FAUNA, MORPHOLOGY AND SYSTEMATICS OF PARASITES
The purpose of the research is to identify the species composition of helminths in lake frogs (Pelophylax ridibundus (Pallas, 1771)) caught in rivers of the Belgorod Region.
Materials and methods. We studied frogs collected using a hydrobiological net in the rivers in fve Belgorod Region districts during the spring-summer 2016–2019. Species identifcation was performed according to morphological characteristics. The sex of the studied frogs was determined by gonads, and the age was determined based on size data. To assess infection of P. ridibundus with individual helminth species and their distribution, we used standard parameters for parasitological survey, namely, the prevalence, the amplitude of infection intensity, and the abundance index.
Results and discussion. As a result of helminthological studies of 122 lake frogs, 17 helminth species were identifed which were widely specifc among representatives of the Ranidae family. Presumably, the identifed species form the basis of the species composition of frog helminths in rivers of the Region. Most of these types of helminths occur throughout the springsummer season without pronounced seasonal dynamics. It was noted that the number of helminth species simultaneously parasitizing in one frog increased with age. Opisthioglyphe ranae is the most often numerically dominant species in the examined areas of the Belgorod Region; and Diplodiscus subclavatus, Pleurogenes claviger and Codonocephalus urnigerus mtc have high abundance at some stations.
EPIZOOTOLOGY, EPIDEMIOLOGY AND MONITORING OF PARASITIC DISEASES
The purpose of the research is identifcation of epidemically and epizootically dangerous fsh species for opisthorchosis in the Novosibirsk Region.
Materials and methods. Helminthological studies were carried out from 2002 to 2020. We studied a total of 2994 fsh specimens belonging to 8 species of Cyprinidae, carps and allies, namely, ide, Leuciscus idus (L.); dace, L. leuciscus (L.); bream, Abramis brama (L.); roach, Rutilus rutilus (L.); verkhovka, Leucaspius delineatus (Heckel); crucian carp, Carassius carassius (L.); gudgeon, Gobio gobio (L.); and minnow, Phoxinus phoxinus (L.). The fsh were identifed to species according to the fsh guide. To identify Opisthorchidae metacercariae in fsh muscles, the compressor method generally accepted in helminthology was used. The Opisthorchidae metacercariae were identifed using the freshwater fsh parasite guide.
Results and discussion. Of 8 studied fsh species of the family Cyprinidae in the Novosibirsk region, the Opisthorchidae metacercariae infection was noted in 7 species (ide, dace, roach, bream, verkhovka, gudgeon, and crucian carp). The following Opisthorchidae species were recorded in the studied fsh: O. felineus, M. bilis, M. xanthosomus, and Metorchis spp. The O. felineus metacercariae were most often found in the supplementary host, in 12.9 % of cases, and M. bilis, M. xanthosomus and Metorchis spp. larvae were found much less often. In terms of epidemy, the ide and bream having large commercial sizes are the most dangerous: the ide as the most heavily infected species, and the bream as the most often caught and eaten by humans. Small non-commercial fsh (the dace, roach, verkhovka, as well as the small ide and bream) are of great epizootological importance, since they are used for food for domestic and wild animals most often. Infected fsh were only found at unregulated marketplaces; the infection prevalence in the roach was 35.5%, of which 22.6% were affected by O. felineus metacercariae, and 12.9% by M. xanthosomus metacercariae.
The purpose of the research is to determine factors affecting the spread rate of thelaziosis in beef breeds grown in the environment of the Labinsk district, the Krasnodar Territory, at the premises of Agrofrma Progress, LLC.
Materials and methods. To determine factors that affect the spread of thelaziosis, a clinical examination of the Aberdeen Angus cattle of different sex and age groups was performed in Agrofrma Progress LLC. Swabs were taken from the conjunctiva of animals with clinical signs of thelaziosis for further microscopic examination. In 2020, 236 cattle were examined including 42 adult animals older than two years, 77 animals at the age of one year and 117 calves from 0 to 6 months. The species of the pathogens was identifed in the study of the conjunctival swabs according to the adult Thelazia morphology (Gorodovich N. M., 1967). To control ectoparasites and prevent thelaziosis, an insectoacaricide from the synthetic pyrethroid group was used. The study was performed on two livestock farms of Agrofrma Progress, LLC located on different terrains: in a temperate steppe zone with a dry climate and artifcial pastures and in a mountainous zone with a humid climate and natural pastures.
