FAUNA, MORPHOLOGY AND SYSTEMATICS OF PARASITES
The purpose of the research is to analyze the current state of the parasitofauna of the Dolginsky herring in the Agrakhan Bay of the Caspian Sea.
Materials and methods. In 2021–2022, parasitological studies of 50 specimens of Dolginsky herring from the Agrakhan Bay of the Caspian Sea were performed. The parasitological autopsy was performed in accordance with the generally accepted methodology, microscopic examinations were performed using Lomo Micmed-5 and MBS-10 microscopes, the type of parasites, the extent of infection (EI), and the intensity of infection (AI) were determined. The species identification of helminths was carried out according to morphological characteristics using the determinants of freshwater fish parasites of the USSR edited by I. E. Bykhovskaya-Pavlovskaya and O. N. Bauer.
Results and discussion. The modern helminth fauna of the Dolginsky herring in the northern part of the Agrakhan Bay includes 8 species of helminths dominated by Pseudopentagramma symmetricum (EI = 80–93.3%, EI – 25–700 sp.), Mazocraes alosae (EI = 71.4%, EI – 5–80 sp.), Anisakis schupakovi (EI = 71.7%, EI – up to 60 sp.). The Corynosoma strumosum scrapers previously discovered by other researchers have not been recorded by us. Due to the fact that herring is the main object of fishing in the Caspian Sea, it is necessary to pay attention to the high rates of invasion by nematodes, which pose an epidemic danger: A. schupakovi, Contracaecum sp., E. excisus.
The purpose of the research is determination of the fauna of blood–sucking arthropods of the Gamasoidea family, whose feeders are small rodent mammals living in the Volgograd region of the Volga-Akhtuba floodplain.
Materials and methods. The research was conducted on the territory of the Volga-Akhtuba floodplain of the Volgograd region in three administrative districts: Svetloyarsky, Sredneakhtubinsky, Leninsky from 2013 to 2019. Collections of ticks of the Gamasoidea family were carried out from the bodies of mouse-like rodents captured using crushers.
Results and discussion. During our research, 3 families of gamase mites have been identified: Laelaptidae Berlese, 1892, Haemogamasidae Berlese, 1889, Liponyssidae Ewing, 1923, belonging to 12 species: Laelaps algericus Hirst, 1925, L. jettmari Vitzthum, 1930, L. hilaris S. L. Koch, 1836, L. pavlovskyi Zachvatkin, 1948, Hyperlaelaps arvalis Zachvatkin, 1948, – Eulaelaps stabularis S. L. Koch, 1839, Haemolaelaps glasgowi Ewing, 1925, Haemogamasus nidi Michael., 1892, Hirstionyssus isabellinus Oudemans, 1913, Hirstionyssus criceti' Sulzer, 1774, Hirstionyssus musculi Johnston, 1849, Hirstionyssus eversmanni Zemskaja, 1955. All gamazid species were collected from small mammals. The species composition of these mammals in the study area is represented by seven species belonging to the family of mysiformes.
The purpose of the research is to study the fauna, expansion, and vertical distribution of ectoparasites in poultry and wild birds in Central Tajikistan.
Materials and methods. The research was conducted in 2014–2024 in the Department of Parasitology of the E. N. Pavlovsky Institute of Zoology and Parasitology of the National Academy of Sciences of Tajikistan. Ectoparasites were collected from domestic chickens, pigeons, rock pigeons, tree sparrows, Spanish sparrows, house sparrows, Senegal turtle doves, rose-colored starlings, barn swallows, common mynas, and rock partridges. A total of 3,232 domestic fowls and 307 wild birds of different sexes and age groups from 290 poultry houses and 229 wild bird nests were examined. A total of 6,756 specimens of ectoparasites were collected including 2,664 Argas persicus ticks and 4,092 specimens of other ectoparasites. Common methods were used to collect scientific material.
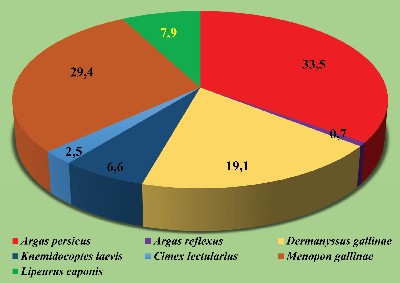
Results and discussion. The examination of 3,232 domestic fowls and wild birds found 7 ectoparasite species in 1,372 birds with the infestation rate being 42.4% as follows: Argas percicus Oken, 1818, Argas reflexus Fabricius, 1794, Dermanyssus gallinae De Geer, 1778, Knemidocoptes laevis Furstenberg 1870, Cimex lectularius Linnaeus, 1758, Menopon gallinae Linnaeus, 1758, and Lipeurus caponis Linnaeus, 1758, which belong to Arthropoda Gravenhorst, 1843. Argas percicus were found in 460 birds, which was 33.5%; Argas reflexus in 10 birds, 0.7%; Dermanyssus gallinae in 263 birds, 19.1%; Knemidocoptes laevis in 91 birds, 6.6%; Cimex lectularius in 35 birds, 2.5%; Menopon gallinae in 404 birds, 29.4%, and Lipeurus caponis in 109 birds, 7.9%.
