FAUNA, MORPHOLOGY AND SYSTEMATICS OF PARASITES
The purpose of the research is studying the morphology of larvae of Trematoda Monorchiidae of the genus Paratimonia and establishing possible causes of their accelerated morphogenesis.
Materials and methods. The material for this study was trematode larvae (metacercariae) from 283 specimens of gastropods Hydrobia acuta that we collected in March 2012 at the estuary of the River Chernaya (Sevastopol, the Black Sea, 44°27′49″ N 33°51′37″ E). The gastropods were studied for helminths using the compression method. Some of specimens of the found trematodes were studied alive and others were fixed in 70% ethyl alcohol and then stained with acetocarmine according to the standard method. The morphological features of metacercaria were studied on live larvae.
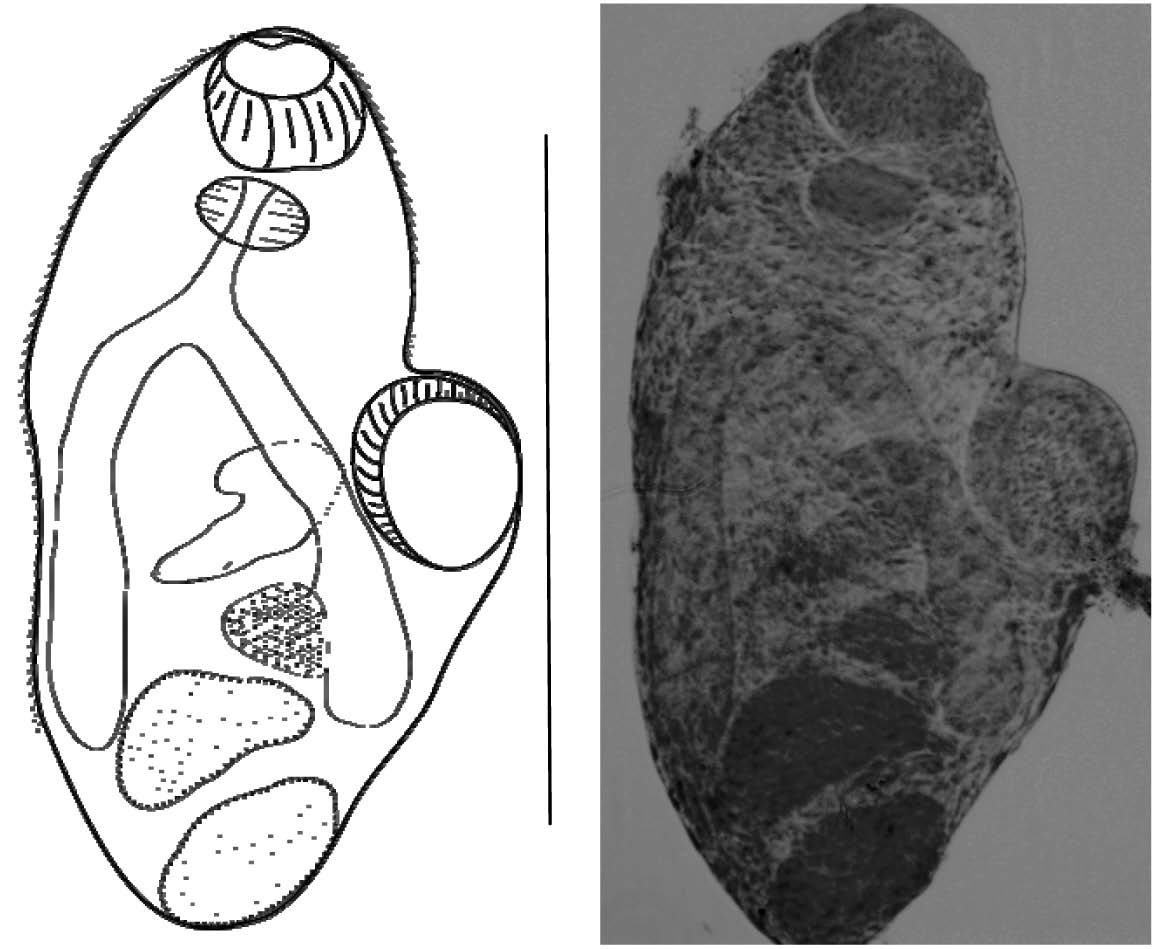
Results and discussion. During helminthological research of gastropods Hydrobia, we recorded metacercariae of the family Monorchiidae. Non-encysted metacercariae were located freely in the host’s body cavity.
The purpose of the research is to study the parasite fauna of the common frog (Rana temporaria Linnaeus, 1758) inhabiting the vicinity of the Visim Nature Biosphere Reserve.
Materials and methods. The species composition, dominance structure and endoparasite infection of 32 individuals of R. temporaria caught along the banks of the upper reaches of the Sulem Riverwere assessed according to the following indicators: the prevalence and intensity of infection and abundance index.
