FAUNA, MORPHOLOGY AND SYSTEMATICS OF PARASITES
The purpose of the research is studying existing fauna and ecology of Galliform helminths in biogeocenoses of Uzbekistan.
Materials and methods. Parasitic worms were collected from chicken-like birds of the terrestrial cenoses of Karakalpakstan and North-eastern Uzbekistan. Birds were studied in all seasons of 2018–2020. Wild birds – Himalayan hen, keklik, grey partridge, quail and pheasant, were hunted by local hunters during hunting seasons, while domestic birds - chickens, turkeys and guinea fowls were uncovered from different types of poultry farms. The study of birds was carried out by well-known methods. It was examined 913 wild and 755 domestic chicken-like animals. The detected cestodes and trematodes were fixed in 70% alcohol, and the nematodes were fixed in Barbagallo liquid. The determination of helminth species was carried out according to the well-known guidelines of domestic and foreign authors.
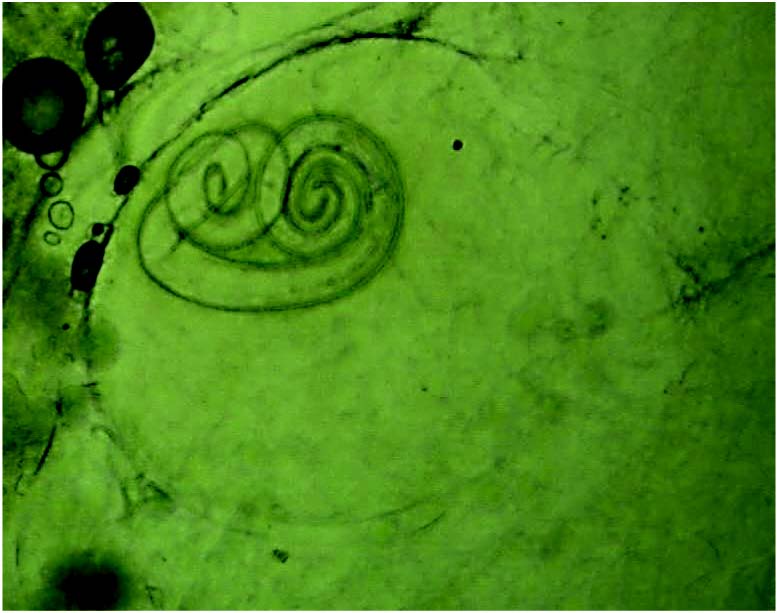
Results and discussion. We found that helminthoses were widespread among representatives of Galliformes in Uzbekistan. Total helminth infections in domestic and wild Galliformes were 50.5%. In infected birds, 44 helminth species were identified, among which 10 species were cestodes, 12 species were trematodes and 22 species were nematodes. Helminth species diversity was the most extensive in the domestic chicken (36 species), turkey (21), and partridge (20). For the first time for the helminth fauna in Galliformes in Uzbekistan, we identified 3 trematode species – Brachylaema fuscatus, Collyriclum faba and Echinostoma miyagawai, and 10 nematode species of the genera Capillaria, Aonchotheca, Ascaridia, Heterakis, Dispharynx, Streptocara, Tetrameres, Diplotriaena and Ornithofilaria.
The purpose of the research is determination of optimal muscle tissue areas for confirmation of diagnosis in the lynx by trichinelloscopy.
Materials and methods. The distribution of Trichinella sp. larvae were studied in spontaneously infected lynxes by the trichinelloscopy method when examining 72 sections in a compressorium. In addition to calculating the total number of isolated larvae and the percentage in muscles, we recalculated per 1 g of animal muscles and performed morphometry of the area and perimeter of Trichinella sp. capsules from various muscles, and calculated the ratio of the capsule length and width, and the M value (arithmetic mean): the area of the capsule and its perimeter. We determined the percentage ratio of the larva size to the capsule and the position in the myosymplast using the Vision Bio system (Epi 2014). The results were statistically processed using the Microsoft Excel software package. The larvae were photographed directly from the screen with digital signal processed by the Vision Bio system (Epi 2014).
Results and discussion. It has been found that the capsules in the muscles are more often rounded (90% of all Trichinella sp. have a length-to-width ratio of 1.1 : 1). However, there are also oval capsules, the largest number of which was recorded in the masticatory muscles (33% of the total capsules in the masticatory muscles). When studying the selective expansion of larvae, it was found that the masticatory muscles, tongue, diaphragm and gastrocnemius muscles were the most populated. Conclusion. We identified high prevalence and intensity of infection in the lynx, which indicates not only the epizootic significance of the lynx in the spread of trichinellosis in the Kirov Region, but also its epidemiological significance as a source of infection. Due to the fact that the meat of this animal is eaten and there is a risk of human infection, it is necessary to examine the carcasses of these animals for trichinellosis by the compressor trichinelloscopy method or by the peptolysis method.
The purpose of the research is identifying a species of the causative agent of canine babesiosis in the Kirov Region.
Materials and methods. To determine the parasite species, we microscopically examined smears from the peripheral blood of sick dogs stained by the Romanowsky-Giemsa method and Leucodif. The microscopy was performed with a binocular microscope Micromed-1. For morphometric assessment of the causative agent, we used a digital camera and software for image analysis ToupView.
