EPIZOOTOLOGY, EPIDEMIOLOGY AND MONITORING OF PARASITIC DISEASES
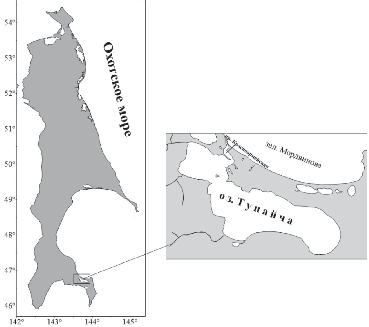
The purpose of the research is to analyze specifics of Anisakis simplex larvae infection in the body cavity of the lake Pacific herring in Lake Tunaicha (from materials of 1980 to 1995).
Materials and methods. Conventional parasitological methods were used for collecting the material. The dissection recorded the number of nematodes in the fish. Parasitological studies of the herring from Lake Tunaicha (southern Sakhalin) were conducted from 1980 to 1995. A total of 4,438 fish caught in the Krasnoarmeyskaya channel and Lake Tunaicha were examined.
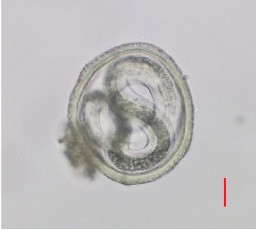
Results and discussion. The parasite fauna in the herring from Lake Tunaicha included six parasite species of which two nematode species (Anisakis simplex l., Hystorethylacium aduncum l.), one acanthocephala species (Corynosoma strumosum juv.), one trematode species (Brachyphalus crenatus) and two parasitic copepod species (Ergasilus wilsoni and E. hypomesi). Among all the above species, A. simplex larvae were of greatest interest for study. The helminth is a typical species of the Pacific herring and poses a threat to human and animal health. The results of the studies found no difference in the infection of herring females or males in Lake Tunaicha. A change in the infection rate was demonstrated in the herring by age and linear dimensions depending on the fish life cycle (spawning and wintering migration periods). The first cases were recorded for herrings infected with Anisakis sp. larvae sized from 14 cm.
The purpose of the research is to conduct a sanitary and parasitological examination of soil biotopes on the territory of Moscow. In addition to traditional soil studies, we conducted coproscopic analyzes of samples of dog feces collected from the soil surface in Spring.
Materials and methods. 83 combined soil samples were taken in 9 administrative districts of Moscow using the envelope method at a depth of up to 10 cm. From each combined sample, 4 samples were taken and examined using the Romanenko method according to MUK 4.2.2661-10 “Methods of sanitary and parasitological research”. From the same areas where soil was collected, 365 dog fecal samples were collected. Feces were studied using a combined flotation method. Soil and fecal samples were taken in Spring of 2023 during a period of positive temperatures immediately after the snow melted. Microscopy was performed using a Motic BA410T microscope. Identification of the detected objects was carried out on the basis of morphometric data. Species differentiation of Toxocara canis and T. cati eggs was carried out based on differences in the size of the eggs and the structure of the outer shell.
Results and discussion. The city's soil is contaminated with pathogens of parasitic diseases in 9.3% of samples. Toxocara eggs were found (5.7%), of which T. canis in 3.9% of samples, and T. cati in 1.8% of samples. Eggs of Capillaria sp. detected in 1.5%, eggs of Trichuris sp. at 0.9%. Eggs of Hymenolepis sp. and coccidia were detected in 0.6% of samples. In dog feces, pathogens of parasitic diseases were detected in 3.3% of samples. Toxocara sp. eggs were found in 1.4% of samples, isospores in 0.8%, sarcocystis in 0.8%, Toxascaris leonina eggs in 0.3%. Toxocara sp. eggs are the leaders in the frequency of detection in the soil; these are mainly viable eggs with larvae. This is consistent with the data that T. canis eggs are most often recorded in anonymized dog feces. Eggs of Trichuris sp. and Capillaria sp. found in soil with formed viable larvae. The findings show the potential of urban soils as a parasite transmission factor for humans and susceptible animals, and dogs play a leading role in the contamination of urban soils with Toxocara sp. eggs.