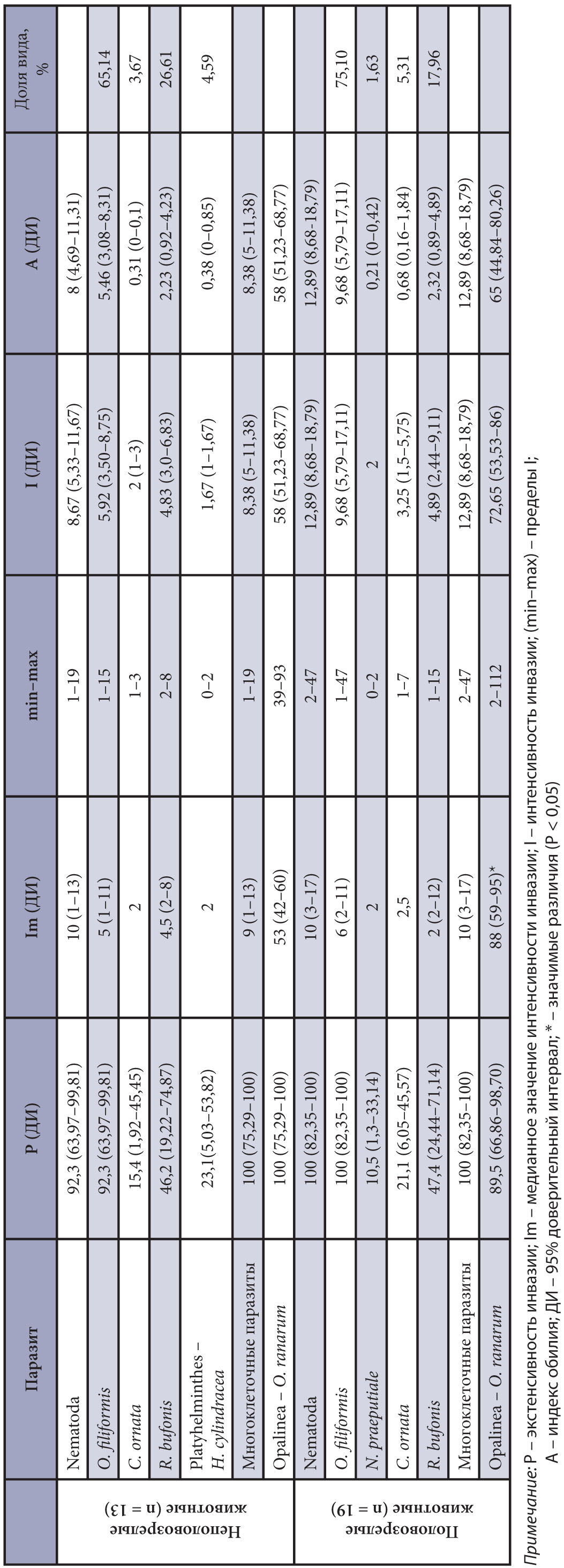
Results and discussion. The species composition of parasites in a common frog from the vicinity of the Visim Nature Biosphere Reserve is presented for the first time. Five species of macroparasites have been identified, classified as Nematoda: Oswaldocruzia filiformis (Goeze, 1782), Neoraillietnema praeputiale (Skrjabin, 1916), Cosmocerca ornata (Dujardin, 1845), Rhabdias bufonis (Schrank, 1788) and as Platyhelminthes: Haplometra cylindracea (Zeder, 1800). One species of endosymbiotic protozoa of Chromista, Opalina ranarum was recorded (Purkinje et Valentin, 1835). The prevalence of the infection of common frogs by helminths reaches 100%, the abundance index is 11.06, and protozoa is 93.8% and 62.16, respectively. Nematodes O. filiformis (the prevalence of infection 96.9%, and abundance index 7.97) and R. bufonis (the prevalence of infection 46.9%, abundance index 2.28) predominate. It was shown that nematode N. praeputiale was not found in the parasitocenosis of immature amphibians, and trematode H. cylindracea was not found in adult animals. The proportion of O. filiformis and C. ornata increases with age in common frogs. It was found that the animals of the July population are infected with nematode R. bufonis largely. Regardless of the age of R. temporaria, the probability of colonization by O. ranarum in spring will be higher.
The purpose of the research is studying helminths of carnivorous birds of the order of owls (Strigiformes) found in the Non-Black Earth Region of the Russian Federation.
Materials and methods. From 2015 to 2020, complete helminthological dissections were carried out by the Skryabin method for 72 birds of the order of owls after their spontaneous death: 8 specimens of the short-eared owl Asio flammeus, 6 specimens of the Ural owl Strix uralensis, 4 specimens of the little owl Athene noctua, 9 specimens of the barn owl Tyto alba, 19 specimens of the tawny owl S. aluco, and 26 specimens of the long-eared owl A. otus. The study material was provided by rehabilitation centers and veterinary clinics in Moscow City and the Moscow, Tula and Kaluga regions. The helminths were fixed according to generally accepted methods; the species was identified taking into account specific morphological characters.
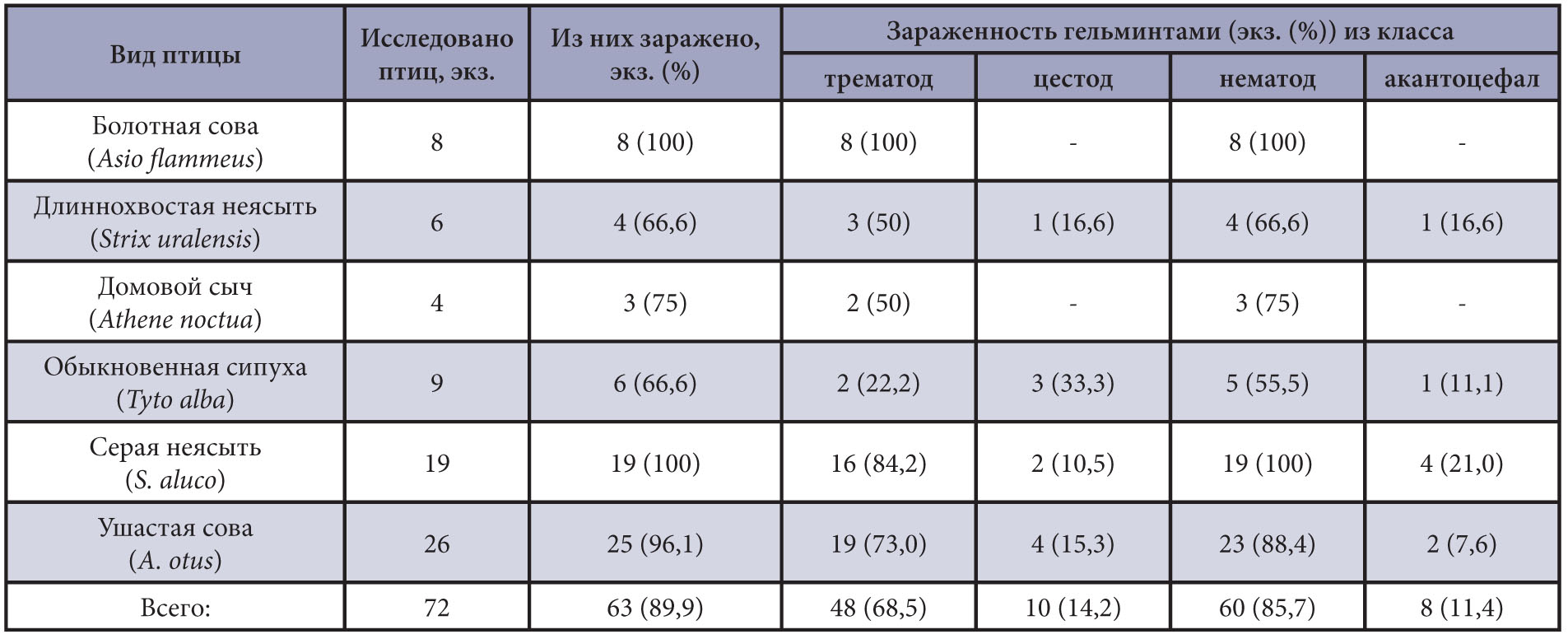
Results and discussion. Total infection rate in owls was 89.9%. All studied birds were found to have mixed infections with two or more types of helminths. We identified 15 helminth species including 3 species of trematodes (Neodiplostomum attenuatum, Strigea falconis, S. strigis), 2 species of cestodes (Cladotaenia globifera, Paruterina candelabraria), 9 species of nematodes (Syngamus trachea, Cyrnea leptoptera, Microtetrameres inermis, Synhimantus laticeps, Porrocaecum depressum, P. spirale, Capillaria tenuissima, Baruscapillaria falconis, and Capillaria sp.) and 1 acanthocephalian species (Centrorhynchus aluconis). For the first time, new hosts were identified for the following helminth species: the barn owl, short-eared owl and little owl for the trematode N. attenuatum, the Ural owl and little owl for S. falconis, the long-eared owl for the nematode S. trachea, the short-eared owl and tawny owl for C. leptoptera, and the tawny owl for M. inermis.