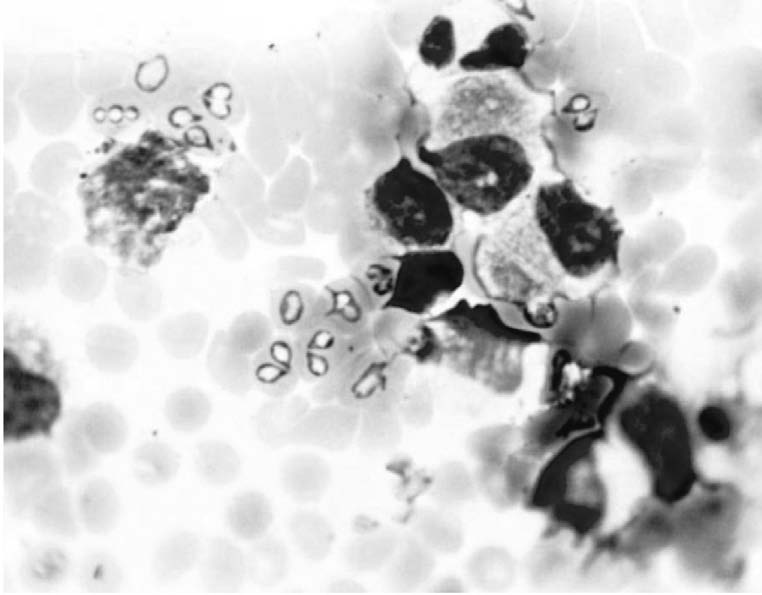
Results and discussion. We found parasites of various shapes and sizes in erythrocytes of the dogs’ blood in an amount from 1 to 4, rarely 8, 16, and 32. Parasites having large paired pear-shaped forms prevailed (100% in Kirov and 92.86% in Vyatskiye Polyany), which were mainly connected by thin ends at an acute angle and located in the center of an erythrocyte. In Vyatskiye Polyany, we found single small pear-shaped parasites in 7.14%, that were also located along the periphery of an erythrocyte. Based on morphological features, the causative agent of “large” Babesia infection (piroplasmosis) of dogs in the Kirov Region is Babesia (Piroplasma) canis (Piana et Galli Walerio, 1895), and of small Babesia infection of dogs is B. (P.) gibsoni (Patton, 1910). In the Kirov City environment, babesiosis proceeds in monoinfection (81.58% prevalence of infection), and the B. canis infection rate is 28.57% in the south of the Region. We recorded a mixed infection of B. canis + Anaplasma sp. (35.71%), B. canis + Anaplasma sp. + Ehrlichia canis (14.29%), B. canis + E. canis (14.29%), and B. gibsoni + Anaplasma sp. (7.14%) in 71.43%.
EPIZOOTOLOGY, EPIDEMIOLOGY AND MONITORING OF PARASITIC DISEASES
The purpose of the research is studying the abundance of Opisthorchis sp. in cyprinid fish.
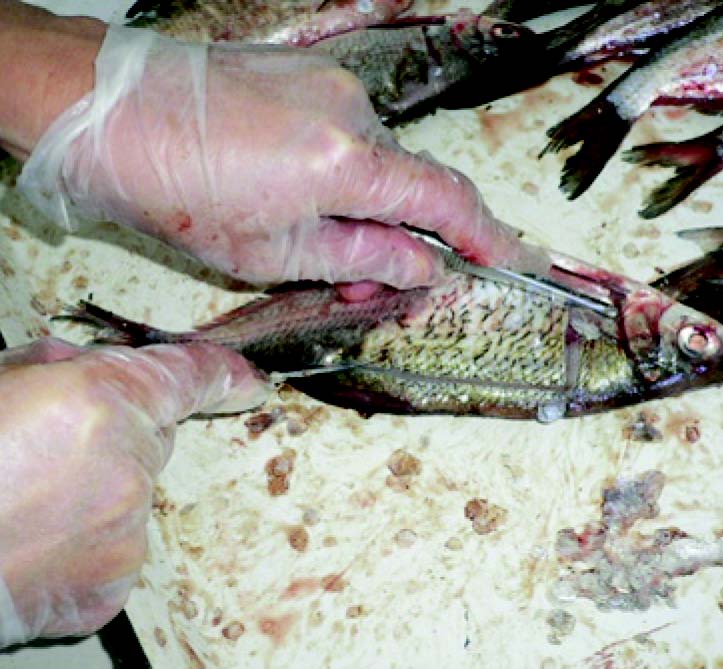
Materials and methods. Diagnostic studies of fish are aimed at identifying the larval stages of Opisthorchis sp. – metacercariae that are infective for carnivores and humans. We examined 183 specimens of fish that belong to 7 species. The fish were examined by the compression method under an MBS-9 microscope.
Results and discussion. The epidemiologically and epizootologically significant fish species in the West Kazakhstan Region are the ide, rudd, roach, bream, tench and silver bream. The infection rate of cat liver fluke metacercariae in these fish species is an indicator of the contamination of the region. The highest prevalence and intensity of infection are recorded in the ide. When studying the age dynamics of fish infected by Opisthorchis sp. metacercariae, we found an increase in infection rate with age. This is the result of a gradual annual accumulation of the parasite in the host. The greatest localization of metacercariae in the fish was observed in the muscles near the dorsal fin where the proportion of accumulated larvae was more than 90%.
The purpose of the research is studying seasonal dynamics of gastrointestinal strongylatosis in bison in the Central Region of the Russian Federation.
Materials and methods. The bison of different age and sex was studied in the Prioksko-Terrasny Nature Reserve, the Moscow Region. Fresh feces collected near feed troughs in enclosures in different seasons for three years were examined according to generally accepted methods. To analyze the infection rate of gastrointestinal strongylates in the European bison by months throughout the year, we took average monthly temperature and humidity values for 2018, 2019, and 2020 into account.