The purpose of the research is to study the epizootiology and pathomorphology of setariosis in cattle on farms in the Altai Territory.
Materials and methods. To make a diagnosis, blood samples were examined for the presence of microsetaria in calves of the current year of birth.
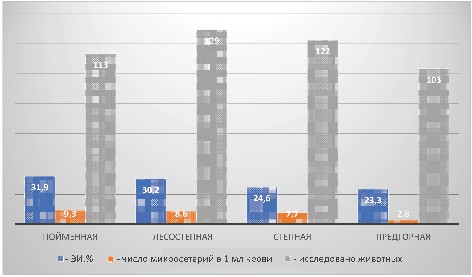
Results and discussion. Microsetariae were found in cattle in all zones of the Altai Territory based on the results of a study of blood samples. Infection fluctuated between 23.3–31.9% depending on the zone and, on average, amounted to 27.6%. The intensity of infection also ranged from 7.4±0.7 to 9.3±0.8 sp. The highest infection was observed in animals aged 4–7 years (33.3%) with infection intensity of 11.3±1.0 sp./animal. Cattle are infected with Setaria sp. in all seasons with changes in different months. The maximum infection rate was observed in June – up to 40.0%. Single specimens of Setaria sp. larvae in the blood of calves up to one year old were found in December, i.e., 7 months after the start of the grazing period and mosquito activity. Pathomorphological examination revealed that in most cases, dying Setaria sp. in abdominal cavity are attached to the capsules of the liver, spleen and mesentery. To prevent microfilariaemia in cattle and the spread of Setaria sp. infection, we recommend using macrocyclic drugs.
BIOCHEMISTRY, BIOTECHNOLOGY AND DIAGNOSTICS
The purpose of the research is to compare the accumulation of phenolic compounds of different species and varieties of mint, zoned in Central Russia against the background of plant infection by Meloidogyne incognita.
Materials and methods. Plants were grown from cuttings in a growing experiment in open ground. Mentha × piperita L. (varieties: Tik-Tak, Orange, Minneola, Mojito, Mitchum, Chocolate), M. spicata L. (varieties Morocco, Crispa) and M. longifolia L. (Longifolia) were taken for the study. A month later, the rooted plants were infected at the rate of 1000 sp. infective larvae of M. incognita per plant. After 8 weeks leaves were fixed in ethanol. The total content of phenolic compounds (PC), phenylpropanoids, flavonoids and catechins was studied using a spectrophotometer. The determination of the total content of PС was carried out using the Folin-Cecolte reagent with measurement at 725 nm, phenylpropanoids – by direct measurement of optical density at 330 nm, flavonoids – by reaction with aluminum chloride at 415 nm, the total content of flavans (catechins - flavan-3-ols), their oligomeric forms – proanthocyanidins, as well as leukoanthocyanidins were assessed by reaction with vanillin at 500 nm.
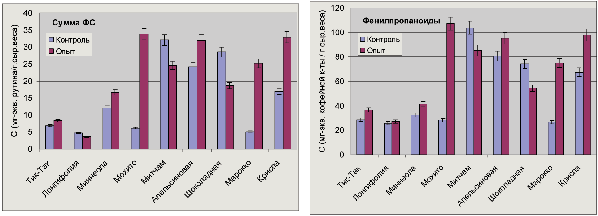
Results and discussion. It has been shown that the accumulation of phenols is related to the species of plants. The varieties Mentha × piperita L. in most cases contained more phenols than M. spicata L. and M. longifolia L. A significant number of PC was noted in the violet-colored varieties Mitchum, Chocolate and Orange. The total content of PC almost completely correlates with the content of their precursors – phenylpropanoids. In terms of the content of flavonoids, the Mitchum variety stands out noticeably, and in terms of the content of catechins, the Orange variety stands out. Nematode infection in most varieties causes a noticeable increase in the total accumulation of soluble PC, phenylpropanoids and flavans, but leads to a decrease in the content of flavonoids.