The purpose of the research is to update and supplement the data on the parasite fauna of bleak Alburnus alburnus (Linnaeus, 1758) from the rivers of the Belgorod region, as well as to analyze the changes that have occurred in the composition of its parasite fauna.
Materials and methods. A parasitological study was carried out on 313 bleak individuals caught with a float rod, mostly in the Seversky Donets River, as well as in other rivers of the Belgorod region (Nezhegol, Mokraya Ivica, Oskolets, Vorskla) in 2018–2021.
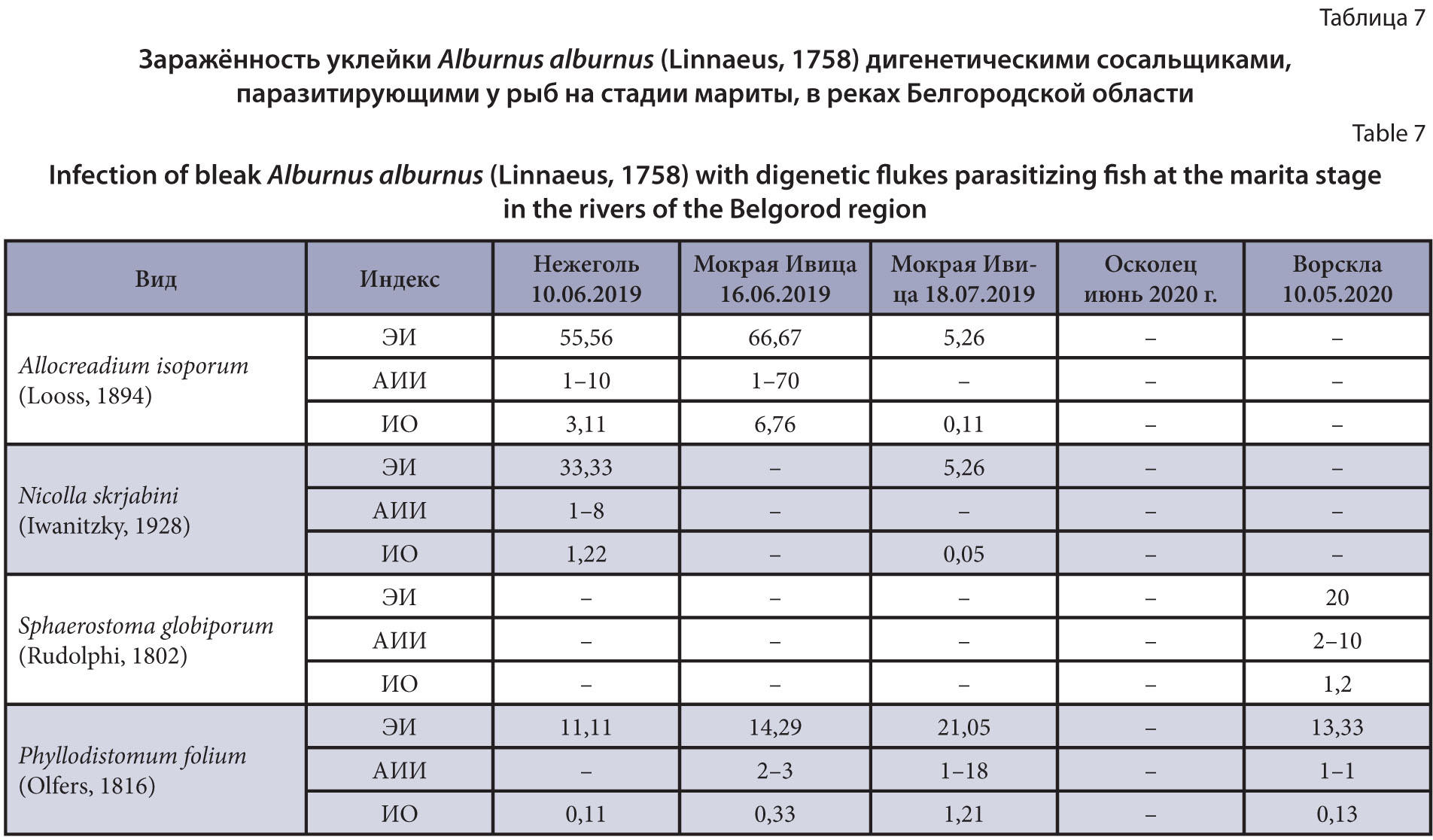
Results and discussion. As a result of parasitological studies of bleaks from rivers of the Belgorod region, at least 38 species of parasites were noted. These are mainly species that are widely specific to carp fish (Cyprinidae) and have a wide distribution. In bleaks from the Seversky Donets River, 33 parasitic species were found (Ciliophora – 2, Myxozoa – 1, Monogenea – 5, Trematoda – 20, Cestoda – 1, Nematoda – 1, Crustacea – 2, Mollusca – 1). Comparison of the revealed composition of the parasite fauna of bleak from the Seversky Donets River with known literary data allowed us to establish that of the previously noted specific parasites, two species are currently missing – Dactylogyrus fraternus and D. parvus, and species with a complex life cycle involving planktonic crustaceans have not been found – Proteocephalus torulosus, Philometra rischta and Neochinorhynchus rutili. At the same time, such species as Ichthyophthirius multifiliis and Gyrodactylus gracilihamatus, which have a wide range of hosts, have been added to the regional parasite fauna of bleak. A characteristic feature of the rivers of the region continues to be the high diversity of the species composition of trematodes found in fish at the metacercaria stage. The data obtained indicate the ongoing degradation of the biohydrocenosis as a result of eutrophication and pollution.