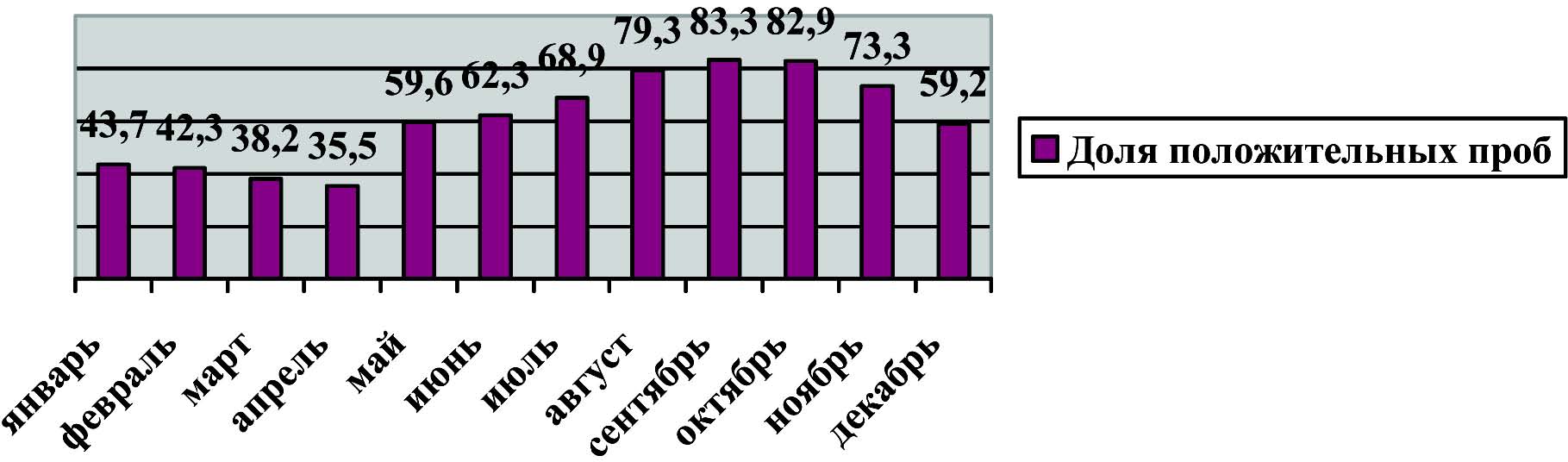
Results and discussion. The maximum number of positive samples was diagnosed in the warm season of the year, namely, in summer and in the first months of autumn: August, September and October 2018 (79.3, 83.3 and 82.9%), August, October, November and December 2019 (73.7, 76.9, 77.1 and 77.8%), and June, July, August and October 2020 (85.6, 87.2, 88.0 and 86.3%). Ambient temperatures and precipitations affect significantly on the time of larvae development in the environment, which can be clearly seen in 2019.
BIOCHEMISTRY, BIOTECHNOLOGY AND DIAGNOSTICS
The purpose of the research is analyzing data on the spread of taeniidoses among carnivores in Moscow, as well as considering issues of their diagnosis and cross-species differentiation.
Taeniidoses occupy a significant place among helminthiases of carnivores. The development cycle of Taenia includes larval parasitism inside the organism of productive animals (cattle, small ruminants, rabbits, etc.), therefore they pose a potential danger to carnivores, as well as humans. Rodents that can also be intermediate hosts of many species of Taenia can play an essential role in the spread of invasion.
PATHOGENEZIS, PATHOLOGY AND ECONOMIC DAMAGE
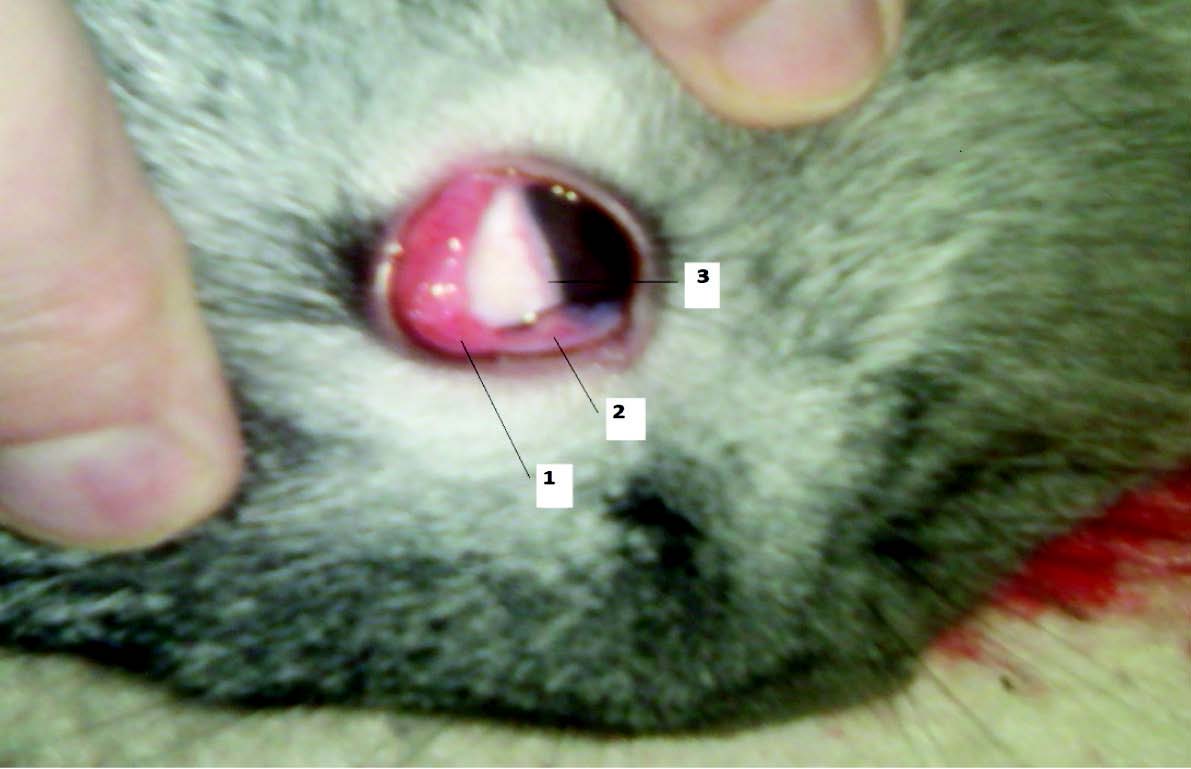
The purpose of the research is studying changes in the structures of the anterior eye of rabbits at acute opisthorchosis and paracoenogonymosis in experiment.
Materials and methods. The studies were performed on sexually mature male rabbits. The first group consisted of animals infected with 50 metacercariae Opisthorhis felineus (Rivolta, 1884) (n = 3), and the second consisted of animals infected with 50 metacercariae Paracoenogonimus ovatus (Katsurada, 1914) (n = 3). The animals from the third group were control (n = 3). The study at opisthorchosis was performed at 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 weeks after infection, and the study at paracoenogonymosis was only performed at 1 and 2 weeks in connection with rapidly proceeding infection. These groups were compared within 1 and 2 weeks and according to specific changes. The clinical study included the upper and lower eyelids turned outwards in animals, and examination of the conjunctival surface of the eyelids, epicanthus (third eyelid), cornea, limbus and sclera of the eyeball, and eyelash less edge of the eyelids at all periods of observation. The measurements were carried out with a millimeter ruler along the longest part of the formation. The data were processed statistically by calculating the arithmetic mean (M) with the standard error of mean (σ) using the Microsoft Excel 2007 software package, and changes in characteristics were assessed at follow-up by the Wilcoxon rank sum test.