The purpose of the research is to provide a comparative assessment of efficacy of different diagnostic methods for sarcocystosis in cattle.
Materials and methods. Seventy-eight bovine carcasses were examined using methods and regulations of veterinary and sanitary examination. Muscles of the esophagus and other parts of the carcass as well as the spleen, lungs, the liver, and kidneys were examined. The compressor research method was used. A total of 156 compressoria from 78 bovine carcasses were analyzed for tissue sarcocystosis. For life-time diagnostics of bovine sarcocystosis, a molecular serologic method (ELISA) was used that was developed based on antibody detection principles.
Results and discussion. Two diagnostic methods, visual inspection and compressor microscopy, identified 13 out of 78 carcasses with Sarcocystis species, which was 16.6%. The number of sarcocystosis animals increased by another 23 cases when studying blood sera from the cattle using ELISA. Thus, we found 36 animals suffering from sarcocystosis out of 78 examined, which was 46%, with tests based on different principles.
The purpose of the research is to monitor farms located in the European part of the Russian Federation to identify resistance to effects of benzimidazole anthelmintics in populations of nematodes Haemonchus contortus dwelling in the gastrointestinal tract of small cattle.
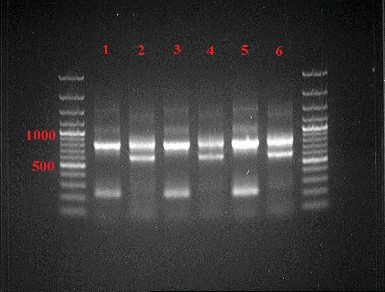
Materials and methods. The studies were conducted in slaughterhouses located in the Moscow Region in 2023–2024. At the first stage, taxonomic identification of parasitic nematodes and larvae (L3) was made, and Strongylata species was determined from sheep. The study material was the abomasum with duodenum fragments and a distal rectum fragment with feces. For molecular studies, we used mature nematodes and H. contortus L3 larvae isolated from the abomasum and feces of small cattle brought to slaughterhouses in the Moscow Region from 8 regions of the European part of the Russian Federation: Moscow, Astrakhan, Oryol, Lipetsk, Tula, Bryansk regions, Stavropol and Dagestan. The studies were conducted at the premises of the Laboratory of Molecular Biology, the VNIIP – FSC VIEV. Statistical processing of the obtained data was made, and mean infection rates of parasitic nematodes (infection intensity and prevalence) were determined. Fifty-six DNA samples of nematodes H. contortus were examined using nested isothermal amplification (PCR) to identify gene alleles that determine resistance to benzimidazole drugs.
Results and discussion. Molecular genetic studies of H. contortus DNA sampled from sheep brought from different Regions only detected homozygous individuals (100%) resistant to benzimidazole in the parasitic nematode population from the Oryol Region. Other regions identified only homozygous and heterozygous individuals susceptible to benzimidazole.
The purpose of the research is to study pathology findings in heterakidosis in broilers.
Materials and methods. The study used pathological material (cecum, liver) from 8 laying hens aged one year. Organ samples were delivered to the Pathology Sector in 10% buffered formalin. They were fixed for 36 hours and examined histologically using paraffin embedding. Semi-automatic Thermo Scientific equipment was used to process tissue samples. Histologic specimens were stained with hematoxylin and eosin. The specimen histoarchitecture was assessed with an Axio A1.0 microscope; photographs were taken using the AxioVision software.