ECOLOGY AND BIOLOGY OF PARASITES
The purpose of the research is studying the peculiarities of parasite infection of the cestodes Lateriporus teres Krabbe, 1869 (Cestoda: Dilepididae) and acanthocephalans Polymorphus phippsi Kostylew, 1922 (Palaeacanthocephala: Polymorphidae) during coexistence in the intestine of the common eider, particularly, the localization of these parasites, the activity of protein and carbohydrate metabolism enzymes on the tegument of the worms, the degree of parasite influence on the host digestion, as well as to assess total digestive activity in the gastrointestinal tract of birds infected with these helminths.
Materials and methods. Using methods of biochemical analysis, the activity of digestive enzymes (protease and glycosidase) and the intensity of a digestion with the participation of these enzymes along the intestine of the common eider were determined. The digestive activity of enzymes in the body of helminthes was measured, and the intensity of membrane digestion on the surface of their tegument was estimated.
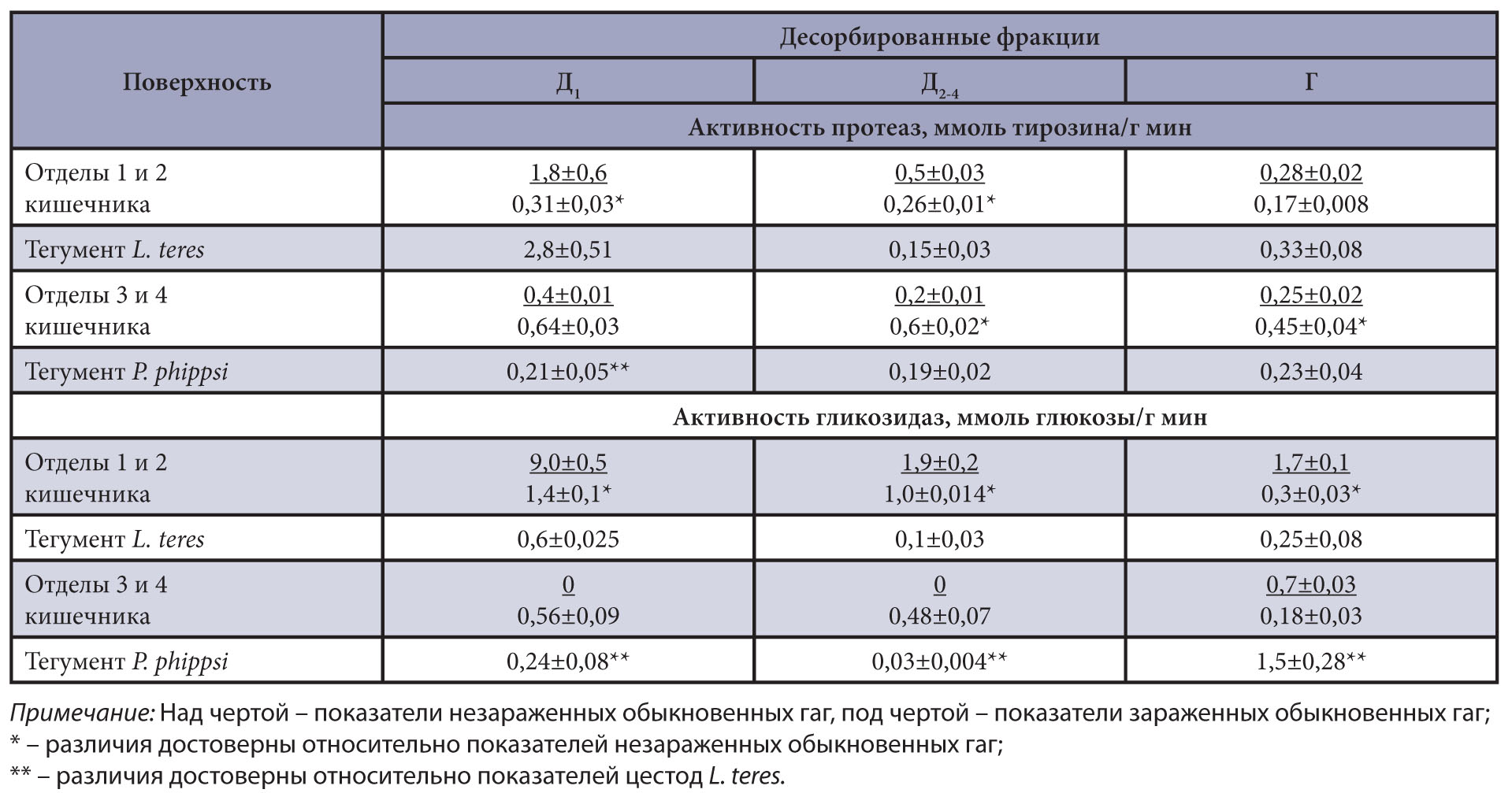
Results and discussion. During coexistence, L. teres were observed mainly in the proximal parts of the intestine of the birds, P. phippsi in the distal parts. Membrane digestion, involving the action of proteases and glycosidases, occurred on the surface of the tegument of both cestodes and acanthocephalans. The protein metabolism intensity in both helminth species was nearly the same, but the glycosidase activity was higher on the tegument of L. teres. The glycosidase activity in the body of the acanthocephalans exceeded that in the cestodes strobile six times. In the intestine parts inhabited by L. teres, both protease and glycosidase activity decreased. In the intestine parts where P. phippsi parasitized, protease activity increased in the intestinal mucosa of the common eider. The total activity of protease and glycosidase along the entire length of the intestine in common eider infected with L. teres and P. phippsi was lower compared to the uninfected birds.