Results and discussion. In the acute phase of opisthorchosis, the structures of the anterior eye are damaged, which occurs after the first week of infection in the form of allergic conjunctivitis, episcleritis. We found follicular formations in the upper eyelid, in the outer corner of the eye with further synulosis by the 5th week, and vascular enhancement of the upper eyelid. Conjunctival and corneal changes a month later were of the type of trachomatous pannus with conjunctival hyperemia of both eyelids, edema, and reddening of the free eyelash less edge. The infection by P. ovatus showed no follicular formations or eyelid edema for two weeks. Thus, at opisthorchosis, we observed the phenomena of combined pathology of the visual organ with a specific component for which an independent name can be distinguished, specific parasite-associated ophthalmitis.
PHARMACOLOGY, TOXICOLOGY
The purpose of the research is studying the pharmacokinetics of moxidectin in the blood serum of cats and dogs after a single administration of antiparasitic drug «Neoterika Protecto tablets».
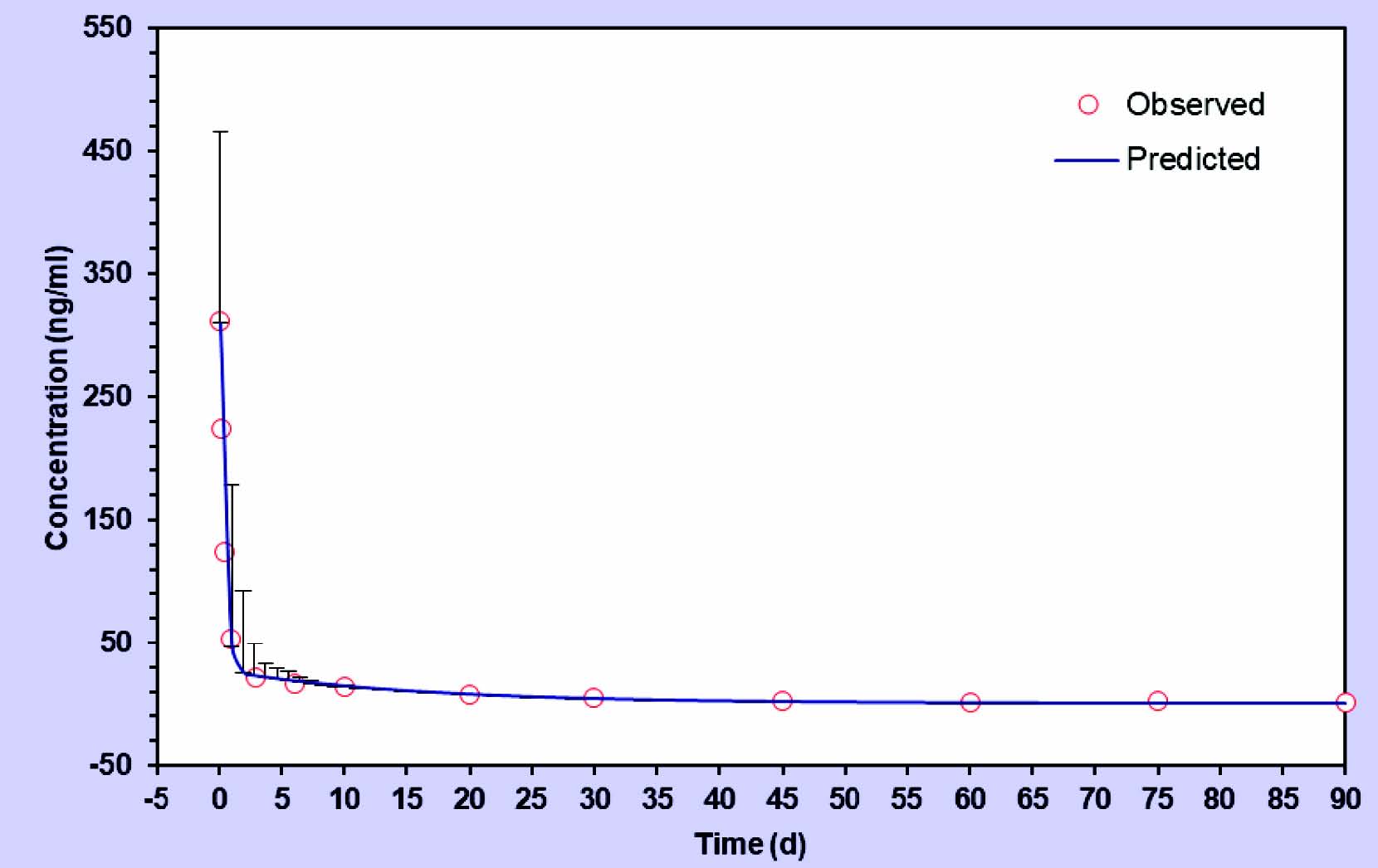
Materials and methods. The studies were performed at the premises of the Kurilovo experimental farm of the VNIIP – FSC VIEV on clinically healthy animals of both sexes aged 1-4 years, namely, 6 cats weighing 1.5–2.0 kg and 6 dogs weighing 10.3–13.8 kg. The drug was administered once orally at the rate of 1.5 mg of moxidectin per 1 kg of body weight. Blood samples were taken in the amount of 2 ml from cats and 4–5 ml from dogs before the drug and after 3, 6, 12, 24 hours, and 3, 6, 10, 20, 45, 60, 75, and 90 days. The study used the high-performance liquid chromatography. We determined the moxidectin content in the blood serum. Based on the results, we calculated the pharmacokinetic parameters of the active substance in the body of cats and dogs.
Results and discussion. It was found that the active substance concentration within 3 hours after a single use of the moxidectin-based drug in the form of tablets reached a level of 134.8–498.0 ng/ml in cats and 479.08–1459.4 ng/ml in dogs; moxidectin was present in the bloodstream of cats and dogs for 90 days. Thus, a single administration of the drug at the recommended therapeutic dose of 1.5 mg/kg allows for the therapeutic moxidectin concentration to be maintained for 90 days.