TREATMENT AND PREVENTION
The purpose of the research is to evaluate the anthelmintic effect of solid dispersion (SD) of albendazole (ABZ) against the main helminthosis of young cattle.
Materials and methods. Experimental samples of SD ABZ were obtained by mechanochemical treatment of albendazole substance and polymer – polyvinylpyrrolidone in a roller mill LE-101 in the ratio of 1 : 9 at an energy intensity level of 1 g for 4 hours at a drum rotation speed of 60–70 rpm. The efficacy of SD ABZ was studied on 60 young cattle naturally infected with gastrointestinal strongylates. The animals were divided into 6 groups of 10 heads each. SD ABZ was administered orally to young animals of the 1st, 2nd and 3rd experimental groups in doses of 1.0; 2.0 and 3.0 mg/kg, respectively, of active substance (AS). Animals of the 4th and 5th groups received the basic drug – albendazole substance in doses of 2.0 and 7.5 mg/kg, respectively. Young animals of the 6th group did not receive the drugs and served as a control. The trials of SD ABZ were conducted on 28 heads of cattle against dictyocaulosis and on 30 heads of young cattle against monieziosis, which were divided into 3 groups of 8-10 heads each. SD ABZ was administered to the animals of the first groups at a dose of 2 mg/kg of AS. The animals of the second experimental groups received the ABZ substance at a dose of 2 mg/kg. The third groups served as control and did not receive treatment. The efficacy of the drugs was determined based on the results of coproovoscopic studies using the flotation method before and 18 days after treatment, and using the Berman method in case of dictyocaulosis.
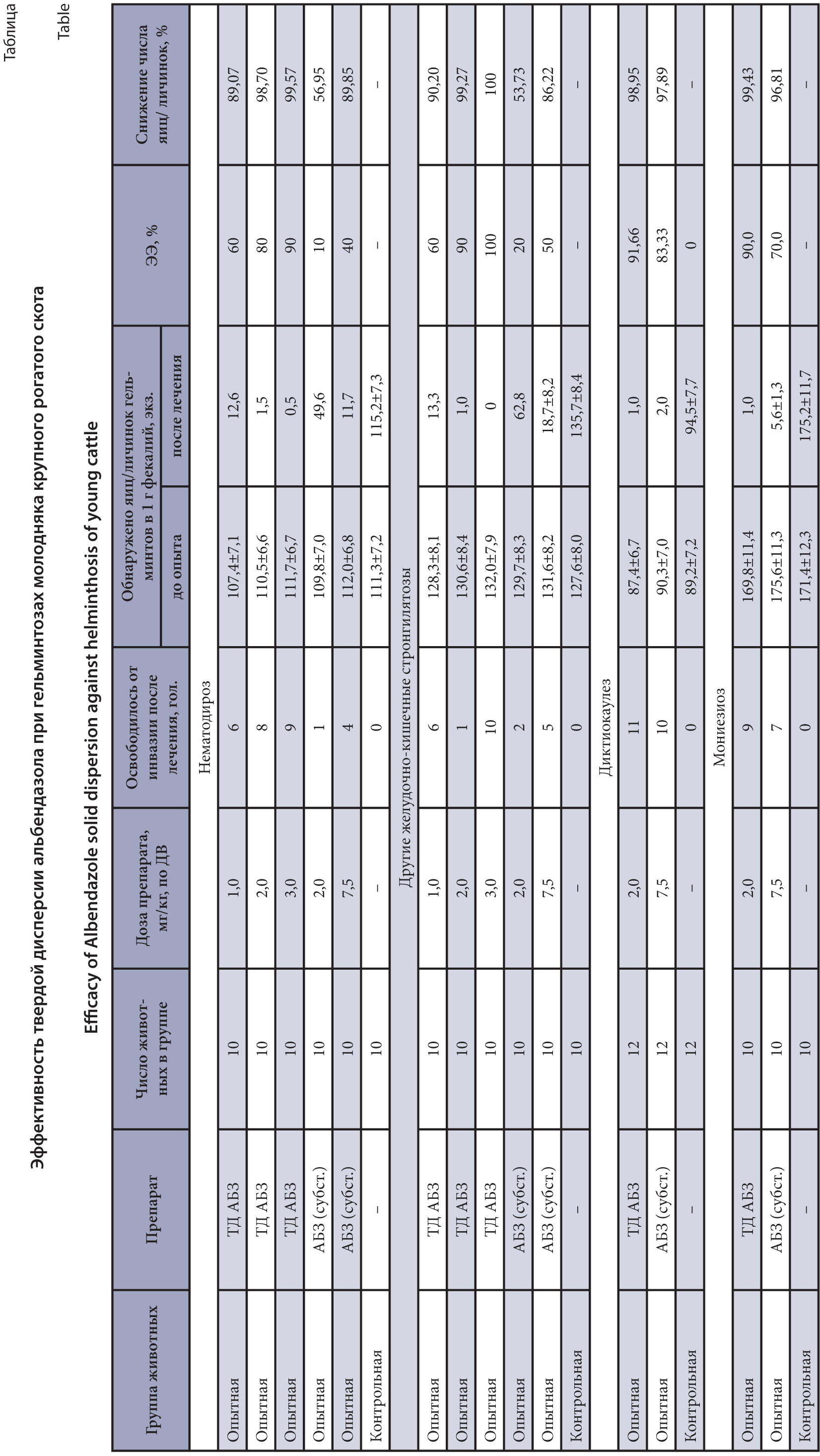
Results and discussion. A high efficacy of the drug (98.7–99.3%) was established at a dose of 2.0 mg/kg of AS at titrating the therapeutic dose of SD ABZ against gastrointestinal strongylatosis of young cattle. We recommend this dose of the drug as a therapeutic one. The results of the SD ABZ study indicate 99.4% efficacy of the drug against monieziosis and 98.9% activity against dictyocaulosis of young cattle at the same dose. The basic drug – ABZ substance at a dose of 7.5 mg/ kg showed 97.8% effect against dictyocaulosis, 96.8% - against monieziosis and 86.2–89.8% effect against gastrointestinal strongylatosis of young cattle.
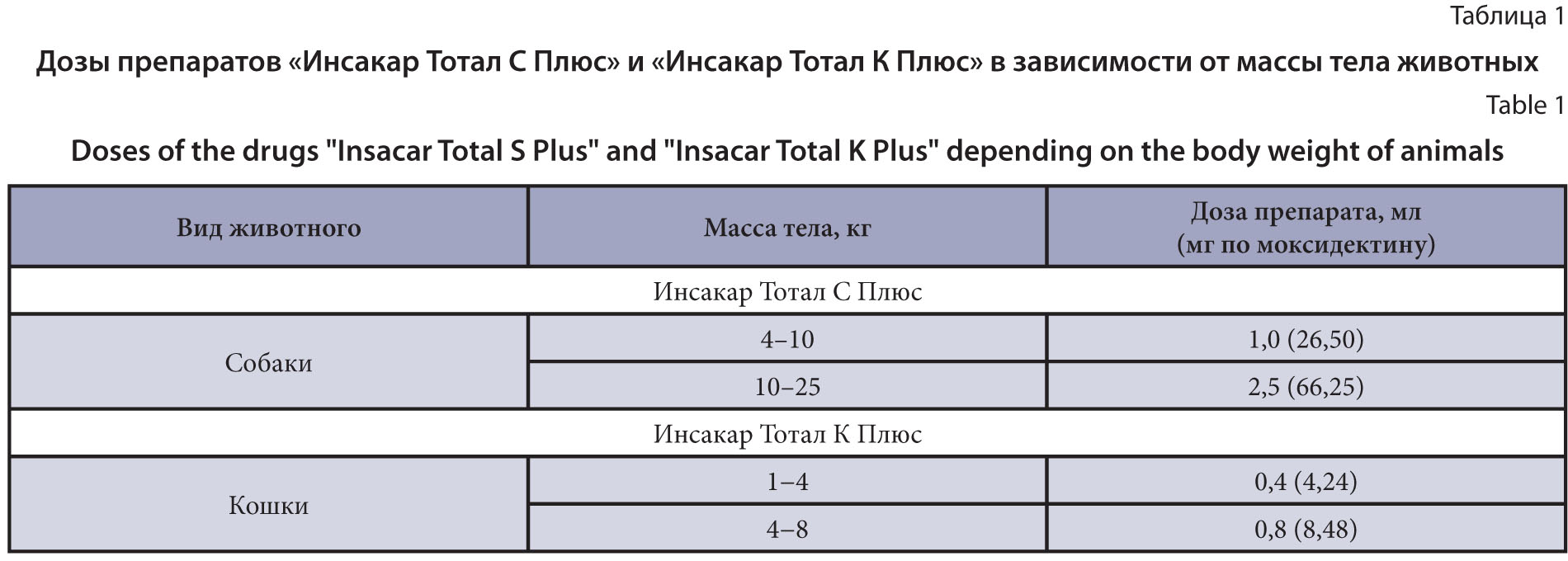
The purpose of the research is to study the efficacy of drugs in a solution formulation for external use to prevent dirofilariosis in dogs and cats.