Results and discussion. For 2019–2020, thelaziosis was recorded in 236 Aberdeen Angus cattle in the Progress agricultural frm of the Labinsk District, the Krasnodar Territory. A pronounced seasonal dynamic was determined; the spread of infection was recorded from the end of May to October; and the infection peak was in August. We observed a clear correlation of the infection with the activity of zoophilic flies, carriers of thelaziosis. The most widespread thelaziosis was observed in young cattle aged up to 6 months, that were kept on livestock sites on flat terrain in a drier climate.
The purpose of the research is to study the spread of coccidia infections in turkey poults on industrial turkey farms in the Central Region of Russia.
Materials and methods. Turkey poults were studied for coccidiosis by the following life-time diagnostic methods: coproscopic examinations according to Darling, McMaster and Fülleborn. The material to evaluate protozoal diseases spreading in turkey poults was results of our own laboratory studies of the biomaterial (dung samples) and carcass dissection fndings. When studying the age dynamics of the turkey poults’ infection with Eimeria spp. on the poultry farms in the Central Region, young birds aged 7 days and older were studied until the completion of the technological cycle of production, every 14 days, by examining at least 20 fresh dung samples and 10 scrapings from the floor. To determine the seasonal dynamics of infection, the samples were taken from the poultry buildings in January in winter season, April in Spring, July in Summer, and October in Autumn.
Results and discussion. The highest coccidia infection rate was detected at the age of 35–49 days in young males (Infection Prevalence, 30–45%), and 35–63 days in females (Infection Prevalence, 5–30%). The turkey poults were infected with Eimeria spp. throughout the year with minor seasonal variations. The young birds’ age had a more noticeable effect on the infection rate in the turkey poults. The external environment (floor, walls, and feeders) was contaminated with infective coccidia elements by 5–31.3%.
The purpose of the research is to study of larval biotopes of the family Culicidae Meigen, 1818 on the territory of the Berezinsky Biosphere Reserve.
Materials and methods. Mosquito larvae collected on the Berezinsky Biosphere Reserve in 2016–2020. A total of 7772 mosquito larvae were collected in the course of 1467 counts. Mosquito larvae were collected in four types of natural reservoirs: permanent open (I); permanent shaded (II); temporary open (III) and temporary shaded (IV). The larvae were collected by dip net. The specimens were identifed using standard keys; in certain cases, the taxonomic collection of the Zoological Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences (St. Petersburg) was used.
Results and discussion.We found larvae of 22 mosquito species on the Berezinsky Biosphere Reserve. The genus Aedes Meigen, 1818 is the most abundant – 16 species (72,7%). The genus Anopheles Meigen, 1818 is represented by 2 species (9,2%), the genus Culiseta Felt, 1904 – 3 species (13,6%) and the genus Culex Linnaeus, 1758 – 1 species (4,5%). The largest number of species (18) is recorded in permanent and temporary open-type reservoirs, 17 – in temporary shaded reservoirs and the smallest number – 6 in permanent shaded reservoirs. Three species, Aedes vexans (Meigen, 1830), Ae. cantans (Meigen, 1818), and Ae. sticticus (Meigen, 1838) were found at all types of water bodies. The main larval breeding habitats are reservoirs of temporary origin with varying degrees of shading (88,0%). There are the highest abundance and mean average density of larvae. Thus, in temporary open water bodies, the abundance is 52,4% (with an average density of 197,0±45,7 sp./m2), and in temporary shaded water bodies, the abundance is 35,5% (with an average density of 287,2±162,1 sp./m2). For permanent reservoirs with varying degrees of shading, a low abundance and an average density of larvae are noted. Thus, in permanent open water bodies, the abundance is 9,6% (with an average density of 27,0±7,7 sp./m2), and in permanent shaded water bodies, the abundance is 2,5% (with an average density of 19,4±6,0 sp./m2). In permanent open water bodies, the greatest species diversity is noted, which is confrmed by the values of the indices (Нʹ = 3,06; D Mg = 2,57 and DSm = 0,16).
PATHOGENEZIS, PATHOLOGY AND ECONOMIC DAMAGE
The purpose of the research is identifying and determining clinical and laboratory features of coinfection caused by Opisthorchis felineus and Lamblia intestinalis.