EPIZOOTOLOGY, EPIDEMIOLOGY AND MONITORING OF PARASITIC DISEASES
Paragonimosis is a severe parasitic disease, which causative agent (on the territory of Russia, trematode Paragonimus westermani ichunensis Chung, Hsu et Kao, 1978) circulates in the south of the Far East. Two forms of paragonimosis are known: pulmonary and muscular (larval) with clinical manifestations like diseases of a different etiology, mimicking the symptoms of malignant tumors, and in cases of late diagnosis and improper treatment, leading to death. Long-term studies of the ecology and biology of the parasite, as well as monitoring the incidence among residents of the southern Far East of Russia made it possible to analyze the situation with paragonimosis in the designated region. Based on the available data, until the mid-1990s, natural sites of disease were found almost everywhere in the river basins inhabited by mollusks of the genus Parajuga and crayfish of the genus Cambaroides as parasite intermediate hosts. During this period, according to official information, the population invasion rate reached 6%. Then, as a result of the mass extinction of freshwater crayfish, the population of P. westermani ichunensis was on the brink of survival, and from that moment on, the number of diagnosed cases of paragonimosis in the inhabitants of the region began to decline, down to zero in recent years. Currently, the population of crayfish Cambaroides is reviving and a case of P. westermani ichunensis infestation of a tiger cub has been recorded, which indicates the population restoration of the parasite itself. This indicates the functioning resumption of the Paragonimus sp. infection centers in the south of the Russian Far East. It is necessary to be prepared for the possibility of an exponential growth in the number of infected animals with such a developmentтof events. Due to the complexity of the disease diagnosing and the lack of certain knowledge about the parasite biology among the majority of medical workers, it is necessary to be ready to low detection rate among the region population.
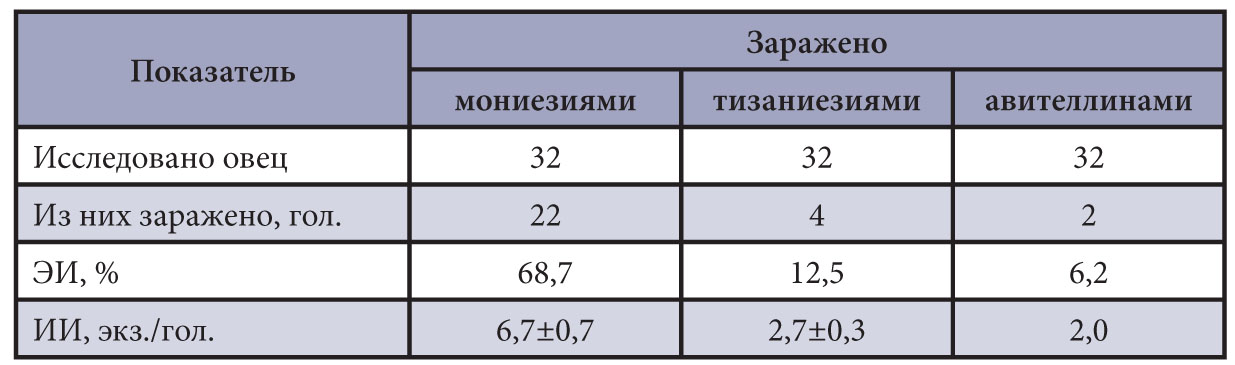
The purpose of the research is analysis of infection with intestinal cestodosis of young sheep in the plain and mountainous zones of the Republic of Dagestan.
Materials and methods. For a number of years, on the basis of the Caspian Zonal Scientific Research Veterinary Institute – Branch of the Federal State Budgetary Scientific Institution “Federal Agrarian Scientific Center of the Republic of Dagestan”, of the laboratory for the study of infective diseases of livestock and birds, we carried out studies of sheep fecal specimens from various regions of the Republic of Dagestan and tested various antiparasitic drugs.
Results and discussion. It has been established that sheep cestodosis are ubiquitous in the Republic, although there are effective antiparasitic drugs, including those of domestic production. The infection extensity by Moniezia sp. in 2015 was 67.8%, Thysaniezia sp. – 12.5%, and Avitellina sp. – 6.2%. In 2016, infections continued to be recorded at a high level. In 2017, monieziosis of lambs was recorded with the infection extensity of 24.0–30.0% and with the infection intensity value of 1.5–6.4 sp. per animal. Avitellinosis was noted in 17.0–23.6 % of sheep with an infection intensity value of 1.0–4.8 sp. per animal. Cestodosis in sheep in 2019 are also found, but less frequently.
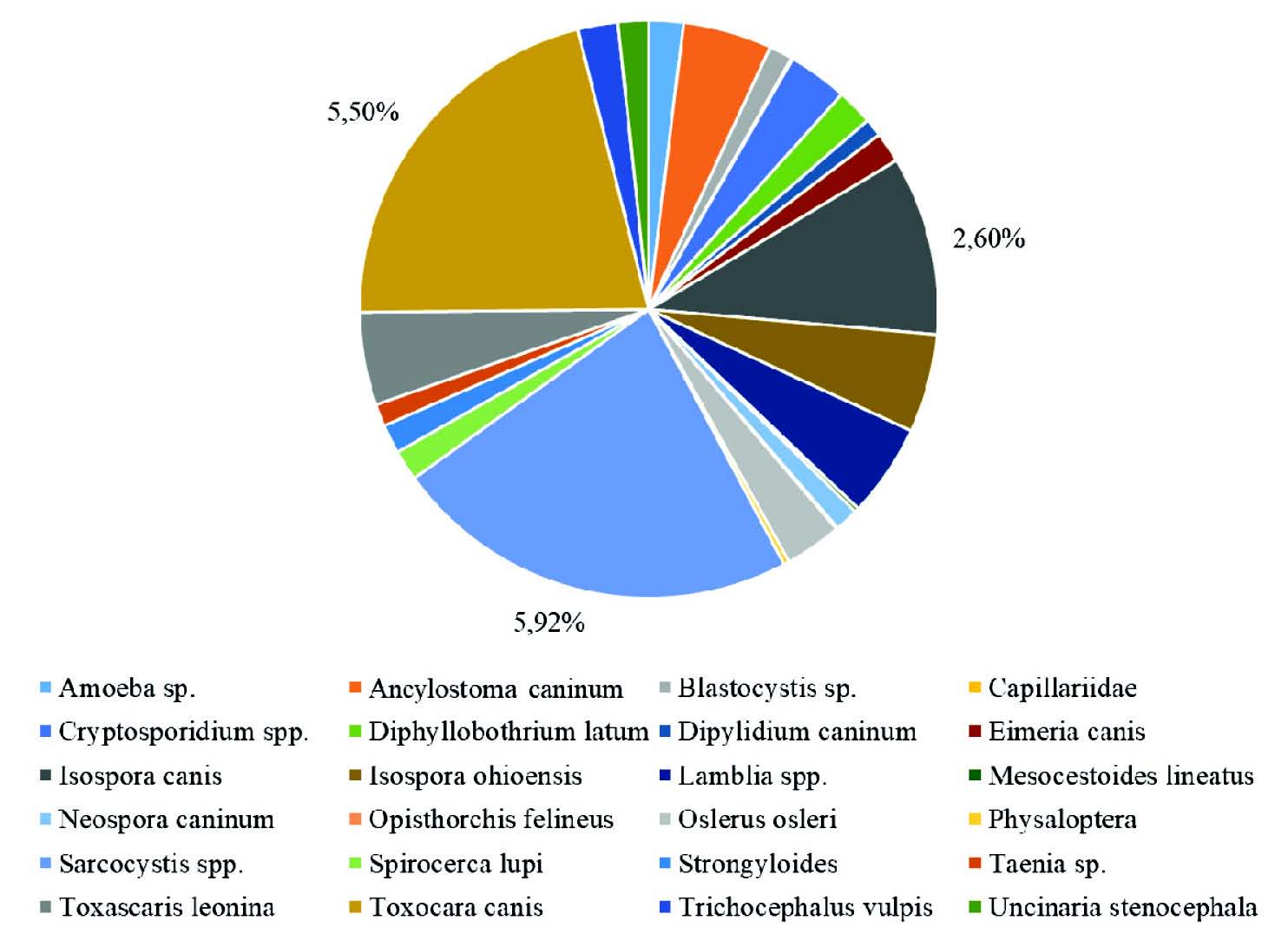
The purpose of the research is comparative analysis of the dynamics of intestinal helminth and protozoa infections in domestic dogs in Perm, and establishment of a relationship between the prevalence of infection with certain pathogens.