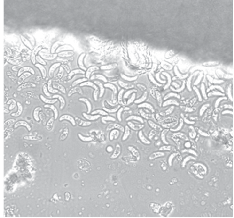
Results and discussion. Visual assessment of the pathological material revealed thickening of the distal cecum while the liver samples had no signs of pathology. It was found that Heterakis spp. was about 1 cm long; helminth eggs were oval-shaped and had a strong, uniform shell; their size was 49 × 26 micrometers in the mean. When dwelling in the cecum, Heterakis spp. causes atony of the distal cecum wall, and development of inflammatory and necrotic processes in the intestinal mucosa, which promotes active growth of bacterial flora, accumulation of bacterial byproducts and intoxication. In places where the helminth is localized, eggs accumulate and a risk of Histomonas spp. infection increases, namely, amoebic (in the intestinal lumen) and spherical (in the intestinal mucosa) forms of the protozoan were identified. It was not possible to differentiate Histomonas spp. in assessing the histological specimens of the liver from the infected birds. In diagnostics, we should consider the great similarity of morphological characteristics of Heterakis spp. and Ascaridia spp. eggs.
PHARMACOLOGY, TOXICOLOGY
The purpose of the research is to evaluate some toxicological parameters of a new combined anthelmintic based on oxantel pamoate, pyrantel pamoate and praziquantel in tablet formulation for dogs and cats.
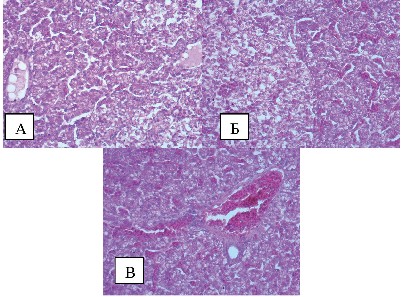
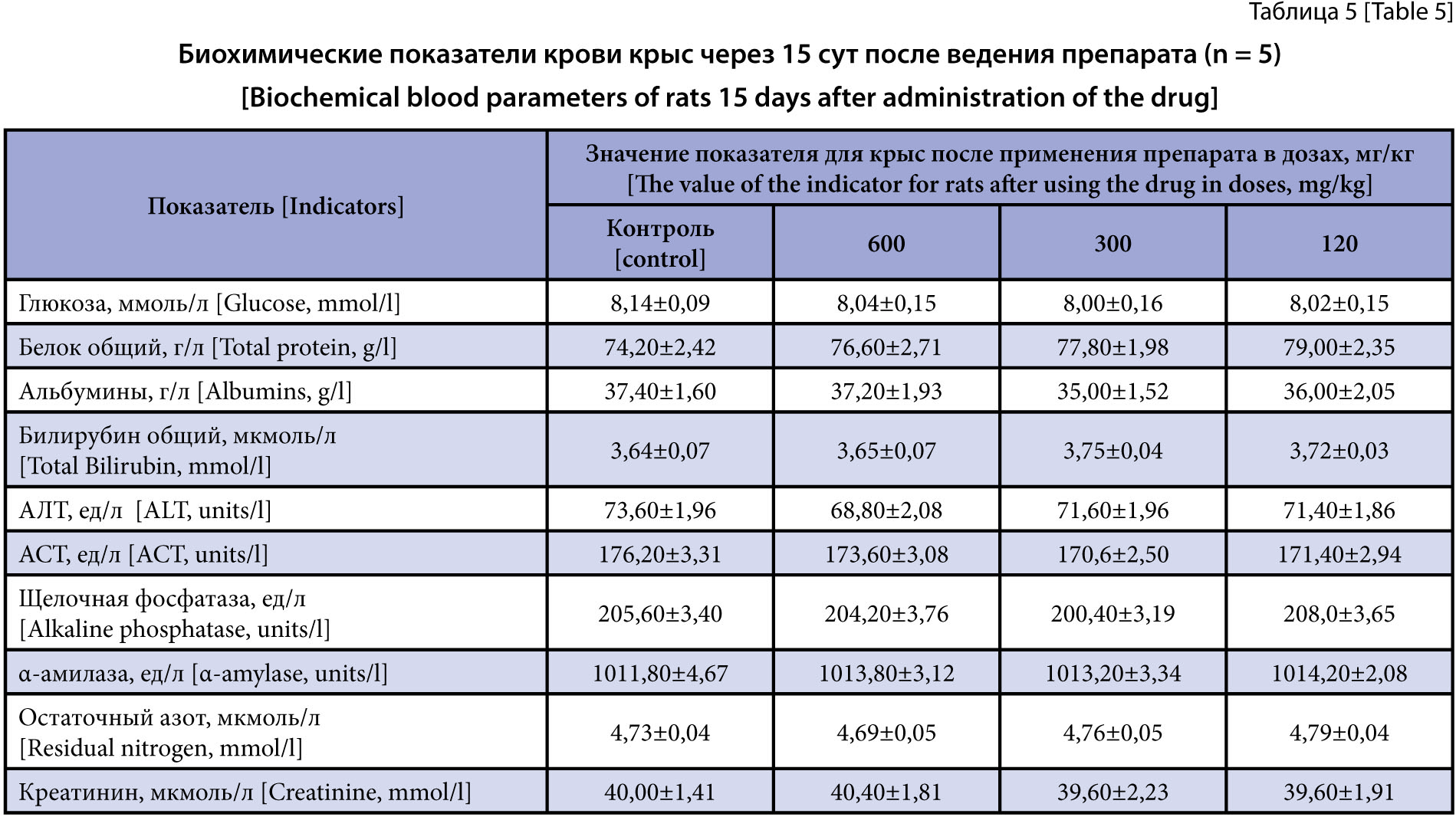