Materials and methods. The VNIIP – FSC VIEV developed two drugs based on imidacloprid, praziquantel, moxidectin, and pyriproxyfen to treat and prevent ecto- and endoparasitosis in dogs and cats. The studies were conducted on 12 cats and 12 dogs of different sexes, age groups and body weights naturally infected with microfilaria of Dirofilaria spp. in Moscow and the Moscow Region during an active mosquito flight from May to September 2021–2022. The animals were treated with the drugs once, on the skin. To detect microfilaria in the blood, the microscopic slide test and the V. B. Yastreb concentration method (2004) were used. The drug prophylactic efficacy was recorded using the “control test” with the calculation of the average number of parasites detected.
Results and discussion. It was found that the studied drugs showed high prophylactic efficacy against microfilaria of Dirofilaria spp. that circulated in the blood of the dogs and cats on day 60 of the study. No side effects or complications were observed when the drugs were used in the animals.
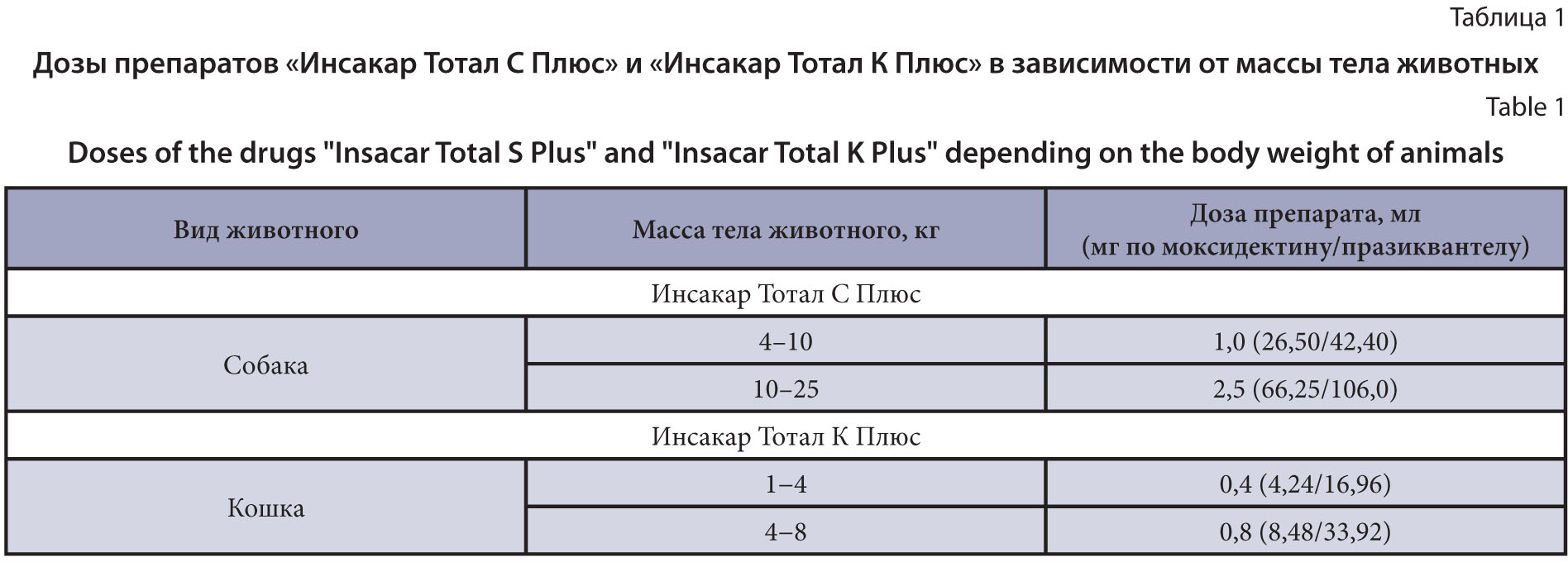
The purpose of the research is to study therapeutic efficacy of drugs in a solution formulation for external use against nematode and cestode infections in dogs and cats of different age groups.
Materials and methods. The VNIIP – FSC VIEV developed two drugs in a solution formulation for external use based on four active components: imidacloprid, praziquantel, moxidectin, and pyriproxyfen for dogs and cats. The research was conducted on 84 dogs and 72 cats of different sexes, age and body weights spontaneously infected with nematode, cestode, and mixed infections in Moscow and the Moscow Region from August 2018 to November 2024. To treat the animals, the drugs were used once by cutaneous application at a dose of 0.1 mL/kg of body weight. The drug therapeutic efficacy was assessed using the "control test" method, with calculating the average number of parasites detected. The infection rate was determined by examining feces by helminthoovoscopy. The clinical state of the animals was determined using common methods in veterinary medicine. The results underwent common statistical processing.
Results and discussion. The studied drugs showed high therapeutic efficacy 10 days after treatment in the dogs and cats with gastrointestinal nematodosis (Toxocara canis, T. mystax, Toxascaris leonina, Uncinaria stenocephala, and Trichocephalus vulpis), cestodosis (Taenia spp., and Dipylidium caninum) and mixed nematode-cestode infections. No side effects or complications were observed when the drugs were used in the animals of different age groups.