Materials and methods. We described a clinical picture and laboratory abnormalities in 50 patients with O. felineus infection. Of these cases, 25 people were diagnosed with lambliosis. The therapy included three consecutive stages: preparatory stage, antiprotozoal and anthelmintic treatments, and rehabilitation stage. The preparatory stage was aimed to improve the biliary tract function, to reduce intoxication symptoms, and to stop acute allergic reactions. The patients received choleretics, antispasmodics, antibacterial drugs, antihistamines, enzymes, and adsorbents for 2–4 weeks. At the end of the preparatory stage, the patients from the second group were prescribed albendazole of 800 mg per day in two doses of 400 mg per os during meals for 5 days. In the second treatment stage, the patients with opisthorchosis received praziquantel at a dose of 75 mg/kg of body weight per os for one day in three doses. The rehabilitation phase lasted for four months. The next step was to assess lamblia eradication results by the control coproprotozooscopy and/or biliprotozooscopy for cysts and/or vegetative forms of L. intestinalis at 7 days, 1 month and 6 months after treatment with albendazole. The control coproovoscopy for O. felineus eggs was performed at 6 months after praziquantel treatment.
Results and discussion. We studied the influence of L. intestinalis on the nature and severity of clinical and laboratory symptoms of opisthorchosis. It was revealed that clinical symptoms (abdominal pain, nausea, low-grade fever or dermatosis) and laboratory syndromes (cytolysis and cholestasis) were more pronounced in case of concomitant helminth and protozoan infections. Lambliosis is more difcult to treat when combined with opisthorchosis.
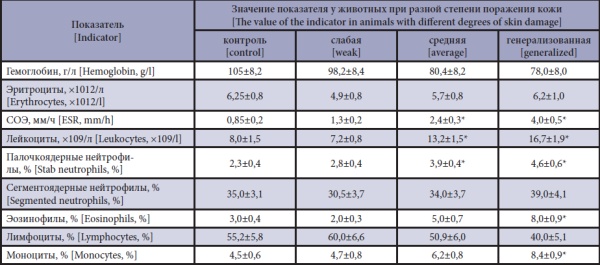
The purpose of the research is to identify a general pattern in the change in hematological and biochemical parameters in any lesions of cattle skin.
Materials and methods. The work was carried out in October-November 2021 in the conditions of farms in the Ipatovsky district of the Stavropol Territory on cattle aged 9–12 months and 90–120 kg of body weight. During the veterinary clinical examination, four groups of fve heads each were formed, one of the groups was a control. Animals of the control group had no clinical signs of dermatitis. The experimental groups of animals were divided depending on the degree of intensity of skin lesions into mild, moderate and generalized forms of manifestation of dermatitis. The results obtained were processed statistically.
Results and discussion. A veterinary clinical examination of this livestock made it possible to establish the dependence in case of damage to the skin not only in changes in temperature, respiratory rate and pulse, but also in blood parameters. The body temperature of calves with a generalized form of dermatitis increased by an average of 0.5 degrees, breathing increased by six units per minute, the pulse rate increased by 15–18 beats per minute. In calves with mild and moderate manifestation of dermatitis, these parameters did not have signifcant changes and were within the normal range. From hematological indicators, hemoglobin had a general tendency to decrease with increasing intensity of the lesion or aggravation of the pathological process. Such indicators as ESR, leukocytes, neutrophils, eosinophils, on the contrary, tended to increase, especially in the generalized form. The slowdown of erythropoiesis and thrombocytopenia in the generalized form of dermatitis is presumably associated with intoxication of the body of calves. An increase in ESR, the number of eosinophils indicates an inflammatory process occurring in the animal's body. From biochemical indicators, an increase in the level of bilirubin, AST and ALT, creatinine, alkaline phosphatase indicates toxic liver damage due to intoxication of the body of calves due to inflammatory factors and decay products of affected skin cells.