Materials and methods. The studies used 70 outbred male rats and 50 outbred male mice. Acute oral toxicity was studied in male mice and male rats weighing 14–16 and 160–180 g, respectively. The subchronic toxicity study with the drug administered repeatedly, orally for 14 days was conducted on male rats weighing 180–200 g. The study monitored the laboratory animals’ overall health status, behavior and possible death, and any intoxication symptoms were recorded. All studies were performed using conventional techniques for experimental (preclinical) studies of new pharmacological substances using the guidelines edited by R. U. Khabriev (2005) and A. I. Mironov et al. (2012). Additionally, the experiments assessed clinical toxicological, biochemical, and morphological parameters of the laboratory animals.
Results and discussion. In evaluation of the drug acute toxicity in the male mice and the female rats, the LD50 exceeded the dose of 6000 mg/kg; the animals showed no signs of intoxication during the entire study. Thus, the drug was classified as substance hazard category 4. Doses 600, 300 and 120 mg/kg of the drug had no negative effect on the organism of the laboratory animals in the subchronic experiment on the male rats; the doses were ineffective (safe). The threshold or toxic dose could not be determined.
TREATMENT AND PREVENTION
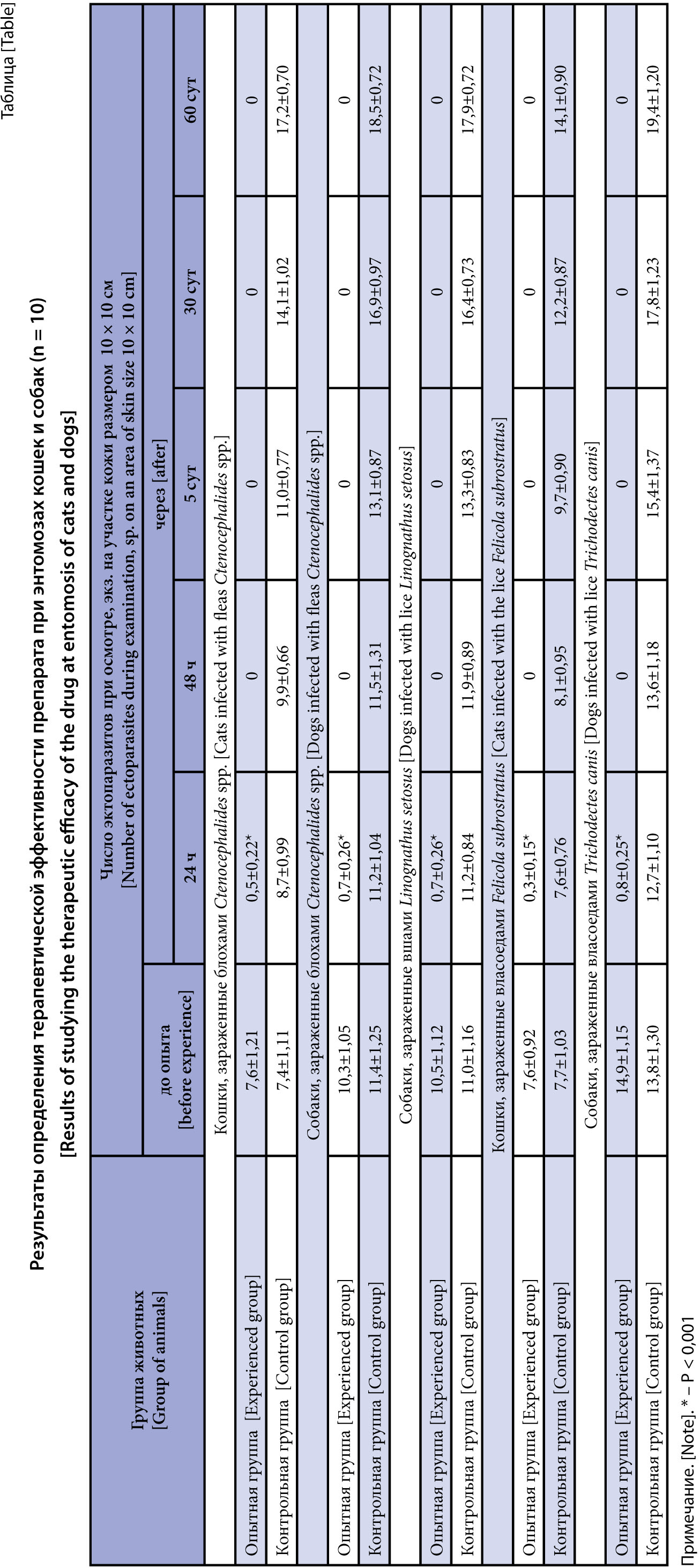
The purpose of the research is to study the efficacy of a Flumethrin-, Moxidectin and Pyriproxyfen-based spray against entomosis in dogs and cats.