Materials and methods. Samples of feces from domestic dogs from Perm were material for the study. Feces were examined by the combined Kotelnikov-Khrenov method and method of successive washing. The results were processed statistically using the Statistica 10.0 software.
Results and discussion. The prevalence of infection with parasites over a 15-year period ranged from 15.38% in 2006 to 44.30% in 2008, and 26.54% in average. The leading position is occupied by Sarcocystis spp. (Lankester, 1882) – 5.92%, Toxocara canis (Werner, 1782) – 5.50% and Isospora canis (Nemesri, 1960) – 2.6%, while the rest of the parasites account for an insignificant amount of identified cases. Statistical analysis of the ten most common parasites among dogs in Perm by years showed a direct relationship between the lungworm Oslerus osleri (sin Filaroides osleri, Cobbold, 1876) and the heteroxenous Coccidia Sarcocystis spp. (rs = 0.572; P < 0.05), as well as a negative correlation between Cryptosporidium spp. (Tyzzer, 1907) and Isospora ohioensis (Dubey, 1975) (rs = -0.526; P < 0.05). When studying Toxocara infection in dogs in different seasons of the year, an increase in the infection prevalence was noted in February with a minimum in July-August. For isosporosis, we identified the spring (March) and more pronounced autumn (September) peaks in infection. Sarcocystosis reached minimum levels of the infection prevalence in September with peaks in May-July. Any correlation between the degree of T. canis, Sarcocystis spp. and I. canis infection in domestic dogs has not been found, which indicates an independent circulation of these pathogens in the urban environment, which does not allow for long-term forecasts of levels of infection, and this must be taken into account when organizing the work of veterinary service.
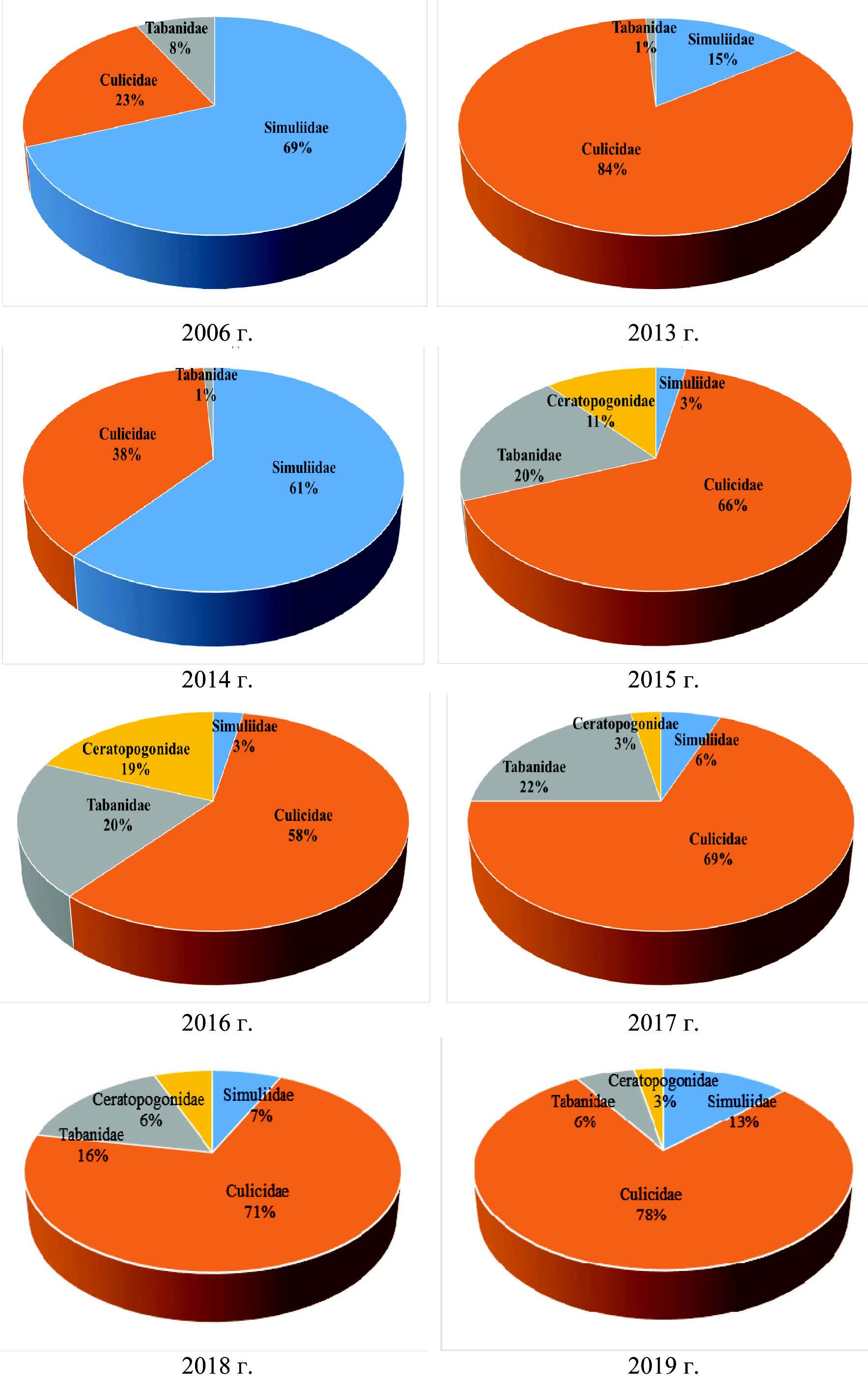
The purpose of the research is comparing abundance levels of blood-sucking dipterans in the forest-steppe zone of the Tyumen Region for 8 years with different meteorological conditions.