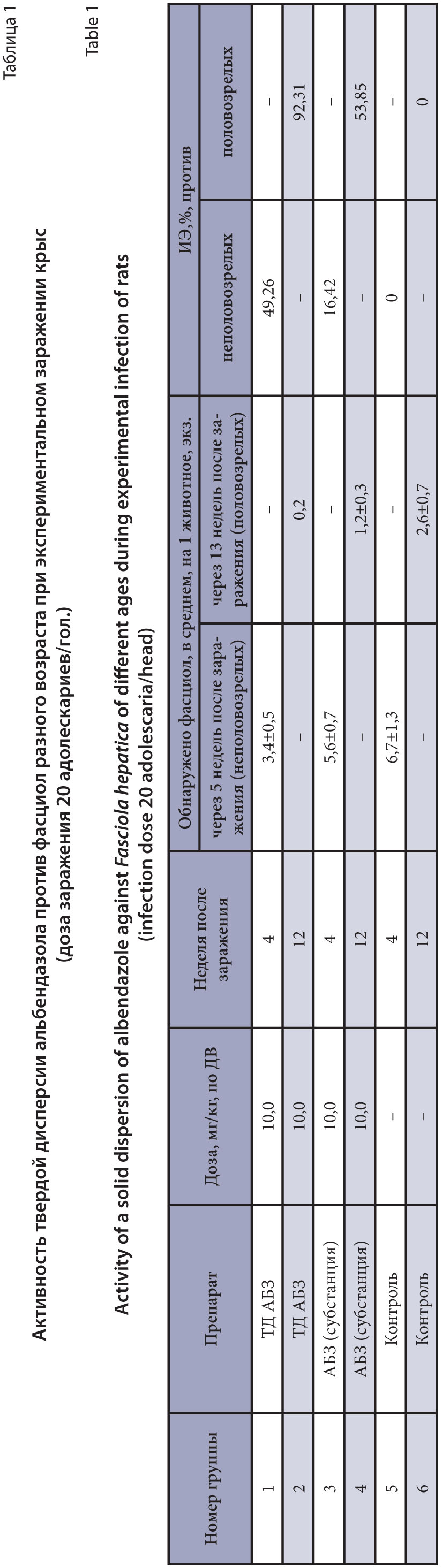
The purpose of the research is to study the anthelmintic efficacy of solid dispersion of albendazole in experimental fasciolosis and dicrocoeliosis of sheep.
Materials and methods. A solid dispersion of albendazole was obtained by mechanochemical processing of albendazole and polyvinylpyrrolidone (1 : 9) in a roller mill LE-101 at an energy intensity level of 1 g for 4 hours at a drum rotation speed of 60–70 rpm. The activity of albendazole solid dispersion against immature and mature Fasciola hepatica was studied on 30 white rats experimentally infected with fasciolae at a dose of 20 adolescaria per animal. The drugs were administered on 4 and 12 weeks after infection. Animals that did not receive the drugs served as controls. The efficacy of the drugs was assessed on 5 and 13 weeks after infection during helminthological necropsy of animal livers. The efficacy of solid dispersion of albendazole was studied on 40 sheep naturally infected with dicrocoeliosis at doses of 5 and 10 mg/kg of active substance (AS) in comparison with the control and the basic drug – albendazole substance. The efficacy of the drugs was studied based on the results of coproovoscopy before and 20 days after treatment.
Results and discussion. . It was found that the solid dispersion of albendazole has 92.3% efficacy against mature fasciolae, against immature ones its efficacy was 49.26%. The basic drug at a dose of 10 mg/kg showed insufficient activity against adults – 53.8% and immature fasciolae – 16.4%. The significant increase in the efficacy of solid dispersion of albendazole was recorded against dicrocoeliosis of sheep. The studied drug showed 79.5% effect at a dose of 5 mg/kg of AS, i.e. practically the same efficiency as the substance of albendazole at a dose of 10 mg/kg. The solid dispersion of albendazole showed 97.0% efficacy at a dose of 10.0 mg/kg of AS.
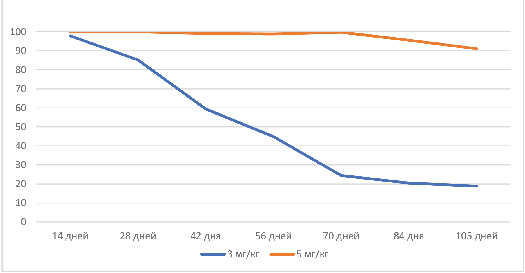
The purpose of the research is to obtain solid dispersions (SD) of fenbendazole (FBZ) with polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP), arabinogalactan (AG) or licorice extract (LE) using mechanochemical methods; to obtain the corresponding supramolecular complexes (SMC) by dissolving the SD in water and to study their anthelmintic activity against strongylatosis in equines; and to determine their prolonged action versus the basic FBZ preparation.