Materials and methods. The therapeutic efficacy of the multicomponent spray against entomosis of cats and dogs was evaluated in the Podolsk Experimental Production Base of the VNIIP – FSC VIEV on 100 animals naturally infected with fleas Ctenocephalides spp. (20 cats and 20 dogs), Linognathus setosus (20 dogs), chewing lice Felicola subrostratus (20 cats) and Trichodectes canis (20 dogs). The animals were divided into experimental and control groups of 10 animals each. The experimental dogs and cats were given the drug topically with a bottle pump directed to the skin and fur from 20–25 cm, treating the entire body of the animal at a dose of 3–6 pumps per 1 kg of animal weight, and the control animals were not given the drug. The animals were observed for 60 days after a single dose of the drug; clinical examination was performed before and at 24, 48 hours and 5, 30 and 60 days after the start of the experiment.
Results and discussion. The examination of the skin and coat of some experimental animals infected with ectoparasites found single ectoparasite imago at 24 hours after treatment. At 48 hours and on day 5, 30 and 60 of the experiment, all animals treated once with the drug were free from ectoparasites, which was evidenced by clinical studies. The study results showed that the study drug had high therapeutic efficacy against ctenocephalidosis, linognathosis, and trichodectosis in dogs and cats.
The purpose of the research is to study the efficacy of Flumethrin-, Moxidectin- and Pyriproxyfen-based spray against Ixodid and Acariform ticks in dogs and cats.
