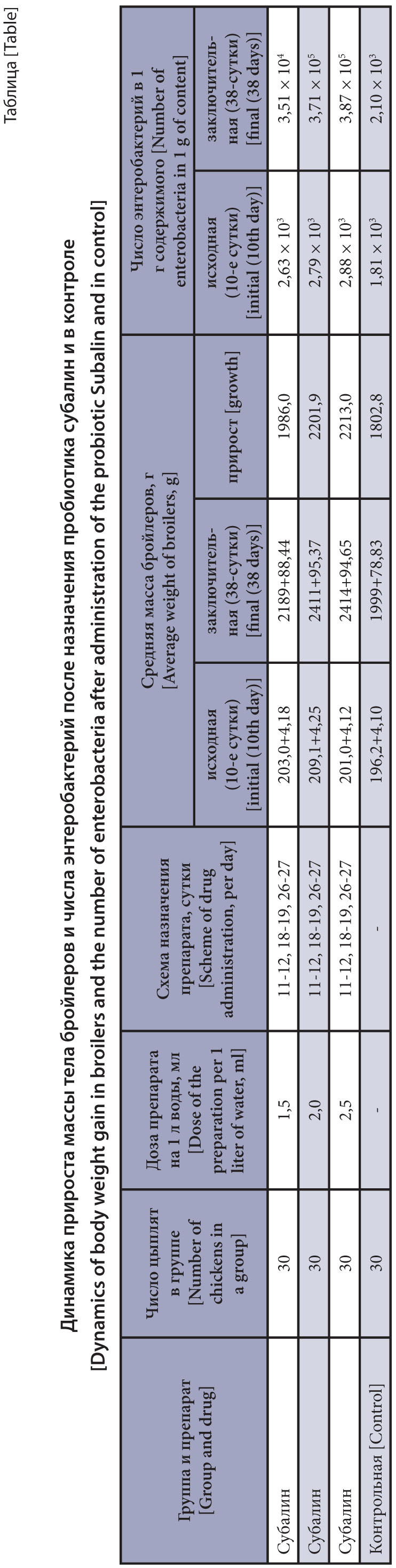
The purpose of the research is to study the probiotic Subalin effects on body weight gain in broiler chickens with spontaneous eimeriosis.
Materials and methods. On a poultry farm in the Moscow Region, the body weight gain dynamics was studied in 120 floormanaged broiler chickens aged 9 to 40 days spontaneously infected with eimeria after administration of different doses of the probiotic Subalin vs. control. The chickens selected for the experiment were divided into four similar groups of 30 birds each. Subalin was administered to the first group chickens at a dose of 1.5 mL per 1 L of drinking water, while the broilers of the second and third groups were administered Subalin at a dose of 2 and 2.5 mL per 1 L of water, respectively. Subalin doses were given to the chickens of groups 1–3 in three stages: on 11–12; 18–19 and 26–27 days of age for consecutive 48 hours. The broilers of group 4 did not receive the drug and served as a control. The chickens of all groups underwent clinical, hematological, and coprological examinations; they were kept in similar conditions on the floor, in isolation, and fed as per zootechnical standards. Control weighing of the chickens was done on days 10 and 40 of their growth.
Results and discussion. The total weight gain of the group 1 chickens was 1985 g in the experiment; 2203 g and 2214 g in groups 2 and 3, respectively, and 1803 g in the control group. The productivity of the experimental chickens was 10.1; 22.2 and 22.8% higher vs. control. The Subalin optimal dose was 2 mL per 1 L of drinking water according to the above scheme. The tested doses of Subalin had positive effects on the number of enterobacteria in the chicken intestines. Blood tests showed no statistically significant changes in clinical or hematological parameters in the experimental and control chickens.