Materials and methods. The studies were carried out in 2006 and 2013–2019 in vicinity of the villages of Isetskoe and Barkhatovo, Isetsky District, Tyumen Region. Tabanid flies were collected and counted using funnel-shaped traps permanently on the same pasture on a regular basis once every 5–7 days during the entire emergence period. When counting the number of mosquitoes, midges and sandflies, we used a net with removable bags. Each count included 10 sweeps with a motion of the figure eight "around itself" in 10 replications.
Results and discussion. The abundance of blood-sucking dipterans is largely determined by natural and climatic conditions and a hydrological regime of rivers, and is liable to significant fluctuations. The maximum abundance of gnats was recorded in 2014, the minimum in 2006. In comparing the average number for seasons with maximum and minimum abundance, a difference of 3.7 times was found. The abundance level and ratio of individual components of the midges complex depending on the season also underwent significant changes. In collected insects, midges dominated in 2006 and 2014, and mosquitoes in 2013 and in 2015–2019. Meteorological and hydrological conditions in winter and spring had the biggest impact on the abundance level of insects of the midges complex. Fluctuations in the abundance were 9 times for mosquitoes, 20 times for tabanid flies, and 39 times for midges and sandflies depending on the season. The main limiting factors for mass development of blood-sucking Diptera in the forest-steppe zone of the Tyumen Region are hard and dry winters which cause death of some insects at the preimaginal stages in development, as well as sharp changes in air temperature in the spring-summer period and small areas of breeding places.
BIOCHEMISTRY, BIOTECHNOLOGY AND DIAGNOSTICS
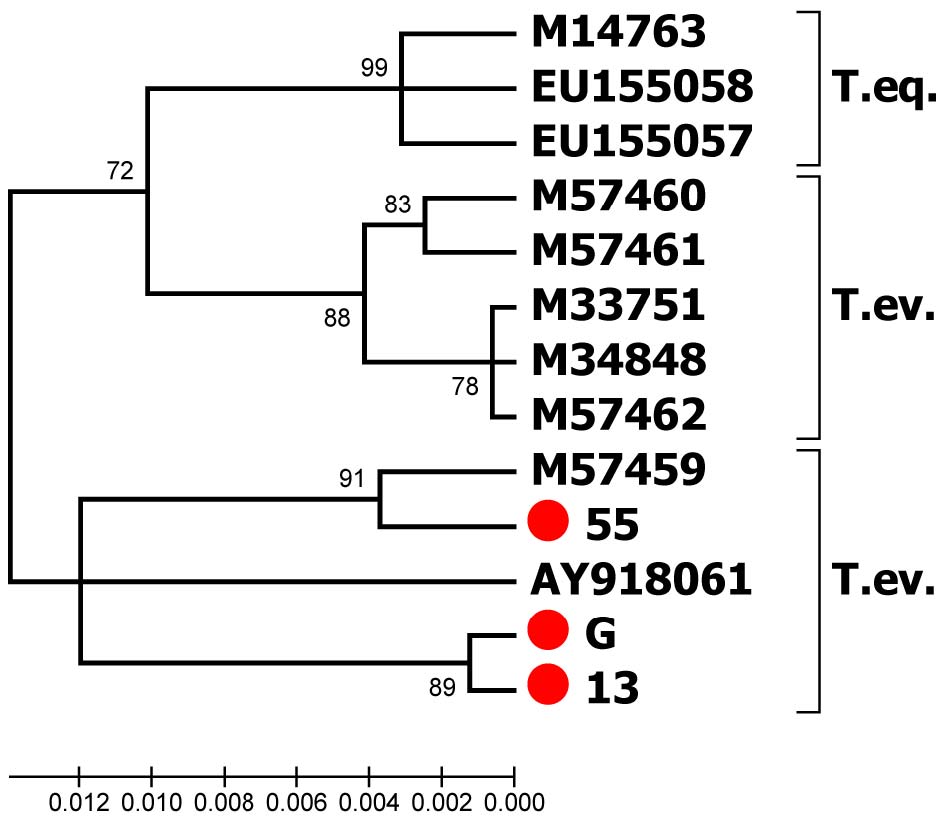
The purpose of the research is developing a method for obtaining erythrocyte antigens containing and not containing Trypanosoma equiperdum and T. evansi DNA, which can later be used in serological reactions to differentiate these types of Trypanosoma.
Materials and methods. The studies were conducted in the Protozoology Laboratory and the Vyshnevolotsk Branch of the Federal State Budget Scientific Institution “Federal Scientific Centre VIEV RAS”, as well as livestock farms of the Russian Federation and other countries using clinical, microscopic, hematological, parasitological, biomolecular and serological methods.
Results and discussion. Studies carried out for the first time have shown that it is possible to use erythrocyte antigens containing the T. equiperdum and T. evansi DNA obtained after 3-fold administration to mice and rabbits of a mixture of trypanosomal antigen with addition of 1.0 ml of an adjuvant (aluminum hydroxide), and bleeding of animals at 25 to 30 days. The formed precipitate was used as an antigen for serological tests. Experiments have shown that blood for preparation of positive serum can be taken when antibodies are in titers of 1:20 in the Prolonged Complement Fixation Test, and at least 1:400 in the Indirect Hemagglutination Test and ELISA, and for negative serum when horse blood serum reacts negatively with antigens of T. equiperdum and T. evansi in the Prolonged Complement Fixation Test, Indirect Hemagglutination Test and ELISA. The test systems of the Prolonged Complement Fixation Test, Indirect Hemagglutination Test and ELISA prepared by us with antigens containing and not containing T. equiperdum and T. evansi DNA resulted in creating a universal test system (Indirect Hemagglutination Test) for differentiating T. equiperdum from T. evansi.
PATHOGENEZIS, PATHOLOGY AND ECONOMIC DAMAGE
The purpose of the research is identifying patients with helicobacteriosis and opisthorchosis, and determining regular features of the course of combined diseases.
Materials and methods. The study involved 50 patients in the Gastroenterology Department with helicobacteriosis diagnosed. Helicobacter pylori was confirmed by the HP test during fibrogastroduodenoscopy. Opisthorchis felineus was detected in patients using the study of feces by the Kato technique and enrichment method. The patients were divided into 2 groups of 25 people each. The first group only consisted of patients with H. pylori. The second group consisted of patients in whom H. pуlori and O. felineus were identified. Initially, the levels of aminotransferases and bilirubin were assessed using a biochemical blood test on a MIURA 200 apparatus. The manifestation of such clinical symptoms as abdominal pain was assessed using a visual analogue scale (VAS). Further, the eradication of H. pylori during therapy was assessed based on the Maastricht V recommendations for 14 days, including the use of three drugs: omeprazole at a dose of 20 mg 2 times a day, clarithromycin – 500 mg 2 times a day, amoxicillin – 1000 mg 2 times a day, and the effectivity of treatment of patients of the second group with opisthorchosis with the use of praziquantel at a dose of 60 mg/kg of body weight during the day three times every 4 hours.