Materials and methods. The therapeutic efficacy of a multicomponent spray against Ixodid and Acariform ticks was evaluated in dogs and cats in the Podolsk Experimental Production Base of the VNIIP – FSC VIEV on 140 animals naturally infected with Ixodid and Acariform ticks. The animals were divided into an experimental group and a control group of 10 animals each. The experimental dogs and cats were given the study drug while the control animals were not given the drug. Clinical examinations at ixodidosis in dogs and cats were performed at 24 and 48 hours, and at 3 and 5 days after the start of the experiment. In Acariformes parasitism, a control examination and microscopy of deep skin scrapings taken at the healthy and affected skin interface were made using a scalpel at 7, 14, 21, 28 and 35 days after the start of the experiment, in treatment of sarcoptic mange, notoedric mange and demodicosis as well as scrapings from the auricle (distal part of the acoustic canal) in otodectic mange.
Results and discussion. It was found that Flumethrin-, Moxidectin- and Pyriproxyfen-based spray had high therapeutic efficacy when used once, externally, against ixodid tick, and in the auricle twice with a 7-day interval against otodectic mange and externally 2–4 times with a 7-day interval against notoedric mange, sarcoptic mange and demodicosis in various disease forms in dogs and cats.
The purpose of the research is to evaluate the insectoacaricidal activity of the drug 5% D-cyphenothrin Emulsion against argasid ticks and biting lice in different concentrations.
Materials and methods. We carried out a parasitological examination of an open-type cinderblock poultry building in peasant household BUGLEN-2 (the Republic of Dagestan) using the avian ectoparasite collecting methods of B. A. Frolov (1975). The studies were performed using procedures outlined in the studies by A. A. Nepoklonov and G. A. Talanov (1973), M. V. Arisov and I. A. Arkhipov (2018) as modified. In the Laboratory of Ectoparasitosis in the VNIIP – FSC VIEV, the acaricidal activity of 5% D-cyphenothrin Emulsion was evaluated against argasid ticks and LD50 and LD95 were determined. The insecticidal activity of the studied drug in different concentrations against the biting lice Menopon gallinae and Menacanthus stramineus was studied on naturally infected chickens that were kept on the farm. Parasitic arthropods were identified to species using identification guides by I. G. Galuzo (1957), N. A. Fillipova (1966) and D. I. Blagoveshchensky (1940).
Results and discussion. In laboratory, we observed rapid death of argasid ticks within 30 minutes after their contact with absorbent paper impregnated with 0.005% and 0.05% concentrations of the studied drug. In the assessment of the 5% D-cyphenothrin Emulsion insecticidal activity against biting lice of two species Menopon gallinae and Menacanthus stramineus on naturally infected chickens, we observed the death of parasitic insects after 24 hours on the birds treated with a 0.005% emulsion. Thus, the minimum effective concentration of 0.005 % of the study drug, 5% D-cyphenothrin Emulsion, was determined for the above parasitic arthropods.