PHARMACOLOGY, TOXICOLOGY
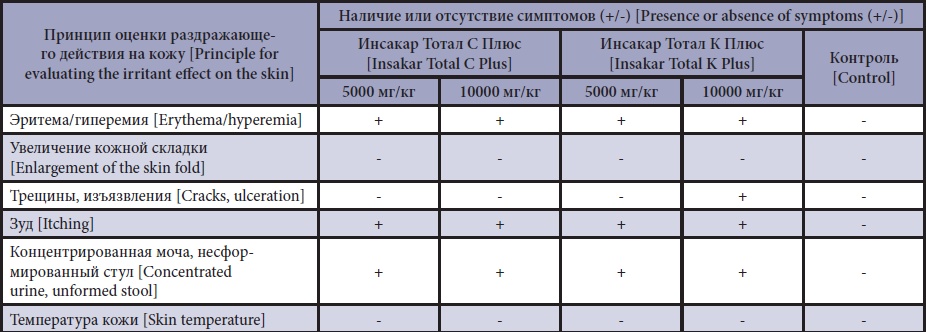
The purpose of the research is to study acute oral toxicity in mice, and acute dermal and subchronic toxicity in rats of multicomponent antiparasitic Insacar Total C Plus (for dogs) and Insacar Total K Plus (for cats).
Materials and methods. The toxicity of the drugs was studied in September-April 2020–2021 at the premises of the VNIIP – FSC VIEV Vivarium. To determine acute oral toxicity, 80 outbred mice weighing 20 g were used, of which 7 test and one control group were formed. The drugs were administered once in a 1 : 3 dilution with polyethylene glycol as a solution through an intragastric tube and an automatic controller. The control animals were intact. After a single administration, the physical condition of the test mice was monitored within 14 days; weight gain, expected clinical toxicity symptoms and possible death were assessed. Before and on days 1, 3, 7, 11 and 14 of the experiment, the test and control mice’s weight gain were evaluated. The toxicity parameters were calculated by the methods of Pershin, Miller and Taintner. In a subchronic experiment, the study drugs were tested on 80 outbred white rats divided into 6 test and 2 control groups. The rats’ coat was also shaved on the back. The solution was applied to the shaved skin area once a day for 7 days at doses of 1,000 mg/kg (0.1 mL/100 g), 500 mg/kg (0.05 mL/100 g) and 200 mg/kg (0.02 mL/100 g) of the animal weight. On day 8 of the experiment, 5 rats from each group were euthanized; their blood samples were taken, and the internal organs were examined. On day 21 of the experiment, the second part of the animals was euthanized to analyze the reversibility of potential pathoanatomical changes after prolonged repeated application of the drug. The results were processed statistically.
Results and discussion.The half-lethal dose (LD 50) after oral administration of the drug for dogs to the mice was 2,475 by the Pershin method, and 2,500±388 mg/kg by the Miller and Taintner method. LD50 of the drug for cats when administered into the mice’s stomach was 2,713 by the Pershin method, and 2,650±403 mg/kg by the Miller and Taintner method (hazard class 3). LD 50 when applied to the rats’ skin was more than 10,000 mg/kg (hazard class 4). When applied once to the rats’ skin, the drugs had a slightly irritating effect. In subchronic experiment on the rats with daily drug application on their skin at doses of 1,000 mg/kg, 500 and 200 mg/kg, no negative effects on the general condition or death of the animals were observed during the entire study. Hematological and biochemical parameters of the test rats that were treated with the drug for dogs at a dose of 200 mg/kg, an increased content of lymphocytes up to 83.40% was observed on day 8 of the experiment, and up to 74.20 % in the control; and an increased glucose level up to 6.08±1.23 mmol/L, and up to 4.82±0.70 mmol/L in the control; LDH was up to 766.00±264.19 U/L, and up to 434.80±525.89 U/L in the control.
The purpose of the research is to study effects of the 2.0% supramolecular complex of ivermectin in overdoses on the clinical condition of horses.
Materials and methods. The experiment was conducted on 20 horses of different breeds in the Seradin Equestrian Center, the North Caucasus Federal District, the Chechen Republic, in October 2020. The horses were divided according to the principle of analogues into 3 test groups and one control group of 5 animals each. The 2.0% supramolecular complex of ivermectin was administered to the horses from group 1 at a therapeutic dose of 0.2 mg/kg; group 2 received a tripled dose of 0.6 mg/kg, and the group 3, a 5-fold increased dose of 1,0 mg/kg for the active substance. The drug was administered once individually in a mixture with compound feed. The body temperature was measured with a non-contact thermometer, and the pulse rate and the respiratory rate were measured per 1 min. Urine of the horses was examined on days 1, 7 and 14 after the drug. The urine color, transparency and consistency were determined. Multifunctional test paper was used to study pH, protein, glucose, ketone bodies, nitrites, bilirubin, and urobilinogen. Blood was taken in the morning from the horses’ jugular vein on days 1, 7 and 14 after the drug. Hematological and biochemical parameters were studied on analyzers.