Results and discussion. In the second group of patients with combined pathology, pain intensity was estimated at 4–5 scores in 20 people (80%), and at 2–3 scores in 25 people (100%) in the first group. The severity of nausea was also higher in 100% of patients in the second group. Values for AST and ALT in blood were higher in patients of the second group – by an average of 50–100% in 18 people (72%); increase in the level of bilirubin by 15% in 23 people (92%). Combined pathology (opisthorchosis and helicobacteriosis) is accompanied by more pronounced clinical symptoms (abdominal pain and nausea). In patients with opisthorchosis and H. pуlori, aminotransferases increased up to three reference values and bilirubin increased by 15% were noted. For helicobacteriosis and opisthorchosis, longer treatment was required. The presence of H. pylori at the same time with opisthorchosis did not affect the efficacy of antiparasitic therapy.
TREATMENT AND PREVENTION
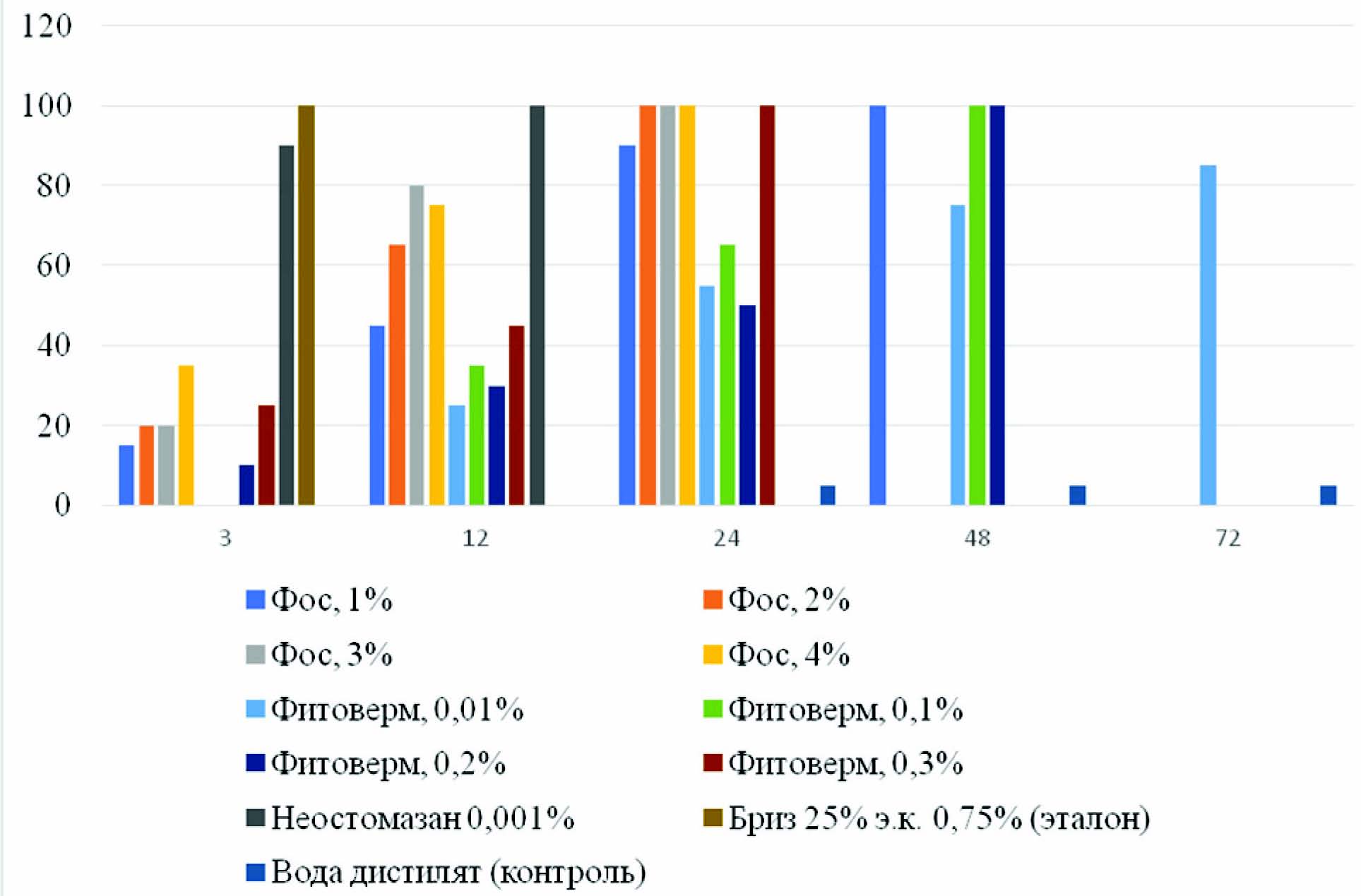
The purpose of the research is studying the efficacy of FOS and Fitoverm drugs against ixodid ticks.
Materials and methods. The study objects were ixodid tick species Ixodes persulcatus (Schulze, 1930), Dermacentor reticulatus (Hermann, 1804) and D. marginatus (Schulzer, 1776) in the imago stage. Ticks were collected in the environment of the Altai plains and mountains from vegetation to the flag under the methodology. The efficacy of drug acaricidal activity was assessed according to the methodological guide. In the laboratory, the ticks were placed in a chamber at a temperature of 7 оC. The effect of drugs was assessed by observation every hour for 2-3 days. Live ticks (20 individuals) were contacted with the drug by immersion three times in the working solution in a permeable fabric container. Neostomosan was used as control. Further tests of FOS and Fitoverm were carried out in the field environment. Briz 25% e.c. was used as control. The plots on which the number of Ixodes had previously been recorded was treated using a sprayer on June 1-2 in the morning. The number of live ticks in the plots was counted 1-2 days after the treatment. The biochemical composition of grass stand on various treated grounds was studied according to standard methods. The results were processed statistically.
Results and discussion. The Siberian Scientific-Research Institute of Horticulture has developed a series of environmentally friendly drugs based on natural biologically active substances that have shown high efficacy against Ixodes. These are FOS and Fitoverm, which provided a 100% lethal effect against Ixodes in working concentrations of 3–4% and 0.1–0.3% under laboratory conditions. Treatment with Fitoverm 0.3%, FOS 3% and synthetic industrial drug Briz 25% of e.c. 0.75% of grass stand at the stage of grazing for cattle in pasture conditions statistically significantly reduces the number of ticks by 71–79%.