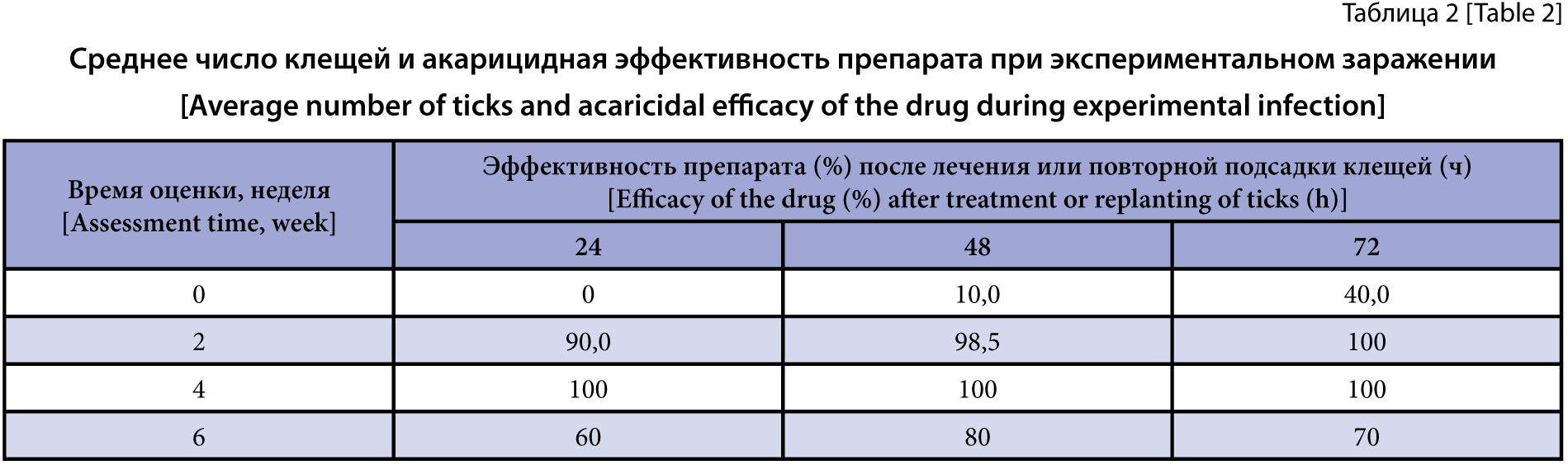
The purpose of the research is to study the efficacy of antiparasitic drug based on Lufenuron, Moxidectin, Praziquantel against ixodidosis in dogs under natural conditions and during experimental infection with ixodid ticks.
Materials and methods. The experiments used the drug in tablet formulation containing Lufenuron in 320 mg, Moxidectin in 9.6 mg and Praziquantel in 160 mg. To study the preventive and therapeutic acaricidal effect of the drug against ixodid ticks in the country part of the Karachaevsky District of the Karachay-Cherkess Republic, two groups (10 dogs each) were formed of Alabai dogs or outbred dogs with a body weight of 16–76 kg. The dogs of the first experimental group were administered the drug in tablets. The dogs of the second group served as controls and were not treated. The experiment used clinically healthy dogs of both sexes over 6 weeks of age, spontaneously infected with Ixodidae. Animals were selected so that they were not exposed to drugs for at least 1 month prior to the experiment. The animals were kept under normal conditions throughout the experiment and received their usual food. Antiparasitic tablets were administered to the dogs individually, once, orally, mixed with food at a dose of 1 tablet per 16–32 kg of body weight. The ixodid infection was diagnosed in the dogs by clinical examination. The genus of Ixodidae was determined by typical morphological characteristics. The drug efficacy was evaluated based on reduced number or absence of ticks on the treated animals (experimental) versus the untreated animals (control). Before the experiment and after the drug, the animals were examined every hour for 48 hours, and condition, separation, separation time from the start of the drug and death of the ticks were recorded; the dogs were then examined every 5–7 days for two months.
Results and discussion. The article presents study data on antiparasitic drug efficacy against ixodidosis in dogs spontaneously infected with Ixodes ricinus, I. persulcatus, and Dermacentor reticulatus. The result of the studies found that the antiparasitic drug (active substances were Lufenuron, Moxidectin, and Praziquantel) had a therapeutic effect that was recorded on day 5 after treatment and was 90%. The preventive efficacy was also above 70%: on day 7 and 14, this value was 90.0 and 86.9%, respectively, which indicated the duration of the preventive effect for 25–28 days. To fully evaluate the acaricidal efficacy against ixodidosis, studies were conducted on experimentally infected animals. Forty percent efficacy was determined at 48 hours after the drug; at 2 weeks after the drug, 90 %, 98.5 and 100 % efficacy were determined against ixodidosis in the dogs at 24 hours, 48 and 72 hours after the transfer of ticks, respectively. At 4 weeks after the drug, 100 % efficacy was determined against ixodidosis in the dogs at 24, 48 and 72 hours after the transfer of ticks, respectively.
ISSN 2541-7843 (Online)