Materials and methods. SMCs were prepared by dissolving in water of the corresponding SD of FBZ and polymeric substances of the following formulations: FBZ : PVP : LE (10 : 45 : 45) and FBZ : PVP : AG (10 : 45 : 45). The obtained SMCs were studied on 72 horses infected with Strongylata. The experimental horses were divided into two groups (n = 42, and n = 30). The animals were given the FBZ SMC : PVP : AG or FBZ SMC : PVP : LE at doses of 3 and 5 mg/kg by the active substance (AS) and the basic FBZ (7.5 mg/kg by the AS). The anthelmintic effect was determined by the number of helminth eggs in 1 g of feces (NHE), the reduction in the number of eggs (RNE,%), and the number of cured animals (NCA, %) within 105 days after deworming. Statistical analysis was performed with the Kruskal-Wallis and Mann-Whitney tests.
Results and discussion. Two weeks after deworming, the RNE in the experimental groups of SMC FBZ : PVP: AG and SMC FBZ : PVP: LE reached 97.92–100%, and 66.74% in the positive control group that was given FBZ. Subsequently, the efficacy decreased, but by week 15, the SMC FBZ : PVP : AG (5 mg/kg) group remained with the RNE of 91.14%, while this rate was 85.19 and 13.78% in the FBZ : PVP : LE (5 mg/kg) and FBZ groups, respectively. The analysis showed statistically significant differences between FBZ SMC and basic FBZ (P < 0.05) in favor of a higher and longer-lasting anthelmintic efficacy of the complexes. Differences between the FBZ : PVP : AG and the FBZ : PVP : LE were not detected at week 2 (P > 0.05), however, at weeks 8 and 15, the SMC FBZ : PVP : AG showed better anthelmintic effects (P < 0.05).
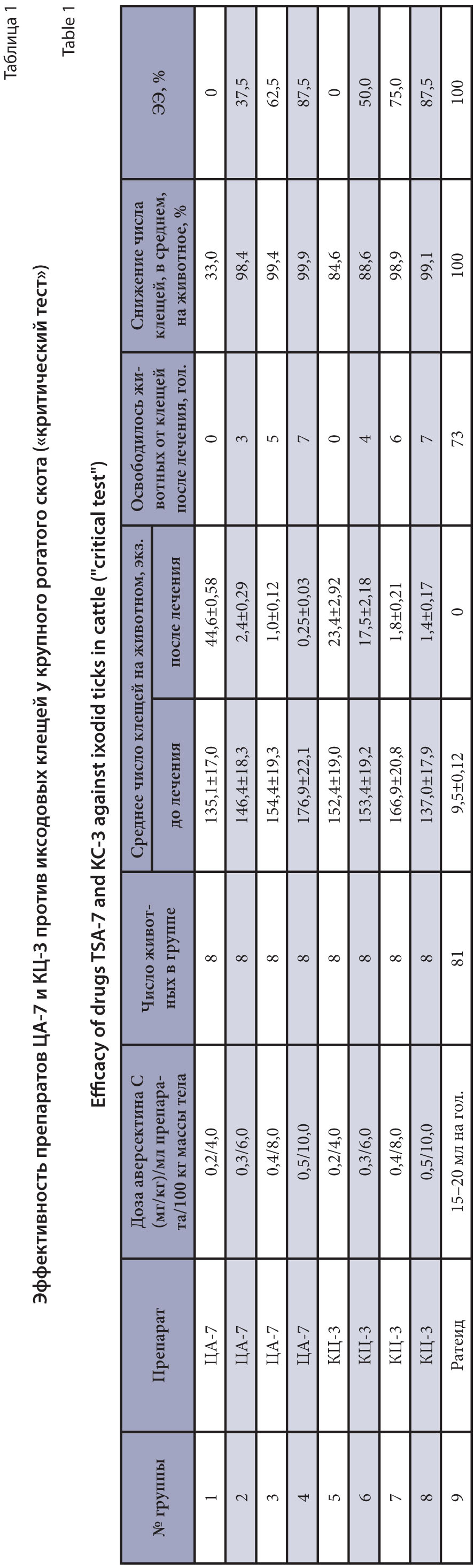
The purpose of the research is to test two new experimental samples of antiparasitic avermectin and pyrethroid combination drugs (CA-7 and KC-3) in a liquid form for dermal application against ixodid ticks and gastrointestinal nematodes of cattle.
Materials and methods. The studies were conducted on 137 animals (cows, bulls, and heifers) of the Simmental breed. Of these, 64 animals most infected with ticks and gastrointestinal nematodes were selected for titration of therapeutic doses and divided into 8 experimental groups of 8 animals each. Drug samples were applied epicutaneously in a range of doses that allowed selecting necessary volumes to obtain the maximum therapeutic effect. To compare the results of the drugs against ticks, the remaining 73 animals were treated in parallel with a commercial insectoacaricidal drug widely used at the experiment site. Faecal samples were collected from the test animals before and on day 7 after application for diagnostics. A coproovoscopic examination was conducted using the Fülleborn flotation method with a saturated sodium chloride solution. The average number of gastrointestinal Strongylata eggs in 1 g of faeces was calculated using a counting chamber. After drug applications, the general condition and local reactions were observed, and the tick and gadfly larvae infection of the animals was recorded. A "critical test" was used to process the obtained data and evaluate the drug efficacy against ixodid ticks and nematodes.