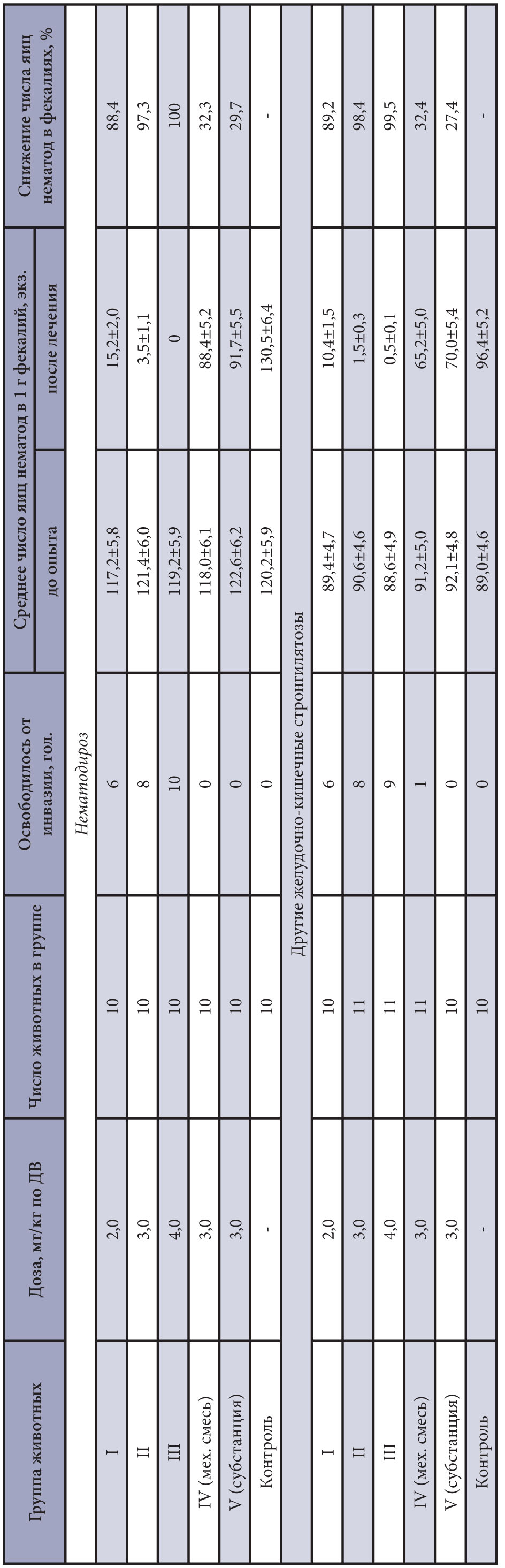
The purpose of the research is to study the efficacy of solid dispersion of fenbendazole (SDF) against nematodoses of young cattle.
Materials and methods. The study of SDF, obtained by mechanochemical processing of fenbendazole substance with polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) polymer, was carried out on 126 young cattle naturally infected with nematodiroses and other gastrointestinal strongylatoses. The animals were divided into 6 experimental groups of 10–11 animals each and SDF was administered once orally at doses of 2.0; 3.0 and 4.0 mg/kg of active substance (a.s.) (I-III groups) in comparison with the mechanical mixture of fenbendazole (FBZ) and PVP in a ratio of 1:9 (IV group) and substance FBZ at a dose of 3.0 mg/kg (group V) against each helminthosis. The control group of animals did not receive the drugs. Anthelmintic efficacy was evaluated in the "control test" based on the data of ovoscopic examination of feces of young cattle by flotation method before and 17 days after drugs administration.
Results and discussion. SDF with PVP at a dose of 2.0; 3.0 and 4.0 mg/kg of a.s. in the form of a 10% powder showed respectively 88.4; 97.3 and 100% efficiency at nematodiroses and 89.2; 98.4 and 99.5 % activity against other types of gastrointestinal strongylates upon obtaining 32.3 and 32.4 % effect of the mechanical mixture of FBZ with PVP and 29.7 and 27.4% efficiency of the base preparation at a dose of 3.0 mg/kg. SDF showed 88.4; 97.3 and 100% of efficacy at doses of 2.0; 3.0 and 4.0 mg/kg of a.s., respectively, against nematodiroses and 89.2; 98.4 and 99.5% against other gastrointestinal strongylatoses in the form of 10% powder. It should be noted that mechanical mixture of PBZ with PVP showed 32.3 and 32.4% efficacy and the efficacy of the basic drug was 29.7 and 27.4% at a dose of 3.0 mg/kg against each helminthosis.
PARASITES OF PLANTS
The purpose of the research is studying the species composition and control measures against parasitic nematodes of wild and cultivated subtropical fruit plants of Central Asia.
Materials and methods. We studied subtropical fruit crops in 198 farms and 1985 household plots located in various soil and climatic zones of over 20,675 hectares in Central Asia. The materials were collected in the autumn (September-October), spring (April-May) and summer (June-August) months in 1970–1990 by the route method. Study subjects were plant parasitic nematodes of 8 species of wild and cultivated subtropical fruit plants in the Central Asian republics. A modified Baermann funnel method was used to isolate plant nematodes from plants and soil near roots. In total, we collected and analyzed more than 5,400 plant and soil samples. To identify the species of plant parasitic nematodes, we used the Atlas of plant parasitic nematodes compiled at the Institute of Parasitology of the Russian Academy of Sciences, as well as morphometric indicators obtained according to the generally accepted De Mann formulae.
Results and discussion. More than 129,000 specimens of plant parasites of 98 species were found in the studied wild and cultivated subtropical fruit crops and soil near their roots. In many farms of the Central Asian republics, we found southern root-knot nematodes, peanut root-knot nematodes, javanese root-knot nematodes, and cotton root-knot nematodes in mixed populations. In Uzbekistan, the prevalence in these crops was from 8 to 61.3%, in Tajikistan – from 78 to 98%, in Turkmenistan – from 6 to 98%, and in Kyrgyzstan – 33%. In addition to root-knot nematodes, representatives of ecto- and endoparasites of the genera Tylenchorhynchus, Merlinius, Quinisulcius, Rotylenchus, Helicotylenchus, Pratylenchus, Paratylenchus, Macroposthonia, Labocriconema and Xiphinema were parasitizing in the above subtropical cultures. Under production conditions, we tested Furadan at a dose of 40 kg/ha, Heterophos at a dose of 60 and 120 kg/ha, and Aldicarb at a dose of 40 kg/ha to control root-knot and other parasitic nematodes. Their efficacy ranged from 89 to 100%. We also used the soil solarization method developed by us, the efficacy of which was 95–98%.
OUR ANNIVERSARIES
ISSN 2541-7843 (Online)