The purpose of the research is studying the influence of various components on the targeted delivery of fenbendazole and evaluation of their efficacy in mice experimentally infected with Trichinella spiralis.
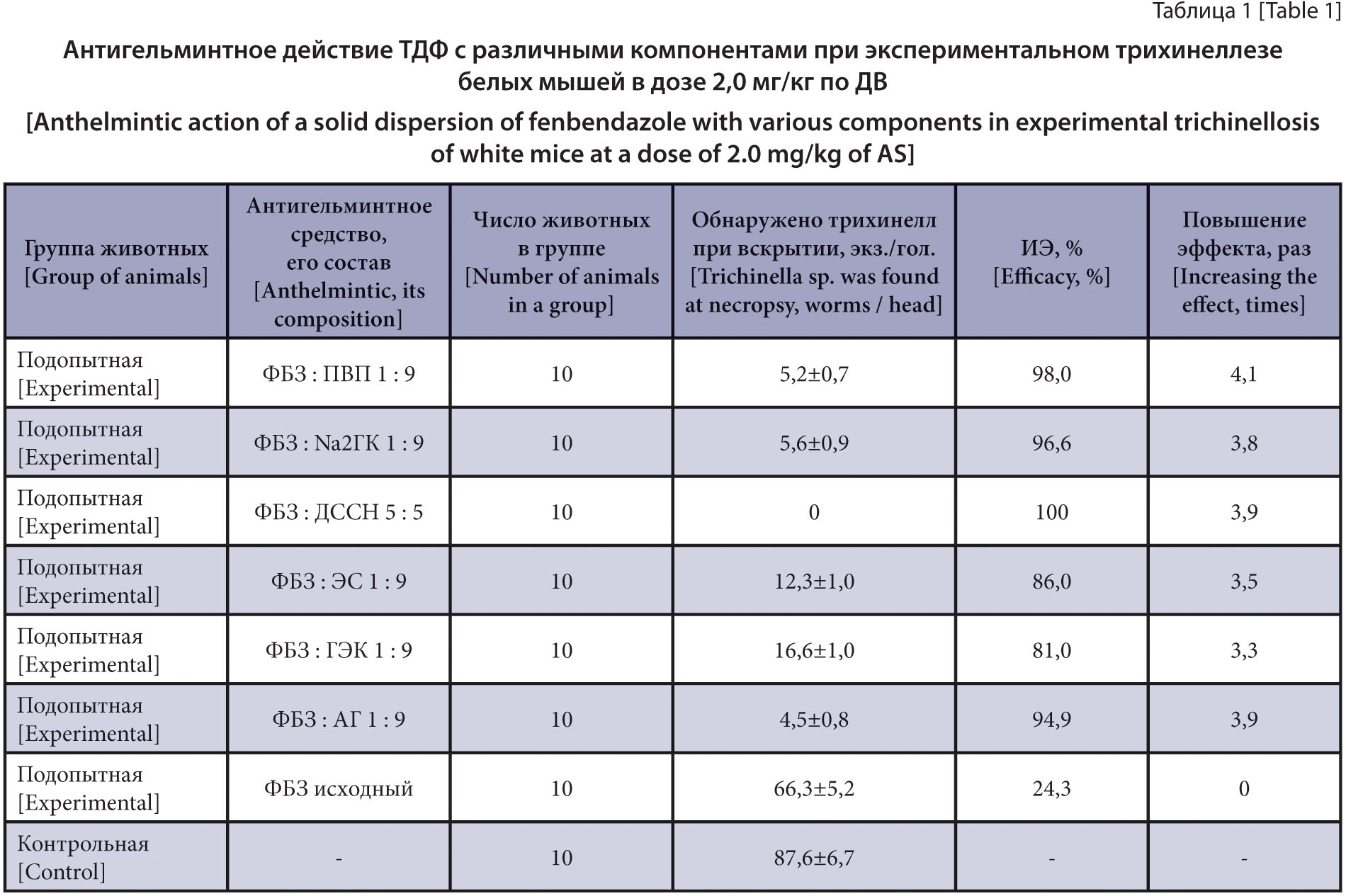
Materials and methods. The experiment used 80 white mice experimentally infected with T. spiralis, at a dose of 200 larvae per animal. Each group of 10 animals was administered intragastrically solid dispersion of fenbendazole (SDF) with polyvinyl pyrrolidone (PVP), arabinogalactan (AG), disodium salt of glycyrrhizinic acid (Na2 GA), sodium dioctyl sulfosuccinate (SDS), licorice extract (LE) and hydroxyethyl starch (HES) at a single dose of 2.0 mg/kg of active substance as compared with the fenbendazole substance at the same dose. The control group did not receive the drug. The anthelmintic efficacy was studied by the results of necropsy of the small intestine of mice on the second day after drugs administration. The concentration of fenbendazole and its metabolites in the small intestine was determined by high-performance liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry detection.
Results and discussion. SDF with PVP, AG, Na2 GA, SDS, LE and HES showed 98.0, 94.9, 96.6, 100, 86.0 and 81.0% efficacy against intestinal nematode T. spiralis at a dose of 2.0 mg/kg of AS (fenbendazole). The maximum concentration of fenbendazole and its metabolites – sulfone and sulfoxide - was determined in the small intestine wall of animals on the second day after SDF with SDS administration and amounted to 3117.8, 614.6 and 2998.6 ng/g respectively. After fenbendazole substance administration, the drug and its metabolites were found in trace quantity.
The purpose of the research is to study the cumulative effect and subchronic toxicity of supramolecular complex of fenbendazole (SMCF).