Results and discussion. The extensive effectiveness (EE) of CA-7 against ixodid ticks was obtained at doses of 0.2; 0.3; 0.4; and 0.5 mg/kg for avermectin C (active substance) or 4.0; 6.0; 8.0 and 10.0 mL/100 of the body weight for the drug, respectively: 0; 37.5; 62.5 and 87.5% with an average decrease in ticks per animal of 33.0; 98.4; 99.4 and 99.9%. CA-7 against gastrointestinal nematodes of cattle in the same doses showed, on average, a decrease in the number of nematode eggs in 1 g of feces, respectively: 65.1; 86.7; 92.4 and 100% with the EE of 50.0; 75.0; 87.5 and 100%. KC-3 when used in the same doses showed the EE against ixodid ticks equal to 0; 50.0; 75.0 and 87.5%, respectively, with a decrease in the number of ticks per animal of 84.6; 88.6; 98.9 and 99.1% and a decrease, on average, in the number of Strongylata eggs in 1 g of feces, respectively, by 73.4; 84.6; 91.5 and 93.8% with the EE 37.5; 75.0; 87.5 and 87.5%. Both drugs showed 100% efficacy against hypoderma at a maximum dose of 0.5 mg/kg of the body weight for avermectin C when applied topically.
PARASITES OF PLANTS
The purpose of the research is to study the species composition, distribution, and dominance of nematodes of fruit trees in southern Uzbekistan (Surkhandarya and Kashkadarya Regions).
Materials and methods. The material was collected by the route method in autumn (September-October), spring (April-May), and summer (June-August) months in 2021 to 2024. The study objects were 8 species of parasitic nematodes of fruit trees in the southern part of Uzbekistan (Surkhandarya and Kashkadarya Regions). A modified Baerman funnel method was used to isolate nematodes from plants and root soil. A total of more than 800 plant and soil samples were collected and analyzed. To identify parasitic nematode species, we used a Nematode Atlas compiled at the Institute of Parasitology of the Russian Academy of Sciences, as well as morphometric parameters obtained using the common de Mann formula.
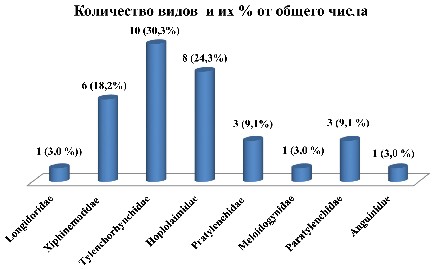
Results and discussion. The phytohelminthological studies conducted on fruit crops (apple, common apricot, peach, cherry, plum, pear, walnut, and pecan) in the Uzbekistan southern regions (Surkhandarya and Kashkadarya Regions) identified 32 species of nematodes that belonged to 2 orders, 4 suborders, 5 superfamilies, 8 families, 10 subfamilies, and 13 genera. In the taxonomic composition of the nematode fauna of fruit trees in southern Uzbekistan, Tуlenchorhynchidae nematodes (10 species) dominated; these species accounted for 30.3% of all species found. Representatives of the Longidoridae, Meloidogyninae and Anguinidae families were observed in small numbers. The species Longidorus elongatus, Xiphinema elongatum, Tylenchorhynchus brassicae, T. claytoni, Bitylenchus dubius, Merlinius brevidens, Rotylenchus robustus, Helicotylenchus dihystera, H. erythrinae, Pratylenchus pratensis, Mеloidogyne incognita and Ditylenchus dipsaci were found in large numbers in southern Uzbekistan, which caused serious damage to the fruit tree productivity.
The purpose of the research is to study determine the ecological composition of nematodofauna of intensive apple (Malus domestica) orchards; analysis of the degree of occurrence and dominance of parasitic nematodafauna species in biotopes; identification of factors influencing the formation of nematodofauna.
Materials and methods. Low-growing apple varieties Gransment and Golden Delicious were selected for the study. Samples were collected during 2023–2024 in intensive apple orchards created in the middle part of the Zarafshan Valley, in the Samarkand region. The obtained individual samples of the root system, root soil at a depth of 0-15 and 15-30 cm of each plant (50 g of each soil sample) were analyzed for the presence of nematodes. In laboratory conditions, the Baerman funnel method was used to isolate nematodes. When identifying species, a formula based on morphometric indicators recommended by de Man, as well as phytohelminthological identifiers were used. Classification of nematodes by ecological groups was based on the classification recommended by Yeates et al.
Results and discussion. When analyzing nematodes isolated from the root system and rhizosphere soil of apple trees, 1277 individuals belonging to 54 species were identified. The identified nematode species were divided into several ecological-trophic groups based on their feeding characteristics and the degree of connection with plants. The studied nematode fauna included 20 species of parasitic nematodes. These parasitic nematodes, in turn, are divided into several smaller groups depending on their feeding characteristics. It was found that endoparasites of the genera Ditylenchus, Pratylenchus and ectoparasites of the genera Xiphinema and Merlinius are relatively widespread among parasitic nematodes. Also, among these species, Longidorus arenosus and L. olegi were found, which are registered as new species for the nematode fauna of Uzbekistan. The research also revealed factors influencing the formation of the nematode community.
ISSN 2541-7843 (Online)