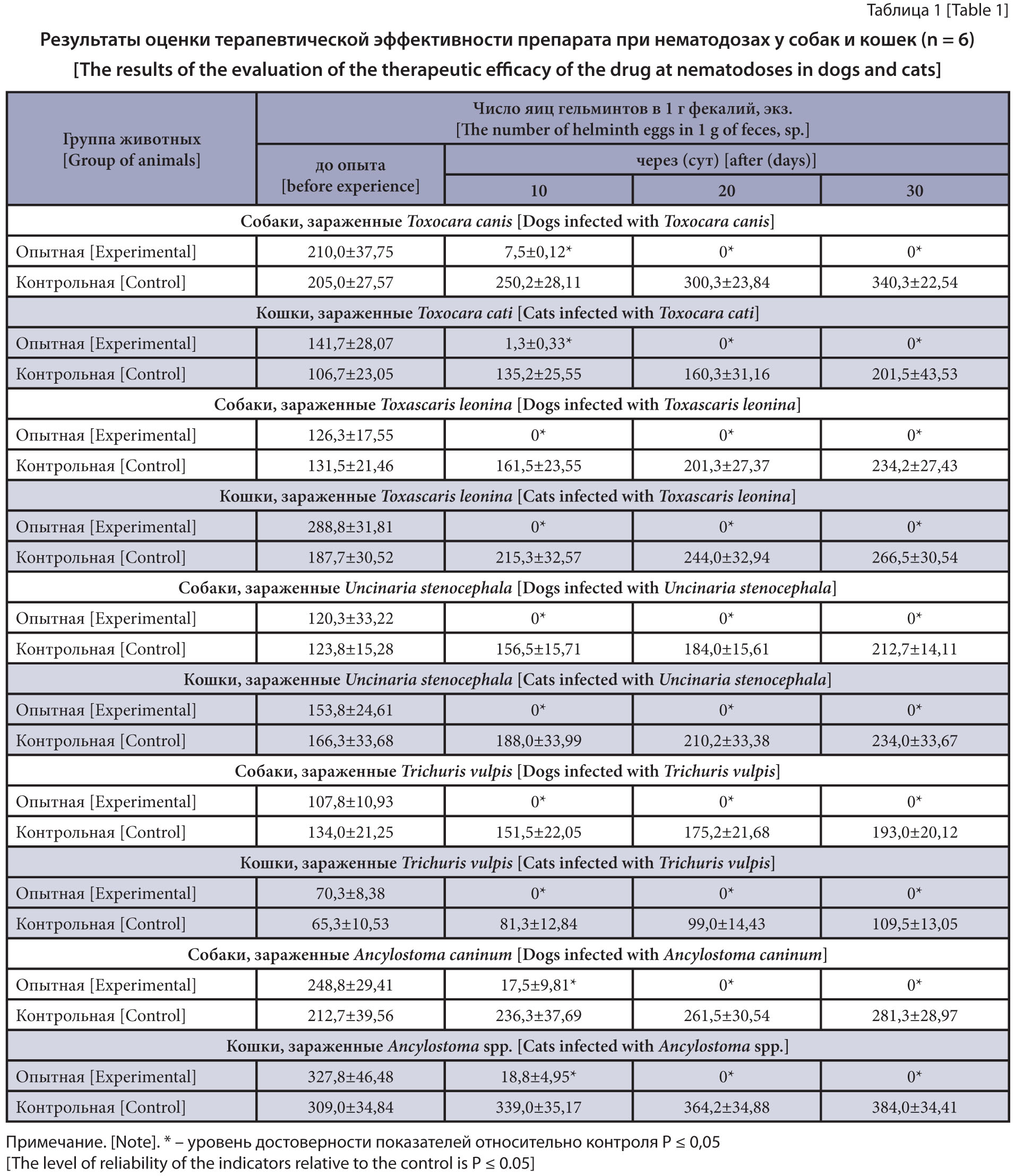
The purpose of the study therapeutic efficacy of combined anthelmintic drug on dogs and cats of different age groups naturally infected with cestodes and nematodes.
Materials and methods. The study drug in the suspension form contains oxantel pamoate, pyrantel pamoate, praziquantel, and additives as active ingredients. The therapeutic efficacy of the drug was evaluated on 228 animals naturally infected with nematodes or cestodes in the Podolsk Experimental Production Base of the VNIIP – FSC VIEV. The animals were divided into experimental and control groups of 6 animals each. The experimental dogs and cats were administered the study drug while the control animals were not given the drug. Clinical examinations and laboratory tests of fecal samples were performed on days 10, 20 and 30 after the start of the experiment. The method of helminthoscopy was used to detect segments and helminthoovoscopy as per Fülleborn to detect helminth eggs/cocoons in animal fecal samples with their subsequent differentiation. The results were statistically processed by the Student method using Microsoft Excel 2016.
Results and discussion. It was found that anthelmintic drug based on oxantel pamoate, pyrantel pamoate and praziquantel had high therapeutic efficacy against parasitism in dogs and cats of nematodes Toxocara spp., Toxascaris leonina, Trichuris vulpis, Uncinaria stenocephala, Ancylostoma spp. and cestodes Echinococcus spp. (except for cats), Mesocestoides spp., Taenia spp., Dipylidium caninum, and Diphyllobothrium latum. When the drug was used in the animals of different age groups, no side effects or complications were recorded.
ISSN 2541-7843 (Online)