Materials and methods. The cumulative effect of SMCF was studied on 20 outbred white rats weighing 180 g that were divided into experimental and control groups of 10 animals each. SMCF was administered intragastrically to rats of the experimental groups for 24 days at the dose of 2000 mg/kg (1/10 of the previously established single LD50 (20000 mg/kg)) on the first day, then the dose was increased by 1.5 times every four day. The main criterion for evaluation of the results was the death of animals; we also observed the overall condition and behavior of rats. Subchronic toxicity was studied on 40 male white rats weighing 220–240 g. The animals were divided into 4 equal groups. The drug was administered daily to rats of the 1st, 2nd and 3rd experimental groups intragastrically using the doses of 1/5 (4000 mg/kg), 1/10 (2000 mg/ kg) and 1/20 (1000 mg/kg) of LD50 (20000 mg/kg) respectively for 7 days. The control group received 1% starch paste in an appropriate volume throughout the experiment. During the experiment, we observed physical signs and behavior of animals, food and water consumption; weight gains of animals on the 1st, 3rd, 5th and 7th days of the experiment. After the drug administration, animals were sacrificed by cervical dislocation. The laboratory examinations for hematological parameters and biochemical parameters were performed after treatment. Samples of organs (liver, heart, lungs, kidneys, spleen) were taken during necropsy to calculate mass coefficients and to make macroscopic examinations.
Results and discussion. We found that the SMCF did not have any cumulative properties. The overall condition and behavior of rats was within the physiological range; animals consumed food and water and showed no signs of intoxication after oral administration of SMCF at doses of 1/5, 1/10 and 1/20 of LD50 for 7 days. The drug did not have influence on weight gains of animals. Hematological and biochemical parameters did not undergo significant changes and were comparable with the parameters of the control group. The mass coefficients of the internal organs did not differ statistically in experimental and control groups of rats.
TREATMENT AND PREVENTION
The purpose of the research is studying the efficacy of "Tarzan, VE" against representatives of the Blattoptera order, Blattella germanica.
Materials and methods. Experimental studies to study the efficacy of "Tarzan, VE" on representatives of the Blattoptera order were performed for two weeks at the premises of the Skryabin MVA (Moscow) and the KemSMU (Kemerovo). The study object was the red German cockroach B. germanica, a laboratory culture of which was grown in the MVA insectarium. Experiments 1 and 2 consisted of three tests of three sets each: a test to study the efficacy of the drug against cockroaches by the topical application; and a test to study the efficacy of "Tarzan, VE" against cockroaches by the forced exposure of arthropods to test surfaces, namely, plywood or glass previously treated with the drug in different concentrations. Dead insects were counted after a day.
Results and discussion. We established the efficacy of "Tarzan, VE" in the form of an active substance in different dilutions against cockroaches B. germanica of both sexes using the topical application. Its efficiency decreases to 97% when diluted 1000 times (0.001N). With forced exposure to treated test surface (plywood), the efficacy of “Tarzan, VE” depended on the substance diluted: 90% at 0.01N, 83.3% at 0.005N, and 50% at 0.001N. The maximum effect of "Tarzan, VE" was observed when using the method of forced exposure of cockroaches to the treated test surface, glass. The efficacy of the drug in this case was 100% regardless of the sex and development stage of cockroaches. It was found that different concentrations of the insecticide had a toxic effect on the imago of both sexes and larval stages of cockroach development. The insecticidal nature of the drug is ensured by the use of zeta-cypermethrin as an active ingredient. "Tarzan, VE" insecticide can be recommended to control and prevent the distribution of B. germanica.
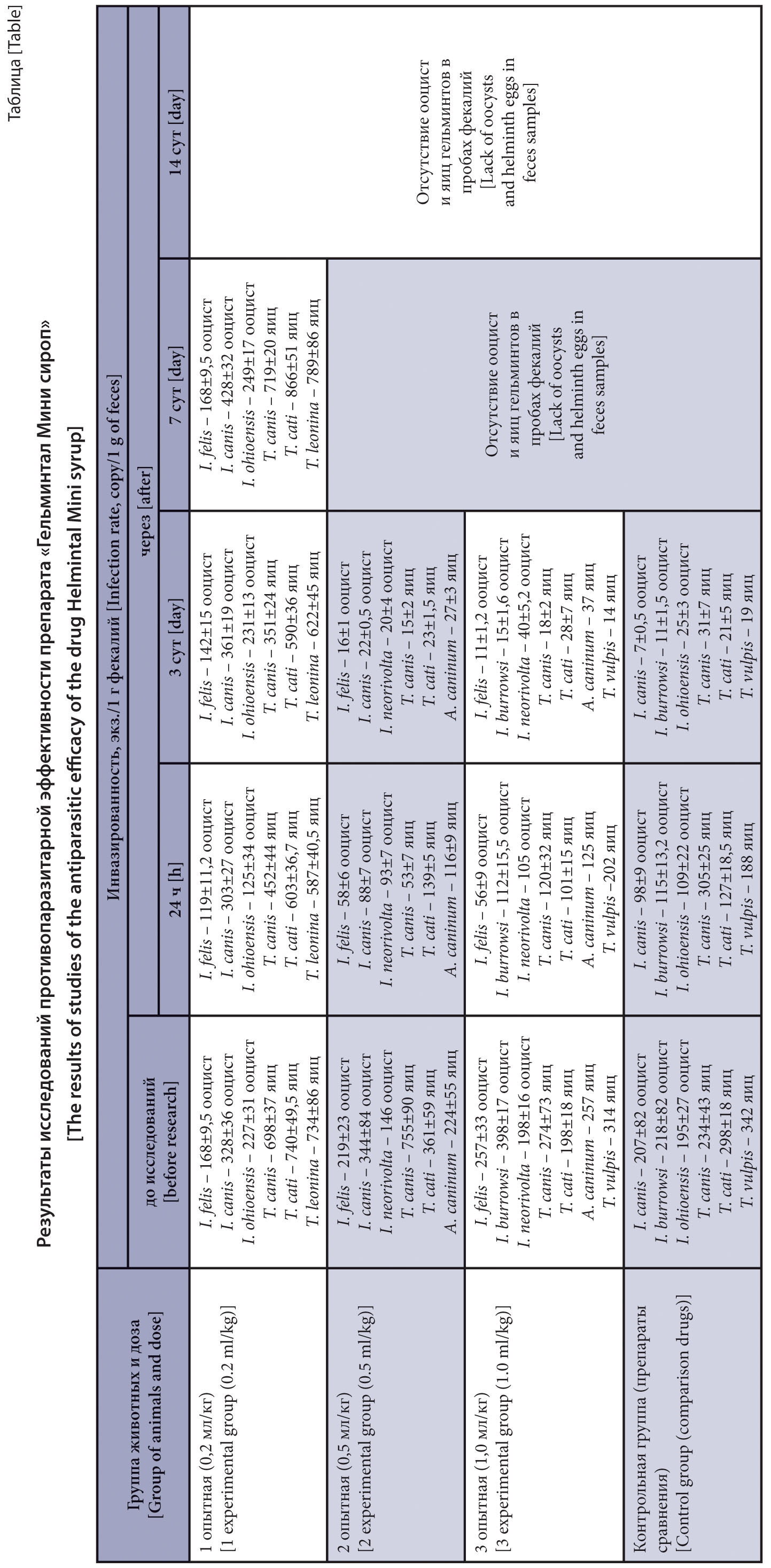
The purpose of the research is comparative assessment of the efficacy and determining the optimal dosage of Helmintal Mini syrup against intestinal parasitoses of animals.