Results and discussion. Clinical fndings of the horses (body temperature, pulse and respiration) did not differ from those of the control animals after the 2.0% supramolecular complex of ivermectin was administered in a therapeutic, tripled and 5-fold increased doses on days 1, 7 and 14. A slight increase in ketone bodies was observed in the urine on day 1, which may indicate the drug effect on the central nervous system at a 5-fold increased dose; all parameters were within the normal range on days 7 and 14. The 2.0% supramolecular complex of ivermectin in overdoses (0.6; 1.0 mg/kg for the active substance) did not adversely affect the horses’ hematological or biochemical blood parameters.
TREATMENT AND PREVENTION
The purpose of the research is to analyze and summarize the literature data and the results of our own studies on the use of drug delivery systems and methods for increasing the solubility and efcacy of anthelmintic drugs.
Helminthoses are one of the most important problems in veterinary medicine and animal husbandry, not only due to the pathological effects, but also due to the spread of anthelmintic resistance. Since the development of new anthelmintic substances takes many years and investment, some strategies are currently focused on modifying existing drugs to increase their efcacy, reduce side effects and overcome anthelmintic resistance. Literature data analysis on various methods and means of increasing the solubility and efcacy of anthelmintic drugs was carried out and the prospects for their use, including using modern nanotechnological methods of drug delivery were given.
The purpose of the research is to outline the growing problem of anthelmintic resistance of horse nematodes in the world, to describe the methods currently used to detect it, and the proposed ways to overcome it.
Materials and methods. A review of the world literature on the resistance of horse nematodes to anthelmintic drugs is carried out.
Results and discussion. Currently, veterinary parasitology is faced with the growing problem of the emergence of resistant races of helminths, against which previously tested anthelmintic drugs in recommended doses are ineffective. This phenomenon has been noted in many animal species and manifests itself in relation to many drugs of the main groups of anthelmintics. This is evidenced by numerous reports. In horse breeding, benzimidazoles have been used for over 40 years, leading to widespread resistance to them in intestinal nematodes. There is a loss or weakening of the effectiveness of treatment of nematodes of horses with anthelmintic drugs: thiabendazole, pyrantel pamoat, drugs from the benzimidazole groups and macrocyclic lactones. There is no doubt that a similar situation of the spread of resistant races of helminths is also typical for Russia, since here the same anthelmintic drugs are used for treatment as abroad. However, this problem in our country remains practically unexplored. In this situation, the uncontrolled use of anthelmintics, which does not take into account the possibility of resistance to them, inevitably leads (and possibly in some cases has already led) to the emergence and spread of resistant populations of helminths, against which existing drugs will be ineffective.
The purpose of the research is to study the therapeutic efcacy of drugs in the form of a solution for external use based on imidacloprid, pyriproxyfen and moxidectin against gastrointestinal nematodes and Diroflaria spp. microflaria in dogs and cats.
Materials and methods. . The studies were carried out on the basis of VNIIP (fl. Federal State Budgetary Scientifc Institution FNTs VIEV RAS) on dogs and cats of different sex and age, body weight spontaneously infected with parasites. The diagnosis, as well as the effectiveness of the drugs, was confrmed in a complex manner based on the anamnestic and epizootological data, the clinical picture and laboratory research methods (detection of helminth eggs in the animal's feces using the Fülleborn method with subsequent differentiation, microscopy of animal blood smears to detect microflariae). To rule out infection of animals (dogs) with babesia, blood samples were taken and a laboratory analysis was performed to detect parasites (Babesia canis).
Results and discussion. 100% effectiveness of Insacar Total C (for dogs) and Insacar Total K (for cats) has been established for nematodes of the gastrointestinal tract (toxocarosis, toxascariosis, uncinariosis, hookworm, trichuriosis) and diroflariosis (the initial stage of the disease). Side effects and complications after treatment of animals with drugs were not revealed
OUR ANNIVERSARIES
ISSN 2541-7843 (Online)