Materials and methods. The studies were performed at the premises of the Lvenok veterinary clinic (Moscow). In total, the experiments involved 68 dogs and cats of various breeds, aged 2 to 11 months, infected with intestinal nematodes and coccidia. The animals were divided into test and control groups; the study drug was administered to the test, and the reference drugs were administered to the control. A drug with a toltrazuril content of 50 mg/ml and a drug with a moxidectin content of 0.6 mg/ml were used as follow-on drugs. The diagnosis and therapeutic efficacy of the drugs were confirmed based on the clinical pattern and laboratory tests by absence/presence of protozoan oocysts and helminth eggs in animal feces in laboratory studies (Fülleborn’s method); and we recorded the dynamics of clinical signs of the diseases.
Results and discussion. In a comparative assessment of the efficacy of Helmintal Mini syrup with follow-on drugs, it showed the same high efficacy at coccidioses and intestinal nematodoses of animals as registered drugs containing similar active substances. The most effective and safe doses of Helmintal Mini syrup have been determined, namely, 0.5 and 1.0 ml per 1 kg of body weight.
The purpose of the research is to identify species of Eimeria spp. in chicken broilers suspected to be infected with coccidia and to determine the effect of coccidiostatics in the course of coccidiosis.
Materials and methods. The study involved 20 six-week-old broiler chickens obtained from a farm heavily affected by coccidia (natural infection – a high oocyst incidence). Each group yielded 10 randomly picked chickens to be used in the experiment. The birds were divided into 2 groups 10 chickens each: control (I); Baycox-treated (II); Baycox was applied for 2 days in a concentration of 25 ppm in drinking water. Samples of broiler chickens’ droppings were tested qualitatively by the flotation method (Willis-Schlaaf) and then quantitatively by the McMaster technique. The chickens were killed 6 days post-treatment and their intestinal mean total lesion scores (MTLS) were graded 0 to 4 on an arbitrary scale described by Johnson and Reid (1970).
Results and discussion. As a result of the research, six species of protozoa of the genus Eimeria were identified: E. acervulina, E. tenella, E. brunetti, E. maxima, E. mivati, E. necatrix, while E. necatrix and E. maxima were the dominant species. This proves the presence of such species as E. mivati, E. acervulina (76.34%) in the anterior segment of the intestine and E. necatrix, E. maxima (83.34%) – in the middle segment of the small intestine. Infections of E. brunetti broilers amounted to 51.11%. The most pathogenic species of E. tenella residing in the cecum was found in 37.53%. MTLS in the group of chickens that received Baycox was 0.33. The post-treatment oocyst indices in the second group amounted to 1 (1–50 oocysts in 1 g of faeces), in the control group MTLS was very high (2,5), the oocyst index exceeding 3.
The purpose of the research is a commission test of the efficacy of the supramolecular complex of ivermectin at gastrointestinal strongylatoses of horses.
Materials and methods. The commission experiment was performed in June 2019 in the North Caucasian Federal District of the Chechen Republic. The efficacy of the supramolecular complex of ivermectin was evaluated on 20 horses of different breeds in the Seradin Equestrian Center. To determine the rate of gastrointestinal nematode infection in horses, we collected fresh feces in the morning, made tissue imprints from perianal folds and examined them by the Fülleborn's method using a saturated solution of sodium chloride.
Results and discussion. The coproovoscopic examination determined a 100% infection of horses with Strongylates and 40.0% infection with Oxyuris sp., with 488.7±24.4 strongylates eggs and 16.9±0.84 Oxyuris sp. eggs found in 1 g of feces, respectively. Seven and 15 days after the supramolecular complex of ivermectin administered to the horses from the first test group at a dose of 0.15 mg/kg for the active substance (7.5 mg/kg for the drug) in a mixture with mixed feed, we did not find any Strongylata eggs or Oxyuris sp. eggs in feces or on tissue imprints. Insufficient efficacy was obtained in the horses from the second test group after being treated with the active substance of ivermectin at a dose of 0.15 mg/kg. The strongylate egg number decreased on average by 244.3±12.21, namely, by 50.1%, and no Oxyuris sp. eggs were found. The efficacy against Oxyuris sp. was 100%. The horses consumed the mixture of drugs with feed readily. There were no side effects after the drugs applied. Thus, we established the high efficacy of the supramolecular complex of ivermectin against gastrointestinal strongylatoses, and the convenience of its use in a mixture with feed to untamed herd horses individually and by group feeding.
The purpose of the research is analysing a complex of veterinary and sanitary preventive measures against trichinellosis on fur farms.
Materials and methods. The system of measures against trichinellosis is based on creating conditions on fur farms that are aimed at prevention of the invasion, and includes occasional immunological screening of animals, examination of dead animals for trichinellosis and observation of veterinary, sanitary and zootechnical requirements for animal management.
Results and discussion. The sero-epizootic monitoring methods of elderly animals implemented on farms based on ELISA and Capillary Ring Precipitin Test allows us to identify infected animals and exclude them from the technology system of maintenance and breeding. The general situation of trichinellosis can be determined by results of studies by a compression or enzyme methods of animal carcasses during the period of mass slaughter for fur.
PARASITES OF PLANTS
The purpose of the research is a demonstration field experiment on testing nematode-resistant potato varieties on a collective farm in focal point of golden potato nematode (GPN).
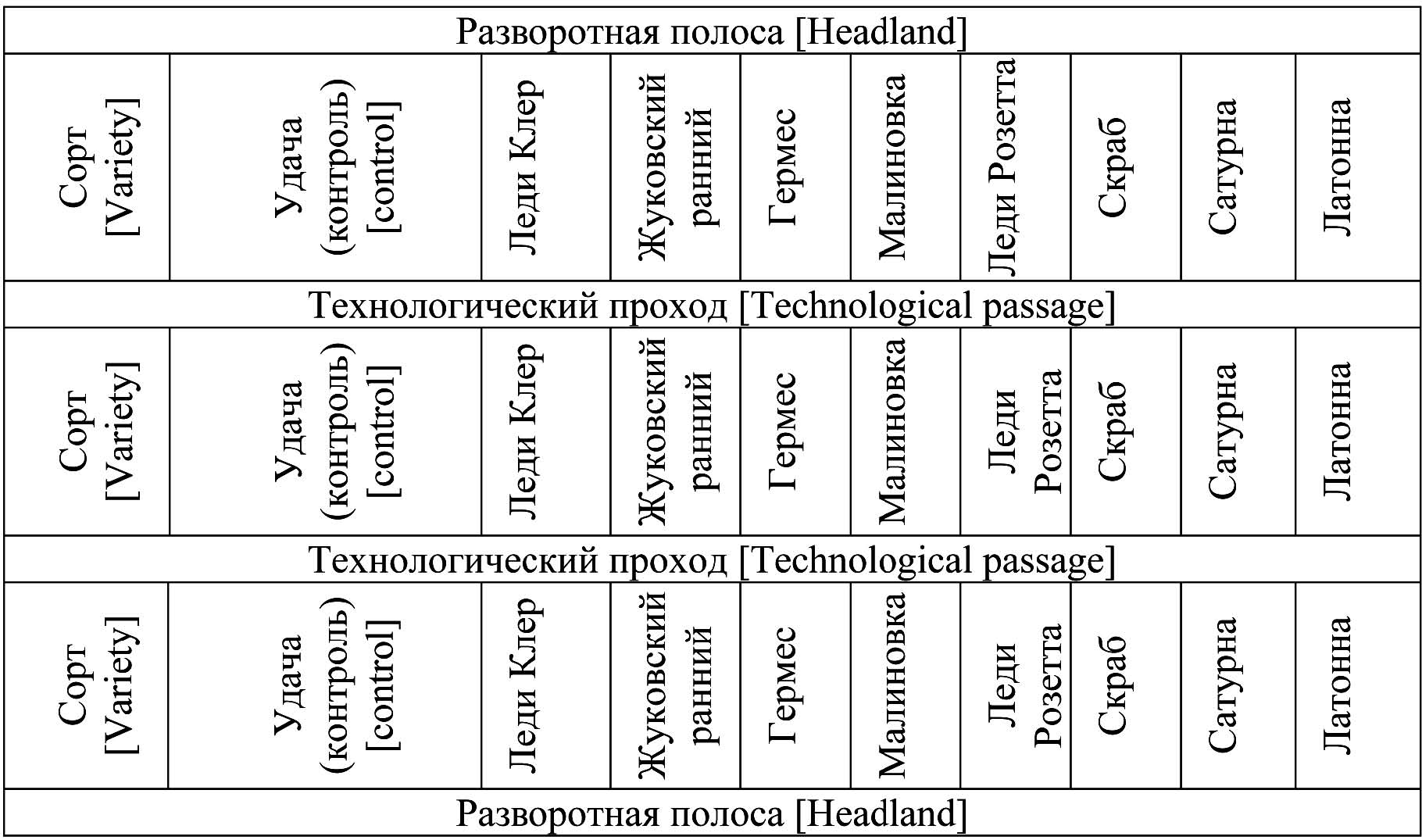
Materials and methods. A demonstration field experiment on testing 7 nematode-resistant and 2 susceptible potato varieties was performed in the village of Parakhino, Gus-Khrustalny District, Vladimir Region, in a small family garden with significant evidences of potato globoderosis. The family garden was divided into 27 plots. The plot area was 100 m2 . In spring and autumn, 500 cm3 soil samples were taken from each plot. The soil samples were studied by the flotation funnel method. In growing season, we measured the height of plants, counted the number of stems, estimated the color, considered the uniformity and projected coverage of grass stand of the soil, assessed the globoderosis development, and determined the number of female GPN and their development on plant roots. During the harvesting period, we took into account the number and weight of potato tubers (standard and nonstandard) in 25 plants on each plot and the number of plants on the plot, and determined potato yields. We calculated the biological and economic effectiveness of growing nematode-resistant potato varieties.
Results and discussion. The demonstration field experiments of 7 nematode-resistant potato varieties using modern mechanized potato cultivation techniques in the globoderosis focus faced by high infective rate (pre-plant density of the GPN population was 9.7–10 thousand eggs and larvae per 100 cm3 of soil) showed that the nematode-resistant varieties of Saturna, Lady Rosetta, Lady Claire, Malinovka, Latonna, Skarb, Zhukovsky Ranny surpassed susceptible cultivar Udacha (standard) in biological effectiveness (57–85%), economic effectiveness (4.9–134%) and economic benefit (87–409%). In susceptible cultivars Udacha and Germes, the globoderosis development was above 53%. In the tested nematode-resistant cultivars, the globoderosis development was poorly expressed (15–26%). Nematode-resistant cultivars Lady Claire, Lady Rosetta and Saturna, which showed the highest levels of profitability, economic efficiency, and high rates of decrease in the GPN population density in the soil can be recommended for cultivation in the fields of the Rossiya agricultural company. Susceptible cultivar Germes, which has shown good performance in terms of economic effectiveness and benefit can be recommended for cultivation in the crop rotation fields of the Rossiya agricultural company. Nematode-resistant cultivars Malinovka, Skarb, Latonna and Zhukovsky Ranny, which showed less economic effectiveness and benefit as compared to potato varieties for chips can be recommended for cultivation in private plots if cultivated using modern technology.
ISSN 2541-7843 (Online)